本文简单解读Connector连接器组件。 本系列的源码工程为:HowTomcatWorksSourceCode。
本文目录为:
一、概述
我们先看一下这个Tomcat的整体架构图:
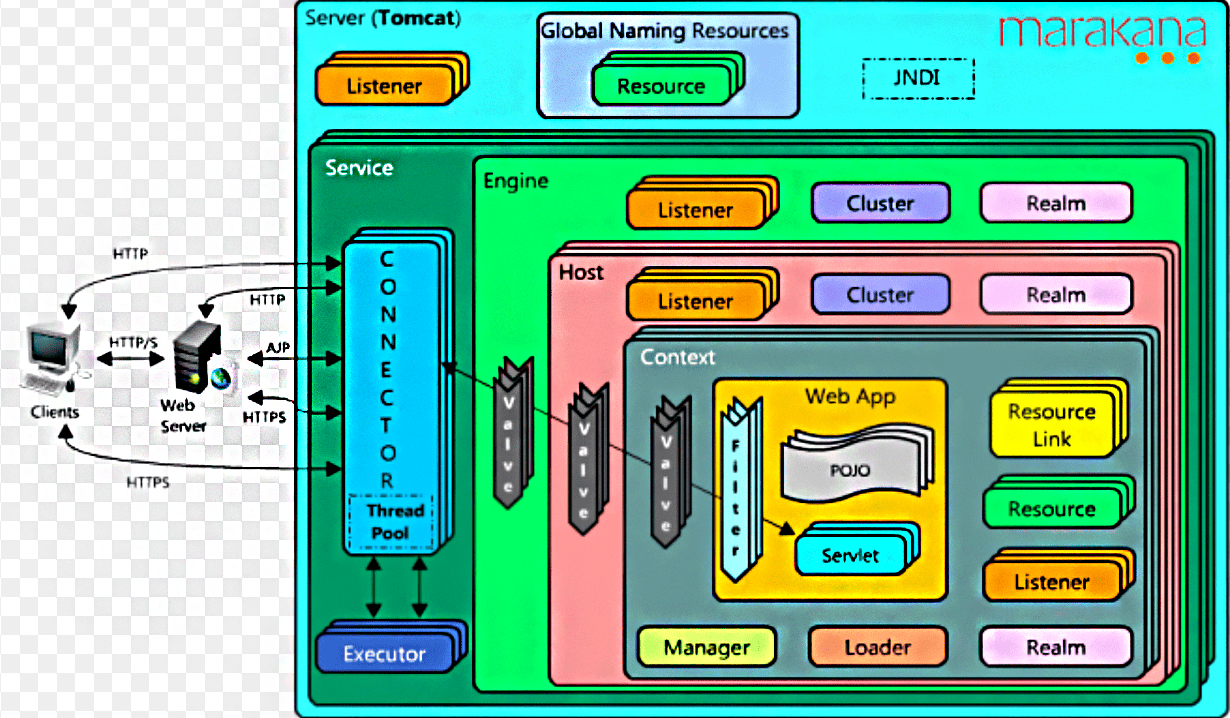
从这个图可以看到Connector连接器是输入Service内部的,由Service创建,连接了Service和Container。
Connector连接器主要功能是将客户端的HTTP请求转发给容器,其最主要的方法就是createRequest和createResponse。
CoyoteAdapter是Connector的适配器,主要提供service方法处理Http请求。
从Service的init方法可以看到,一个服务(Service)是可以由多个Connector连接器的。
/**
* Invoke a pre-startup initialization. This is used to allow connectors to bind to restricted ports under Unix
* operating environments.
*/
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
if (engine != null) {
engine.init();
}
// Initialize any Executors
for (Executor executor : findExecutors()) {
if (executor instanceof JmxEnabled) {
((JmxEnabled) executor).setDomain(getDomain());
}
executor.init();
}
// Initialize mapper listener
mapperListener.init();
// Initialize our defined Connectors
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
//初始化连接器
for (Connector connector : connectors) {
connector.init();
}
}
}
二、源码解读
2.1 Connector
tomcat中Connector类主要源码如:
public class Connector extends LifecycleMBeanBase {
//默认的连接器使用的协议HTTP/1.1 NIO
/**
* Defaults to using HTTP/1.1 NIO implementation.
