本文简单解读Connector连接器组件内的NioEndpoint。
本系列的源码工程为:HowTomcatWorksSourceCode。
本文目录为:
一、概述
上一篇文章有讲到ProtocolHandler的实现类,Tomcat 8和之后默认的协议处理器是AbstractHttp11Protocol。AbstractHttp11Protocol的构造方法创建了NioEndpoint。
public Http11NioProtocol() {
this(new NioEndpoint());
}
public Http11NioProtocol(NioEndpoint endpoint) {
super(endpoint);
}
NioEndpoint是按照acceptor+poller+Workers的线程模型实现的”端点”。
/**
* NIO tailored thread pool, providing the following services:
* <ul>
* <li>Socket acceptor thread</li>
* <li>Socket poller thread</li>
* <li>Worker threads pool</li>
* </ul>
*
* TODO: Consider using the virtual machine's thread pool.
*
* @author Mladen Turk
* @author Remy Maucherat
*/
public class NioEndpoint extends AbstractNetworkChannelEndpoint<NioChannel,SocketChannel> {
//......
}
Connector连接器相关组件工作原理如下:
- 其内部主要由acceptor创建ServerSocket,接受来自客户端的连接Socket,封装为Event,发布到事件队列中。
- 再由poller拉取Event将socket封装为SocketWrapper,并创建SocketProcessor(worker任务),提交到Worker线程池。
- Worker线程池的任务SocketProcessor由Http11Processor处理。
- Http11Processor调用CoyoteAdapter处理。CoyoteAdapter连接容器将请求交给Container去处理。
</strong> 其中NioEndpoint是非常核心的组件,实现了acceptor+poller+Workers的线程模型,非常值得重点研究。其也体现Java同步NIO的网络编程模型。Connector整体的工作原理如下图:
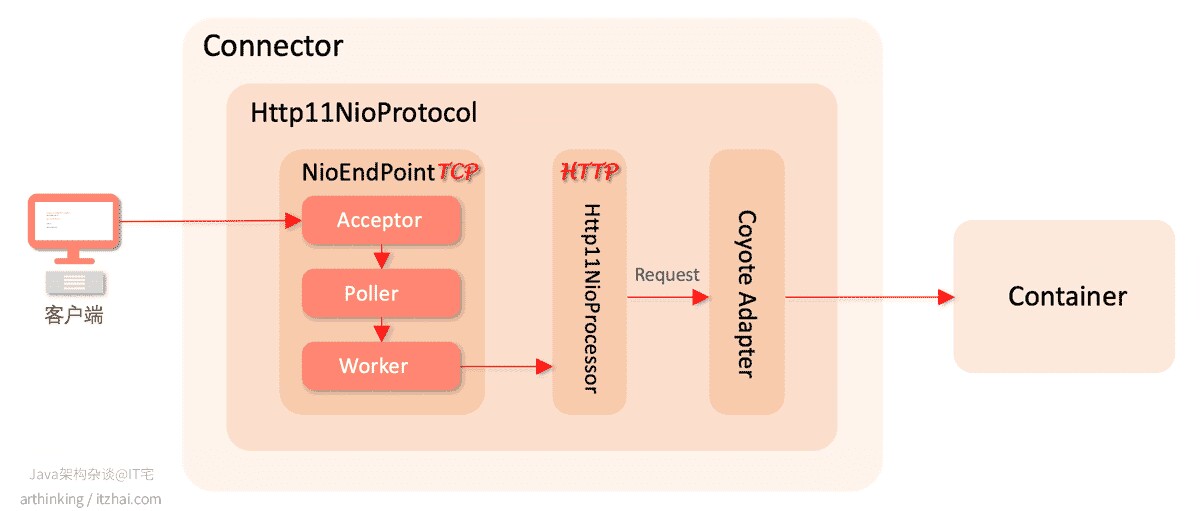
图片来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/arthinking/p/14509130.html.
图表帮助我们记忆和理解,如果要探究这些图表/流程是从哪里来的,还是需要去研究源码。
Nio2Endpoint是异步AIO实现的网络编程模型,本系列文章不作解读,读者可以自己研究。
本文主要解读NioEndpoint的源码,同时简单解读Http11Processor这个类。
二、NioEndpoint
在ProtocolHandler#create方法中默认创建Http11NioProtocol,如下:
static ProtocolHandler create(String protocol)
throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException,
InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {
if (protocol == null || "HTTP/1.1".equals(protocol) ||
org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol.class.getName().equals(protocol)) {
return new org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol();
} else if ("AJP/1.3".equals(protocol) ||
org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpNioProtocol.class.getName().equals(protocol)) {
return new org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpNioProtocol();
} else {
// Instantiate protocol handler
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(protocol);
return (ProtocolHandler) clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();
}
}
Http11NioProtocol构造器中创建了NioEndpoint:
public Http11NioProtocol() {
this(new NioEndpoint());
}
下面进入NioEndpoint的源码。
2.1 NioEndpoint
NioEndpoint的类继承关系如下:
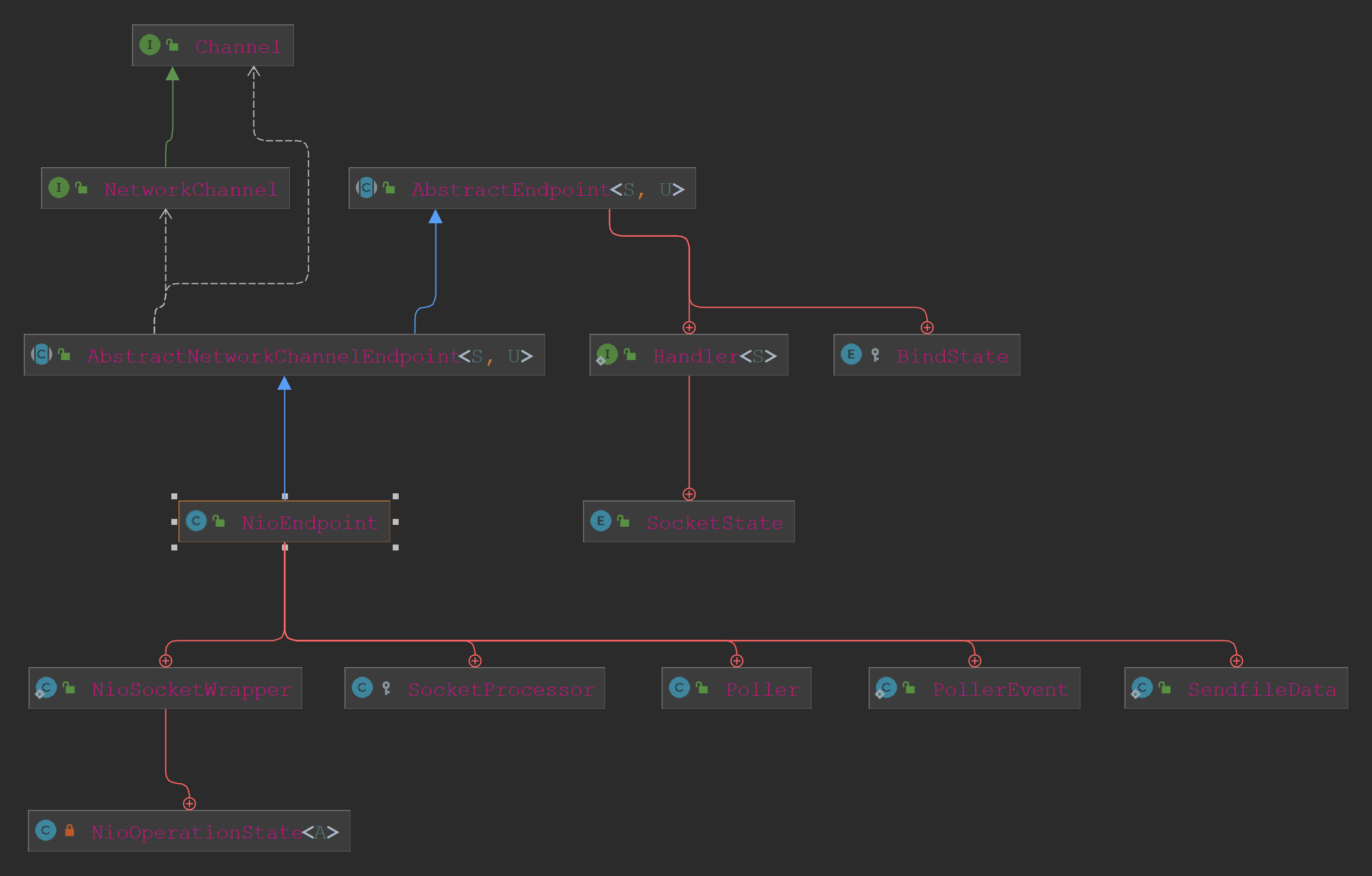
在其注释中表明了acceptor+poller+Workers的线程模型。
/**
* NIO tailored thread pool, providing the following services:
* <ul>
* <li>Socket acceptor thread</li>
* <li>Socket poller thread</li>
* <li>Worker threads pool</li>
* </ul>
*
* TODO: Consider using the virtual machine's thread pool.
*
* @author Mladen Turk
* @author Remy Maucherat
*/
NioEndpoint的三个内部对象(类)分别代表了acceptor+poller+Workers:Acceptor,Poller,SocketProcessor。
/**
* This class is the equivalent of the Worker, but will simply use in an
* external Executor thread pool.
*/
protected class SocketProcessor extends SocketProcessorBase<NioChannel> {
//......
}
2.2 Acceptor
我们首先来到Acceptor的源码。
public class Acceptor<U> implements Runnable {
//......
//endpoint
private final AbstractEndpoint<?,U> endpoint;
/*
* Tracked separately rather than using endpoint.isRunning() as calls to
* endpoint.stop() and endpoint.start() in quick succession can cause the
* acceptor to continue running when it should terminate.
*/
//停止标志,volatile类型
private volatile boolean stopCalled = false;
private final CountDownLatch stopLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
protected volatile AcceptorState state = AcceptorState.NEW;
public Acceptor(AbstractEndpoint<?,U> endpoint) {
this.endpoint = endpoint;
}
//最重要的执行方法
@Override
public void run() {
int errorDelay = 0;
long pauseStart = 0;
try {
// Loop until we receive a shutdown command
while (!stopCalled) {
// Loop if endpoint is paused.
// There are two likely scenarios here.
// The first scenario is that Tomcat is shutting down. In this
// case - and particularly for the unit tests - we want to exit
// this loop as quickly as possible. The second scenario is a
// genuine pause of the connector. In this case we want to avoid
// excessive CPU usage.
// Therefore, we start with a tight loop but if there isn't a
// rapid transition to stop then sleeps are introduced.