*/
public Connector() {
this("HTTP/1.1");
}
//构造器方法,主要是创建协议处理器
public Connector(String protocol) {
configuredProtocol = protocol;
ProtocolHandler p = null;
try {
p = ProtocolHandler.create(protocol);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInstantiationFailed"), e);
}
if (p != null) {
protocolHandler = p;
protocolHandlerClassName = protocolHandler.getClass().getName();
} else {
protocolHandler = null;
protocolHandlerClassName = protocol;
}
// Default for Connector depends on this system property
setThrowOnFailure(Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE"));
}
public Connector(ProtocolHandler protocolHandler) {
protocolHandlerClassName = protocolHandler.getClass().getName();
configuredProtocol = protocolHandlerClassName;
this.protocolHandler = protocolHandler;
// Default for Connector depends on this system property
setThrowOnFailure(Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE"));
}
// //创建httpRequest对象
/**
* Create (or allocate) and return a Request object suitable for specifying the contents of a Request to the
* responsible Container.
*
* @param coyoteRequest The Coyote request with which the Request object will always be associated. In normal usage
* this must be non-null. In some test scenarios, it may be possible to use a null request
* without triggering an NPE.
*
* @return a new Servlet request object
*/
public Request createRequest(org.apache.coyote.Request coyoteRequest) {
return new Request(this, coyoteRequest);
}
//创建httpResponse对象
/**
* Create and return a Response object suitable for receiving the contents of a Response from the responsible
* Container.
*
* @param coyoteResponse The Coyote request with which the Response object will always be associated. In normal
* usage this must be non-null. In some test scenarios, it may be possible to use a null
* response without triggering an NPE.
*
* @return a new Servlet response object
*/
public Response createResponse(org.apache.coyote.Response coyoteResponse) {
int size = protocolHandler.getDesiredBufferSize();
if (size > 0) {
return new Response(coyoteResponse, size);
} else {
return new Response(coyoteResponse);
}
}
//暂停方法
/**
* Pause the connector.
*/
public void pause() {
try {
if (protocolHandler != null) {
protocolHandler.pause();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerPauseFailed"), e);
}
}
//恢复方法
/**
* Resume the connector.
*/
public void resume() {
try {
if (protocolHandler != null) {
protocolHandler.resume();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerResumeFailed"), e);
}
}
//初始化方法,创建CoyoteAdapter作为Connector的适配器。执行protocolHandler的初始化操作
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
if (protocolHandler == null) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInstantiationFailed"));
}
// Initialize adapter
adapter = new CoyoteAdapter(this);
protocolHandler.setAdapter(adapter);
// Make sure parseBodyMethodsSet has a default
if (null == parseBodyMethodsSet) {
setParseBodyMethods(getParseBodyMethods());
}
if (AprStatus.isAprAvailable() && AprStatus.getUseOpenSSL() &&
protocolHandler instanceof AbstractHttp11Protocol) {
AbstractHttp11Protocol<?> jsseProtocolHandler = (AbstractHttp11Protocol<?>) protocolHandler;
if (jsseProtocolHandler.isSSLEnabled() && jsseProtocolHandler.getSslImplementationName() == null) {
// OpenSSL is compatible with the JSSE configuration, so use it if APR is available
jsseProtocolHandler.setSslImplementationName(OpenSSLImplementation.class.getName());
}
}
try {
protocolHandler.init();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInitializationFailed"), e);
}
}
//启动方法。主要是启动protocolHandler
/**
* Begin processing requests via this Connector.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if a fatal startup error occurs
*/
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Validate settings before starting
String id = (protocolHandler != null) ? protocolHandler.getId() : null;
if (id == null && getPortWithOffset() < 0) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("coyoteConnector.invalidPort", Integer.valueOf(getPortWithOffset())));
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Configure the utility executor before starting the protocol handler
if (protocolHandler != null && service != null) {
protocolHandler.setUtilityExecutor(service.getServer().getUtilityExecutor());
}
try {