// < 1ms - tight loop
// 1ms to 10ms - 1ms sleep
// > 10ms - 10ms sleep
while (endpoint.isPaused() && !stopCalled) {
if (state != AcceptorState.PAUSED) {
pauseStart = System.nanoTime();
// Entered pause state
state = AcceptorState.PAUSED;
}
if ((System.nanoTime() - pauseStart) > 1_000_000) {
// Paused for more than 1ms
try {
if ((System.nanoTime() - pauseStart) > 10_000_000) {
Thread.sleep(10);
} else {
Thread.sleep(1);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
if (stopCalled) {
break;
}
state = AcceptorState.RUNNING;
try {
//if we have reached max connections, wait
endpoint.countUpOrAwaitConnection();
// Endpoint might have been paused while waiting for latch
// If that is the case, don't accept new connections
if (endpoint.isPaused()) {
continue;
}
U socket = null;
try {
// Accept the next incoming connection from the server
// socket
//调用ServerSocket的accept,获得客户端连接Socket
socket = endpoint.serverSocketAccept();
} catch (Exception ioe) {
// We didn't get a socket
endpoint.countDownConnection();
if (endpoint.isRunning()) {
// Introduce delay if necessary
errorDelay = handleExceptionWithDelay(errorDelay);
// re-throw
throw ioe;
} else {
break;
}
}
// Successful accept, reset the error delay
errorDelay = 0;
// Configure the socket
if (!stopCalled && !endpoint.isPaused()) {
// setSocketOptions() will hand the socket off to
// an appropriate processor if successful
//处理客户端连接Socket
if (!endpoint.setSocketOptions(socket)) {
endpoint.closeSocket(socket);
}
} else {
endpoint.destroySocket(socket);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
String msg = sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail");
log.error(msg, t);
}
}
} finally {
stopLatch.countDown();
}
state = AcceptorState.ENDED;
}
//Acceptor的执行状态
public enum AcceptorState {
NEW, RUNNING, PAUSED, ENDED
}
}
首先,Acceptor自身实现了Runnable,可以作为一个任务来新建线程来执行run方法。
protected void startAcceptorThread() {
acceptor = new Acceptor<>(this);
String threadName = getName() + "-Acceptor";
acceptor.setThreadName(threadName);
Thread t = new Thread(acceptor, threadName);
t.setPriority(getAcceptorThreadPriority());
t.setDaemon(getDaemon());
t.start();
}
在AbstractEndpoint#startAcceptorThread方法启动Acceptor线程,这里Daemon默认为true。
然后Acceptor的run方法是一个”死循环”,一直等待获取客户端连接。这里”socket = endpoint.serverSocketAccept();”这行代码accept客户端连接Socket。
@Override
protected SocketChannel serverSocketAccept() throws Exception {
SocketChannel result = serverSock.accept();
// Bug does not affect Windows platform and Unix Domain Socket. Skip the check.
if (!JrePlatform.IS_WINDOWS && getUnixDomainSocketPath() == null) {
SocketAddress currentRemoteAddress = result.getRemoteAddress();
long currentNanoTime = System.nanoTime();
if (currentRemoteAddress.equals(previousAcceptedSocketRemoteAddress) &&
currentNanoTime - previousAcceptedSocketNanoTime < 1000) {
throw new IOException(sm.getString("endpoint.err.duplicateAccept"));
}
previousAcceptedSocketRemoteAddress = currentRemoteAddress;
previousAcceptedSocketNanoTime = currentNanoTime;
}
return result;
}
最后,setSocketOptions方法将Socket封装为SocketWrapper,创建Event,然后注册到事件队列。
/**
* Process the specified connection.
* @param socket The socket channel
* @return <code>true</code> if the socket was correctly configured
* and processing may continue, <code>false</code> if the socket needs to be
* close immediately
*/
@Override
protected boolean setSocketOptions(SocketChannel socket) {
NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = null;
try {
// Allocate channel and wrapper
NioChannel channel = null;
if (nioChannels != null) {
channel = nioChannels.pop();
}
if (channel == null) {
SocketBufferHandler bufhandler = new SocketBufferHandler(
socketProperties.getAppReadBufSize(),
socketProperties.getAppWriteBufSize(),
socketProperties.getDirectBuffer());
channel = createChannel(bufhandler);
}
NioSocketWrapper newWrapper = new NioSocketWrapper(channel, this);
channel.reset(socket, newWrapper);
connections.put(socket, newWrapper);
socketWrapper = newWrapper;
// Set socket properties
// Disable blocking, polling will be used
socket.configureBlocking(false);
if (getUnixDomainSocketPath() == null) {
socketProperties.setProperties(socket.socket());
}
socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(getConnectionTimeout());
socketWrapper.setWriteTimeout(getConnectionTimeout());
socketWrapper.setKeepAliveLeft(NioEndpoint.this.getMaxKeepAliveRequests());
poller.register(socketWrapper);
return true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
try {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.socketOptionsError"), t);
} catch (Throwable tt) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(tt);
}
if (socketWrapper == null) {
destroySocket(socket);
}
}
// Tell to close the socket if needed
return false;
}
注册方法如下:
/**
* Registers a newly created socket with the poller.
*
* @param socketWrapper The socket wrapper
*/
public void register(final NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper) {
socketWrapper.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);//this is what OP_REGISTER turns into.
PollerEvent pollerEvent = createPollerEvent(socketWrapper, OP_REGISTER);
addEvent(pollerEvent);
}
private void addEvent(PollerEvent event) {
events.offer(event);
if (wakeupCounter.incrementAndGet() == 0) {
selector.wakeup();
}
}
到这一步,客户端连接Socket被转换为Event注册到事件队列里面了。 events自身是一个简化的并发队列:
public class SynchronizedQueue<T> {
public static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 128;
private Object[] queue;
private int size;
private int insert = 0;
private int remove = 0;
public SynchronizedQueue() {
this(DEFAULT_SIZE);
}
public SynchronizedQueue(int initialSize) {
queue = new Object[initialSize];
size = initialSize;
}
public synchronized boolean offer(T t) {
queue[insert++] = t;
// Wrap
if (insert == size) {
insert = 0;
}
if (insert == remove) {
expand();
}
return true;
}
public synchronized T poll() {
if (insert == remove) {
// empty
return null;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T) queue[remove];
queue[remove] = null;
remove++;
// Wrap
if (remove == size) {
remove = 0;
}
return result;
}
private void expand() {
int newSize = size * 2;
Object[] newQueue = new Object[newSize];
System.arraycopy(queue, insert, newQueue, 0, size - insert);
System.arraycopy(queue, 0, newQueue, size - insert, insert);
insert = size;
remove = 0;
queue = newQueue;
size = newSize;
}
public synchronized int size() {
int result = insert - remove;
if (result < 0) {
result += size;
}
return result;
}
public synchronized void clear() {
queue = new Object[size];
insert = 0;
remove = 0;
}
}
2.3 Poller
Poller同样实现了Runnable,内部run方法也是一个”死循环”。其run方法如下:
/**
* The background thread that adds sockets to the Poller, checks the
* poller for triggered events and hands the associated socket off to an
* appropriate processor as events occur.
*/
@Override
public void run() {
// Loop until destroy() is called
while (true) {
boolean hasEvents = false;
try {
if (!close) {
//获取事件
hasEvents = events();
if (wakeupCounter.getAndSet(-1) > 0) {
// If we are here, means we have other stuff to do
// Do a non blocking select
keyCount = selector.selectNow();
} else {
keyCount = selector.select(selectorTimeout);
}
wakeupCounter.set(0);
}
if (close) {
events();
timeout(0, false);
try {
selector.close();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.selectorCloseFail"), ioe);
}
break;
}
// Either we timed out or we woke up, process events first
if (keyCount == 0) {
hasEvents = (hasEvents | events());
}
} catch (Throwable x) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(x);
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.selectorLoopError"), x);
continue;
}
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator =
keyCount > 0 ? selector.selectedKeys().iterator() : null;
// Walk through the collection of ready keys and dispatch
// any active event.
while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey sk = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = (NioSocketWrapper) sk.attachment();
// Attachment may be null if another thread has called
// cancelledKey()
//处理单个Socket
if (socketWrapper != null) {
processKey(sk, socketWrapper);
}
}
// Process timeouts
timeout(keyCount,hasEvents);
}
getStopLatch().countDown();
}
这里两个最重要的方法events()-获取事件和注册SelectionKey;processKey-处理单个Socket。
/**
* Processes events in the event queue of the Poller.
*
* @return <code>true</code> if some events were processed,
* <code>false</code> if queue was empty
*/
//处理队列中注册的事件/Event
public boolean events() {
boolean result = false;
PollerEvent pe = null;
for (int i = 0, size = events.size(); i < size && (pe = events.poll()) != null; i++ ) {
result = true;
NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = pe.getSocketWrapper();
SocketChannel sc = socketWrapper.getSocket().getIOChannel();
int interestOps = pe.getInterestOps();
if (sc == null) {
log.warn(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.nullSocketChannel"));
socketWrapper.close();
} else if (interestOps == OP_REGISTER) {
try {
//注册SelectionKey
sc.register(getSelector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ, socketWrapper);
} catch (Exception x) {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.registerFail"), x);
}
} else {
final SelectionKey key = sc.keyFor(getSelector());
if (key == null) {
// The key was cancelled (e.g. due to socket closure)
// and removed from the selector while it was being
// processed. Count down the connections at this point
// since it won't have been counted down when the socket
// closed.
socketWrapper.close();
} else {
final NioSocketWrapper attachment = (NioSocketWrapper) key.attachment();
if (attachment != null) {
// We are registering the key to start with, reset the fairness counter.
try {
int ops = key.interestOps() | interestOps;
attachment.interestOps(ops);
key.interestOps(ops);
} catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) {
socketWrapper.close();
}
} else {
socketWrapper.close();
}
}
}
if (running && eventCache != null) {
pe.reset();
eventCache.push(pe);
}
}
return result;
}
处理单个Socket的流程最终交给SocketProcessor处理的。
protected void processKey(SelectionKey sk, NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper) {
try {
if (close) {
socketWrapper.close();
} else if (sk.isValid()) {
if (sk.isReadable() || sk.isWritable()) {
if (socketWrapper.getSendfileData() != null) {
processSendfile(sk, socketWrapper, false);
} else {
unreg(sk, socketWrapper, sk.readyOps());
boolean closeSocket = false;
// Read goes before write
if (sk.isReadable()) {
if (socketWrapper.readOperation != null) {
if (!socketWrapper.readOperation.process()) {
closeSocket = true;
}
} else if (socketWrapper.readBlocking) {
synchronized (socketWrapper.readLock) {
socketWrapper.readBlocking = false;
socketWrapper.readLock.notify();
}
} else if (!processSocket(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ, true)) {
closeSocket = true;
}
}
if (!closeSocket && sk.isWritable()) {
if (socketWrapper.writeOperation != null) {
if (!socketWrapper.writeOperation.process()) {
closeSocket = true;
}
} else if (socketWrapper.writeBlocking) {
synchronized (socketWrapper.writeLock) {
socketWrapper.writeBlocking = false;
socketWrapper.writeLock.notify();
}
//处理单个Socket
} else if (!processSocket(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE, true)) {
closeSocket = true;
}
}
if (closeSocket) {
socketWrapper.close();
}
}
}
} else {
// Invalid key
socketWrapper.close();
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) {
socketWrapper.close();
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.keyProcessingError"), t);
}
}
单个Socket交给SocketProcessor处理,SocketProcessor本身类似于Worker,实现Runnable,作为task提交到Executor去处理。
public boolean processSocket(SocketWrapperBase<S> socketWrapper,
SocketEvent event, boolean dispatch) {
try {
if (socketWrapper == null) {
return false;
}
//创建或者复用SocketProcessor
SocketProcessorBase<S> sc = null;
if (processorCache != null) {
sc = processorCache.pop();
}
if (sc == null) {
sc = createSocketProcessor(socketWrapper, event);
} else {
sc.reset(socketWrapper, event);
}
Executor executor = getExecutor();
if (dispatch && executor != null) {
//提交到线程池执行
executor.execute(sc);
} else {
sc.run();
}
} catch (RejectedExecutionException ree) {
getLog().warn(sm.getString("endpoint.executor.fail", socketWrapper) , ree);
return false;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
// This means we got an OOM or similar creating a thread, or that
// the pool and its queue are full
getLog().error(sm.getString("endpoint.process.fail"), t);
return false;
}
return true;
}
下面来到SocketProcessor/Worker的源码。
2.4 SocketProcessor(worker)
SocketProcessor类似于Worker线程。
/**
* This class is the equivalent of the Worker, but will simply use in an
* external Executor thread pool.
*/
protected class SocketProcessor extends SocketProcessorBase<NioChannel> {
public SocketProcessor(SocketWrapperBase<NioChannel> socketWrapper, SocketEvent event) {
super(socketWrapper, event);
}
@Override
protected void doRun() {
/*
* Do not cache and re-use the value of socketWrapper.getSocket() in
* this method. If the socket closes the value will be updated to
* CLOSED_NIO_CHANNEL and the previous value potentially re-used for
* a new connection. That can result in a stale cached value which
* in turn can result in unintentionally closing currently active
* connections.