protocolHandler.start();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Includes NPE - protocolHandler will be null for invalid protocol if throwOnFailure is false
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerStartFailed"), e);
}
}
//停止方法。主要是停止protocolHandler
/**
* Terminate processing requests via this Connector.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if a fatal shutdown error occurs
*/
@Override
protected void stopInternal() throws LifecycleException {
setState(LifecycleState.STOPPING);
try {
if (protocolHandler != null) {
protocolHandler.stop();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerStopFailed"), e);
}
// Remove the utility executor once the protocol handler has been stopped
if (protocolHandler != null) {
protocolHandler.setUtilityExecutor(null);
}
}
//销毁方法,销毁protocolHandler
@Override
protected void destroyInternal() throws LifecycleException {
try {
if (protocolHandler != null) {
protocolHandler.destroy();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerDestroyFailed"), e);
}
if (getService() != null) {
getService().removeConnector(this);
}
super.destroyInternal();
}
}
可以看到Connector主要是创建HttpRequest和HttpResponse,其他的启动、关闭、暂停等方法基本是调用协议处理器的对应方法。
题外话:Tomcat基本的代码中,变量、属性、方法都是按照一定的类型顺序来到创建的,比如:类变量、构造器、实例变量、实例变量的get和set方法、公共方法这样,很标准化,源码阅读者能够集中到某一区域去解读相关代码。
在Connector的init方法的这行代码中创建了适配器CoyoteAdapter:
// Initialize adapter
adapter = new CoyoteAdapter(this);
protocolHandler.setAdapter(adapter);
我们继续来到CoyoteAdapter的源码。
2.2 CoyoteAdapter
这里看下CoyoteAdapter的主要代码:
/**
* Implementation of a request processor which delegates the processing to a Coyote processor.
*
* @author Craig R. McClanahan
* @author Remy Maucherat
*/
public class CoyoteAdapter implements Adapter {
// ----------------------------------------------------------- Constructors
/**
* Construct a new CoyoteProcessor associated with the specified connector.
*
* @param connector CoyoteConnector that owns this processor
*/
public CoyoteAdapter(Connector connector) {
super();
this.connector = connector;
}
// ----------------------------------------------------- Instance Variables
/**
* The CoyoteConnector with which this processor is associated.
*/
private final Connector connector;
// -------------------------------------------------------- Adapter Methods
//异步处理Http请求
@Override
public boolean asyncDispatch(org.apache.coyote.Request req, org.apache.coyote.Response res, SocketEvent status)
throws Exception {
Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
if (request == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("coyoteAdapter.nullRequest"));
}
boolean success = true;
AsyncContextImpl asyncConImpl = request.getAsyncContextInternal();
req.setRequestThread();
try {
if (!request.isAsync()) {
// Error or timeout
// Lift any suspension (e.g. if sendError() was used by an async
// request) to allow the response to be written to the client
response.setSuspended(false);
}
if (status == SocketEvent.TIMEOUT) {
if (!asyncConImpl.timeout()) {
asyncConImpl.setErrorState(null, false);
}
} else if (status == SocketEvent.ERROR) {
// An I/O error occurred on a non-container thread which means
// that the socket needs to be closed so set success to false to
// trigger a close
success = false;
Throwable t = (Throwable) req.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
Context context = request.getContext();
ClassLoader oldCL = null;
try {
oldCL = context.bind(null);
if (req.getReadListener() != null) {
req.getReadListener().onError(t);
}
if (res.getWriteListener() != null) {
res.getWriteListener().onError(t);
}
res.action(ActionCode.CLOSE_NOW, t);
asyncConImpl.setErrorState(t, true);
} finally {
context.unbind(oldCL);
}
}
// Check to see if non-blocking writes or reads are being used
if (!request.isAsyncDispatching() && request.isAsync()) {
WriteListener writeListener = res.getWriteListener();
ReadListener readListener = req.getReadListener();
if (writeListener != null && status == SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE) {
Context context = request.getContext();
ClassLoader oldCL = null;
try {
oldCL = context.bind(null);
res.onWritePossible();
if (request.isFinished() && req.sendAllDataReadEvent() && readListener != null) {
readListener.onAllDataRead();
}
// User code may have swallowed an IOException
if (response.getCoyoteResponse().isExceptionPresent()) {