*/
Poller poller = NioEndpoint.this.poller;
if (poller == null) {
socketWrapper.close();
return;
}
try {
int handshake = -1;
try {
if (socketWrapper.getSocket().isHandshakeComplete()) {
// No TLS handshaking required. Let the handler
// process this socket / event combination.
handshake = 0;
} else if (event == SocketEvent.STOP || event == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT ||
event == SocketEvent.ERROR) {
// Unable to complete the TLS handshake. Treat it as
// if the handshake failed.
handshake = -1;
} else {
handshake = socketWrapper.getSocket().handshake(event == SocketEvent.OPEN_READ, event == SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE);
// The handshake process reads/writes from/to the
// socket. status may therefore be OPEN_WRITE once
// the handshake completes. However, the handshake
// happens when the socket is opened so the status
// must always be OPEN_READ after it completes. It
// is OK to always set this as it is only used if
// the handshake completes.
event = SocketEvent.OPEN_READ;
}
} catch (IOException x) {
handshake = -1;
if (logHandshake.isDebugEnabled()) {
logHandshake.debug(sm.getString("endpoint.err.handshake",
socketWrapper.getRemoteAddr(), Integer.toString(socketWrapper.getRemotePort())), x);
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) {
handshake = -1;
}
if (handshake == 0) {
SocketState state = SocketState.OPEN;
// Process the request from this socket
if (event == null) {
state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ);
} else {
state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, event);
}
if (state == SocketState.CLOSED) {
socketWrapper.close();
}
} else if (handshake == -1 ) {
getHandler().process(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.CONNECT_FAIL);
socketWrapper.close();
} else if (handshake == SelectionKey.OP_READ){
socketWrapper.registerReadInterest();
} else if (handshake == SelectionKey.OP_WRITE){
socketWrapper.registerWriteInterest();
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException cx) {
socketWrapper.close();
} catch (VirtualMachineError vme) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(vme);
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.processing.fail"), t);
socketWrapper.close();
} finally {
socketWrapper = null;
event = null;
//return to cache
if (running && processorCache != null) {
processorCache.push(this);
}
}
}
}
这里面run方法主要是调用ConnectionHandler的处理方法,在这行代码:
state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, event);
继续进入ConnectionHandler的process方法:
@Override
public SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<S> wrapper, SocketEvent status) {
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.process", wrapper.getSocket(), status));
}
if (wrapper == null) {
// Nothing to do. Socket has been closed.
return SocketState.CLOSED;
}
S socket = wrapper.getSocket();
// We take complete ownership of the Processor inside of this method to ensure
// no other thread can release it while we're using it. Whatever processor is
// held by this variable will be associated with the SocketWrapper before this
// method returns.
Processor processor = (Processor) wrapper.takeCurrentProcessor();
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.connectionsGet", processor, socket));
}
// Timeouts are calculated on a dedicated thread and then
// dispatched. Because of delays in the dispatch process, the
// timeout may no longer be required. Check here and avoid
// unnecessary processing.
if (SocketEvent.TIMEOUT == status && (processor == null || !processor.isAsync() && !processor.isUpgrade() ||
processor.isAsync() && !processor.checkAsyncTimeoutGeneration())) {
// This is effectively a NO-OP
return SocketState.OPEN;
}
if (processor != null) {
// Make sure an async timeout doesn't fire
getProtocol().removeWaitingProcessor(processor);
} else if (status == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT || status == SocketEvent.ERROR) {
// Nothing to do. Endpoint requested a close and there is no
// longer a processor associated with this socket.
return SocketState.CLOSED;
}
try {
if (processor == null) {
String negotiatedProtocol = wrapper.getNegotiatedProtocol();
// OpenSSL typically returns null whereas JSSE typically
// returns "" when no protocol is negotiated
if (negotiatedProtocol != null && negotiatedProtocol.length() > 0) {
UpgradeProtocol upgradeProtocol = getProtocol().getNegotiatedProtocol(negotiatedProtocol);
if (upgradeProtocol != null) {
processor = upgradeProtocol.getProcessor(wrapper, getProtocol().getAdapter());
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.processorCreate", processor));
}
} else if (negotiatedProtocol.equals("http/1.1")) {
// Explicitly negotiated the default protocol.
// Obtain a processor below.
} else {
// TODO:
// OpenSSL 1.0.2's ALPN callback doesn't support
// failing the handshake with an error if no
// protocol can be negotiated. Therefore, we need to
// fail the connection here. Once this is fixed,
// replace the code below with the commented out
// block.
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.negotiatedProcessor.fail",
negotiatedProtocol));
}
return SocketState.CLOSED;
/*
* To replace the code above once OpenSSL 1.1.0 is used. // Failed to create processor. This
* is a bug. throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString(
* "abstractConnectionHandler.negotiatedProcessor.fail", negotiatedProtocol));
*/
}
}
}
if (processor == null) {
processor = recycledProcessors.pop();
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.processorPop", processor));
}
}
if (processor == null) {
processor = getProtocol().createProcessor();
register(processor);
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.processorCreate", processor));
}
}
processor.setSslSupport(wrapper.getSslSupport());
SocketState state = SocketState.CLOSED;
do {
state = processor.process(wrapper, status);
if (state == SocketState.UPGRADING) {
// Get the HTTP upgrade handler
UpgradeToken upgradeToken = processor.getUpgradeToken();
// Restore leftover input to the wrapper so the upgrade
// processor can process it.
ByteBuffer leftOverInput = processor.getLeftoverInput();
wrapper.unRead(leftOverInput);
if (upgradeToken == null) {
// Assume direct HTTP/2 connection
UpgradeProtocol upgradeProtocol = getProtocol().getUpgradeProtocol("h2c");
if (upgradeProtocol != null) {
// Release the Http11 processor to be re-used
release(processor);
// Create the upgrade processor
processor = upgradeProtocol.getProcessor(wrapper, getProtocol().getAdapter());
} else {
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(
sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.negotiatedProcessor.fail", "h2c"));
}
// Exit loop and trigger appropriate clean-up
state = SocketState.CLOSED;
}
} else {
HttpUpgradeHandler httpUpgradeHandler = upgradeToken.getHttpUpgradeHandler();
// Release the Http11 processor to be re-used
release(processor);
// Create the upgrade processor
processor = getProtocol().createUpgradeProcessor(wrapper, upgradeToken);
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(
sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.upgradeCreate", processor, wrapper));
}
// Initialise the upgrade handler (which may trigger
// some IO using the new protocol which is why the lines
// above are necessary)
// This cast should be safe. If it fails the error
// handling for the surrounding try/catch will deal with
// it.
if (upgradeToken.getInstanceManager() == null) {
httpUpgradeHandler.init((WebConnection) processor);
} else {
ClassLoader oldCL = upgradeToken.getContextBind().bind(null);
try {
httpUpgradeHandler.init((WebConnection) processor);
} finally {
upgradeToken.getContextBind().unbind(oldCL);
}
}
if (httpUpgradeHandler instanceof InternalHttpUpgradeHandler) {
if (((InternalHttpUpgradeHandler) httpUpgradeHandler).hasAsyncIO()) {
// The handler will initiate all further I/O
state = SocketState.ASYNC_IO;
}
}
}
}
} while (state == SocketState.UPGRADING);
if (state == SocketState.LONG) {
// In the middle of processing a request/response. Keep the
// socket associated with the processor. Exact requirements
// depend on type of long poll
longPoll(wrapper, processor);
if (processor.isAsync()) {
getProtocol().addWaitingProcessor(processor);
}
} else if (state == SocketState.OPEN) {
// In keep-alive but between requests. OK to recycle
// processor. Continue to poll for the next request.
release(processor);
processor = null;
wrapper.registerReadInterest();
} else if (state == SocketState.SENDFILE) {
// Sendfile in progress. If it fails, the socket will be
// closed. If it works, the socket either be added to the
// poller (or equivalent) to await more data or processed
// if there are any pipe-lined requests remaining.
} else if (state == SocketState.UPGRADED) {
// Don't add sockets back to the poller if this was a
// non-blocking write otherwise the poller may trigger
// multiple read events which may lead to thread starvation
// in the connector. The write() method will add this socket
// to the poller if necessary.
if (status != SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE) {
longPoll(wrapper, processor);
getProtocol().addWaitingProcessor(processor);
}
} else if (state == SocketState.ASYNC_IO) {
// Don't add sockets back to the poller.
// The handler will initiate all further I/O
if (status != SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE) {
getProtocol().addWaitingProcessor(processor);
}
} else if (state == SocketState.SUSPENDED) {
// Don't add sockets back to the poller.
// The resumeProcessing() method will add this socket
// to the poller.
} else {
// Connection closed. OK to recycle the processor.
// Processors handling upgrades require additional clean-up
// before release.
if (processor != null && processor.isUpgrade()) {
UpgradeToken upgradeToken = processor.getUpgradeToken();
HttpUpgradeHandler httpUpgradeHandler = upgradeToken.getHttpUpgradeHandler();
InstanceManager instanceManager = upgradeToken.getInstanceManager();
if (instanceManager == null) {
httpUpgradeHandler.destroy();
} else {
ClassLoader oldCL = upgradeToken.getContextBind().bind(null);
try {
httpUpgradeHandler.destroy();
} finally {
try {
instanceManager.destroyInstance(httpUpgradeHandler);
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
getLog().error(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.error"), e);
}
upgradeToken.getContextBind().unbind(oldCL);
}
}
}
release(processor);
processor = null;
}
if (processor != null) {
wrapper.setCurrentProcessor(processor);
}
return state;
} catch (SocketException e) {
// SocketExceptions are normal
getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.socketexception.debug"), e);
} catch (IOException e) {
// IOExceptions are normal
getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.ioexception.debug"), e);
} catch (ProtocolException e) {
// Protocol exceptions normally mean the client sent invalid or
// incomplete data.
getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.protocolexception.debug"), e);
}
// Future developers: if you discover any other
// rare-but-nonfatal exceptions, catch them here, and log as
// above.
catch (OutOfMemoryError oome) {
// Try and handle this here to give Tomcat a chance to close the
// connection and prevent clients waiting until they time out.
// Worst case, it isn't recoverable and the attempt at logging
// will trigger another OOME.
getLog().error(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.oome"), oome);
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
// any other exception or error is odd. Here we log it
// with "ERROR" level, so it will show up even on
// less-than-verbose logs.
getLog().error(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.error"), e);
}
// Make sure socket/processor is removed from the list of current
// connections
release(processor);
return SocketState.CLOSED;
}
这个方法很长,里面主要的操作就是创建和复用Processor,Processor处理单个Socket。
state = processor.process(wrapper, status);
这里的Processor是protocolProcessor与协议有关的,主要是HTTP。上面的SocketProcessor是与协议无关的。
下面进入Processor的相关源码,主要是Http11Processor这个HTTP/1.1协议的处理器。
三、Http11Processor
Http11Processor的类继承关系如下:
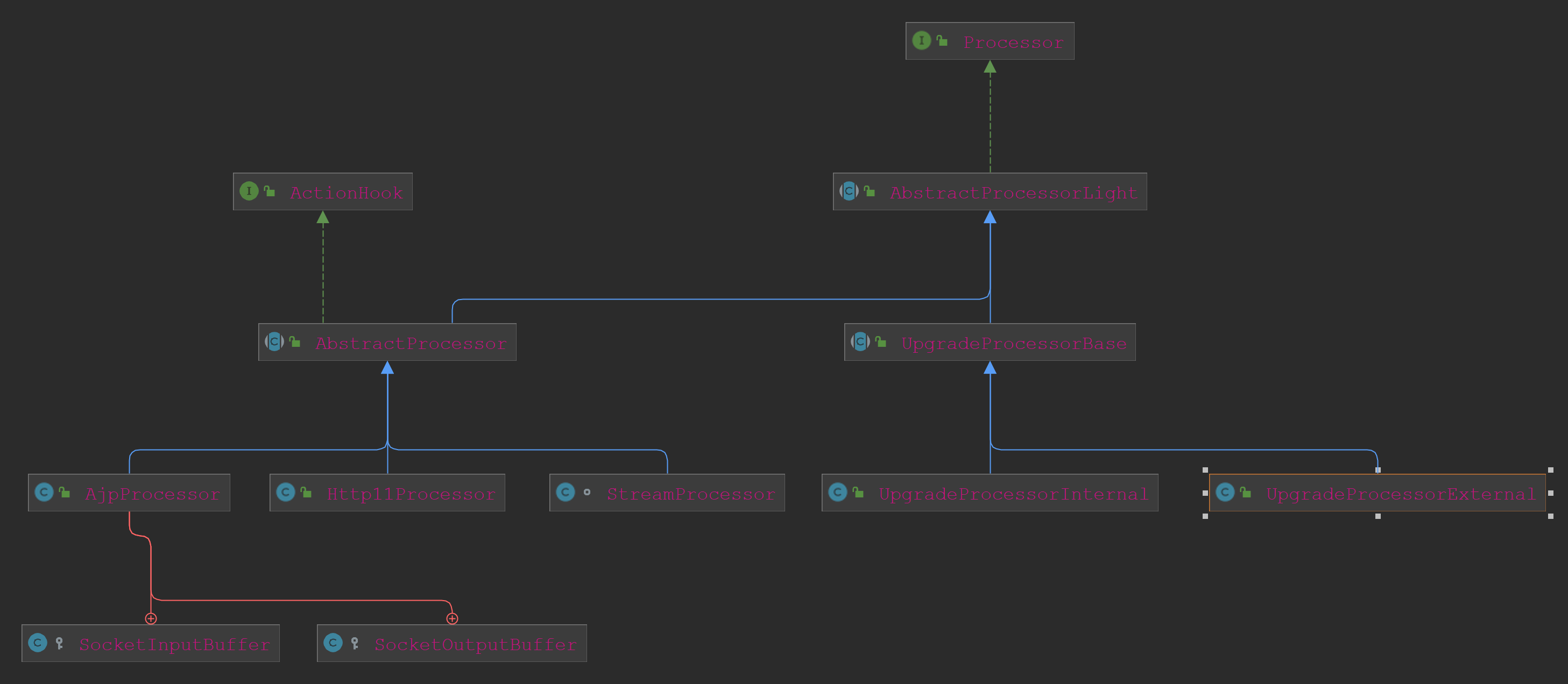
我们首先跟踪方法”processor.process(wrapper, status)”来到AbstractProcessorLight#process方法。
@Override
public SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper, SocketEvent status) throws IOException {
SocketState state = SocketState.CLOSED;
Iterator<DispatchType> dispatches = null;
do {
if (dispatches != null) {
DispatchType nextDispatch = dispatches.next();
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug("Processing dispatch type: [" + nextDispatch + "]");
}
state = dispatch(nextDispatch.getSocketStatus());
if (!dispatches.hasNext()) {
state = checkForPipelinedData(state, socketWrapper);
}
} else if (status == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT) {
// Do nothing here, just wait for it to get recycled
} else if (isAsync() || isUpgrade() || state == SocketState.ASYNC_END) {
state = dispatch(status);
state = checkForPipelinedData(state, socketWrapper);
} else if (status == SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE) {
// Extra write event likely after async, ignore
state = SocketState.LONG;
} else if (status == SocketEvent.OPEN_READ) {
state = service(socketWrapper);
} else if (status == SocketEvent.CONNECT_FAIL) {
logAccess(socketWrapper);
} else {
// Default to closing the socket if the SocketEvent passed in
// is not consistent with the current state of the Processor
state = SocketState.CLOSED;
}
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(
"Socket: [" + socketWrapper + "], Status in: [" + status + "], State out: [" + state + "]");
}
if (isAsync()) {
state = asyncPostProcess();
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(
"Socket: [" + socketWrapper + "], State after async post processing: [" + state + "]");
}
}
if (dispatches == null || !dispatches.hasNext()) {
// Only returns non-null iterator if there are
// dispatches to process.
dispatches = getIteratorAndClearDispatches();
}
} while (state == SocketState.ASYNC_END || dispatches != null && state != SocketState.CLOSED);
return state;
}
跟踪service方法来Http11Processor#service方法:
@Override
public SocketState service(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper) throws IOException {
RequestInfo rp = request.getRequestProcessor();
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PARSE);
// Setting up the I/O
setSocketWrapper(socketWrapper);
// Flags
keepAlive = true;
openSocket = false;
readComplete = true;
boolean keptAlive = false;
SendfileState sendfileState = SendfileState.DONE;
while (!getErrorState().isError() && keepAlive && !isAsync() && upgradeToken == null &&
sendfileState == SendfileState.DONE && !protocol.isPaused()) {
// Parsing the request header
try {
if (!inputBuffer.parseRequestLine(keptAlive, protocol.getConnectionTimeout(),
protocol.getKeepAliveTimeout())) {
if (inputBuffer.getParsingRequestLinePhase() == -1) {
return SocketState.UPGRADING;
} else if (handleIncompleteRequestLineRead()) {
break;
}
}
// Process the Protocol component of the request line
// Need to know if this is an HTTP 0.9 request before trying to
// parse headers.
prepareRequestProtocol();
if (protocol.isPaused()) {
// 503 - Service unavailable
response.setStatus(503);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, null);
} else {
keptAlive = true;
// Set this every time in case limit has been changed via JMX
request.getMimeHeaders().setLimit(protocol.getMaxHeaderCount());
// Don't parse headers for HTTP/0.9
if (!http09 && !inputBuffer.parseHeaders()) {
// We've read part of the request, don't recycle it
// instead associate it with the socket
openSocket = true;
readComplete = false;
break;
}
if (!protocol.getDisableUploadTimeout()) {
socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(protocol.getConnectionUploadTimeout());
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("http11processor.header.parse"), e);
}
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CONNECTION_NOW, e);
break;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
UserDataHelper.Mode logMode = userDataHelper.getNextMode();
if (logMode != null) {
String message = sm.getString("http11processor.header.parse");
switch (logMode) {
case INFO_THEN_DEBUG:
message += sm.getString("http11processor.fallToDebug");
//$FALL-THROUGH$
case INFO:
log.info(message, t);
break;
case DEBUG:
log.debug(message, t);
}
}
// 400 - Bad Request
response.setStatus(400);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t);
}
// Has an upgrade been requested?
if (isConnectionToken(request.getMimeHeaders(), "upgrade")) {
// Check the protocol
String requestedProtocol = request.getHeader("Upgrade");
UpgradeProtocol upgradeProtocol = protocol.getUpgradeProtocol(requestedProtocol);
if (upgradeProtocol != null) {
if (upgradeProtocol.accept(request)) {
// Create clone of request for upgraded protocol
Request upgradeRequest = null;
try {
upgradeRequest = cloneRequest(request);
} catch (ByteChunk.BufferOverflowException ioe) {
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_REQUEST_ENTITY_TOO_LARGE);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, null);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, ioe);
}
if (upgradeRequest != null) {
// Complete the HTTP/1.1 upgrade process
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS);
response.setHeader("Connection", "Upgrade");
response.setHeader("Upgrade", requestedProtocol);
action(ActionCode.CLOSE, null);
getAdapter().log(request, response, 0);
// Continue processing using new protocol
InternalHttpUpgradeHandler upgradeHandler = upgradeProtocol
.getInternalUpgradeHandler(socketWrapper, getAdapter(), upgradeRequest);
UpgradeToken upgradeToken = new UpgradeToken(upgradeHandler, null, null, requestedProtocol);
action(ActionCode.UPGRADE, upgradeToken);
return SocketState.UPGRADING;
}
}
}
}
if (getErrorState().isIoAllowed()) {
// Setting up filters, and parse some request headers
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PREPARE);
try {
prepareRequest();
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("http11processor.request.prepare"), t);
}
// 500 - Internal Server Error
response.setStatus(500);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t);
}
}
int maxKeepAliveRequests = protocol.getMaxKeepAliveRequests();
if (maxKeepAliveRequests == 1) {
keepAlive = false;
} else if (maxKeepAliveRequests > 0 && socketWrapper.decrementKeepAlive() <= 0) {
keepAlive = false;
}
// Process the request in the adapter
if (getErrorState().isIoAllowed()) {
try {
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_SERVICE);
getAdapter().service(request, response);
// Handle when the response was committed before a serious
// error occurred. Throwing a ServletException should both
// set the status to 500 and set the errorException.
// If we fail here, then the response is likely already
// committed, so we can't try and set headers.
if (keepAlive && !getErrorState().isError() && !isAsync() &&
statusDropsConnection(response.getStatus())) {
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, null);
}
} catch (InterruptedIOException e) {
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CONNECTION_NOW, e);
} catch (HeadersTooLargeException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("http11processor.request.process"), e);
// The response should not have been committed but check it
// anyway to be safe
if (response.isCommitted()) {
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_NOW, e);
} else {
response.reset();
response.setStatus(500);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, e);
response.setHeader("Connection", "close"); // TODO: Remove
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString("http11processor.request.process"), t);
// 500 - Internal Server Error
response.setStatus(500);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t);
getAdapter().log(request, response, 0);
}
}
// Finish the handling of the request
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDINPUT);
if (!isAsync()) {
// If this is an async request then the request ends when it has
// been completed. The AsyncContext is responsible for calling
// endRequest() in that case.
endRequest();
}
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDOUTPUT);
// If there was an error, make sure the request is counted as
// and error, and update the statistics counter
if (getErrorState().isError()) {
response.setStatus(500);
}
if (!isAsync() || getErrorState().isError()) {
request.updateCounters();
if (getErrorState().isIoAllowed()) {
inputBuffer.nextRequest();
outputBuffer.nextRequest();
}
}
if (!protocol.getDisableUploadTimeout()) {
int connectionTimeout = protocol.getConnectionTimeout();
if (connectionTimeout > 0) {
socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(connectionTimeout);
} else {
socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(0);
}
}
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_KEEPALIVE);
sendfileState = processSendfile(socketWrapper);
}
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDED);
if (getErrorState().isError() || (protocol.isPaused() && !isAsync())) {
return SocketState.CLOSED;
} else if (isAsync()) {
return SocketState.LONG;
} else if (isUpgrade()) {
return SocketState.UPGRADING;
} else {
if (sendfileState == SendfileState.PENDING) {
return SocketState.SENDFILE;
} else {
if (openSocket) {
if (readComplete) {
return SocketState.OPEN;
} else {
return SocketState.LONG;
}
} else {
return SocketState.CLOSED;
}
}
}
}
方法很长,主要的操作是解析请求,然后调用适配器的service方法来处理请求和响应对象。
getAdapter().service(request, response);
Adapter的默认实现是CoyoteAdapter,其Service方法连接了Container/容器,将请求和响应对象转交给容器及其阀来处理。
// Calling the container
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
Tomcat处理HTTP请求是按照:Acceptor—>Poller—>SocketProcessor(Worker)和Executor—>Http11Processor—>Http11Processor—>CoyoteAdapter—>Container和Valve—>Servlet,的执行流程的。
Acceptor,Poller,Executor的创建和启动在NioEndpoint的start方法内,如下:
/**
* Start the NIO endpoint, creating acceptor, poller threads.
*/
@Override
public void startInternal() throws Exception {
if (!running) {
running = true;
paused = false;
if (socketProperties.getProcessorCache() != 0) {
processorCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getProcessorCache());
}
if (socketProperties.getEventCache() != 0) {
eventCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getEventCache());
}
int actualBufferPool =
socketProperties.getActualBufferPool(isSSLEnabled() ? getSniParseLimit() * 2 : 0);
if (actualBufferPool != 0) {
nioChannels = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
actualBufferPool);
}
// Create worker collection
if (getExecutor() == null) {
createExecutor();
}
initializeConnectionLatch();
// Start poller thread
poller = new Poller();
Thread pollerThread = new Thread(poller, getName() + "-Poller");
pollerThread.setPriority(threadPriority);
pollerThread.setDaemon(true);
pollerThread.start();
startAcceptorThread();
}
}
Tomcat处理HTTP请求是外层组件到内层组件,而创建和启动组件一般是内层组件到外层组件,正好相反。
后面文件笔者将会结合这个系列全部的源码解读内容,实际调试和追究一笔HTTP请求在Tomcat的执行流程。
四、参考材料
1.《深入剖析Tomcat》