throw response.getCoyoteResponse().getErrorException();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
// Need to trigger the call to AbstractProcessor.setErrorState()
// before the listener is called so the listener can call complete
// Therefore no need to set success=false as that would trigger a
// second call to AbstractProcessor.setErrorState()
// https://bz.apache.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=65001
writeListener.onError(t);
res.action(ActionCode.CLOSE_NOW, t);
asyncConImpl.setErrorState(t, true);
} finally {
context.unbind(oldCL);
}
} else if (readListener != null && status == SocketEvent.OPEN_READ) {
Context context = request.getContext();
ClassLoader oldCL = null;
try {
oldCL = context.bind(null);
// If data is being read on a non-container thread a
// dispatch with status OPEN_READ will be used to get
// execution back on a container thread for the
// onAllDataRead() event. Therefore, make sure
// onDataAvailable() is not called in this case.
if (!request.isFinished()) {
req.onDataAvailable();
}
if (request.isFinished() && req.sendAllDataReadEvent()) {
readListener.onAllDataRead();
}
// User code may have swallowed an IOException
if (request.getCoyoteRequest().isExceptionPresent()) {
throw request.getCoyoteRequest().getErrorException();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
// Need to trigger the call to AbstractProcessor.setErrorState()
// before the listener is called so the listener can call complete
// Therefore no need to set success=false as that would trigger a
// second call to AbstractProcessor.setErrorState()
// https://bz.apache.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=65001
readListener.onError(t);
res.action(ActionCode.CLOSE_NOW, t);
asyncConImpl.setErrorState(t, true);
} finally {
context.unbind(oldCL);
}
}
}
// Has an error occurred during async processing that needs to be
// processed by the application's error page mechanism (or Tomcat's
// if the application doesn't define one)?
if (!request.isAsyncDispatching() && request.isAsync() && response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}
if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
Throwable t = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
if (t != null) {
asyncConImpl.setErrorState(t, true);
}
}
if (!request.isAsync()) {
request.finishRequest();
response.finishResponse();
}
// Check to see if the processor is in an error state. If it is,
// bail out now.
AtomicBoolean error = new AtomicBoolean(false);
res.action(ActionCode.IS_ERROR, error);
if (error.get()) {
if (request.isAsyncCompleting() || request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
// Connection will be forcibly closed which will prevent completion/dispatch happening at the usual
// point. Trigger post processing here.
res.action(ActionCode.ASYNC_POST_PROCESS, null);
}
success = false;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
success = false;
// Ignore
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
success = false;
log.error(sm.getString("coyoteAdapter.asyncDispatch"), t);
} finally {
if (!success) {
res.setStatus(500);
}
// Access logging
if (!success || !request.isAsync()) {
long time = 0;
if (req.getStartTimeNanos() != -1) {
time = System.nanoTime() - req.getStartTimeNanos();
}
Context context = request.getContext();
if (context != null) {
context.logAccess(request, response, time, false);
} else {
log(req, res, time);
}
}
req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(null);
req.clearRequestThread();
// Recycle the wrapper request and response
if (!success || !request.isAsync()) {
updateWrapperErrorCount(request, response);
request.recycle();
response.recycle();
}
}
return success;
}
//service方法,处理单个Http请求
@Override
public void service(org.apache.coyote.Request req, org.apache.coyote.Response res) throws Exception {
Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
if (request == null) {
// Create objects
request = connector.createRequest(req);
response = connector.createResponse(res);
// Link objects
request.setResponse(response);
response.setRequest(request);
// Set as notes
req.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, request);
res.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, response);
// Set query string encoding
req.getParameters().setQueryStringCharset(connector.getURICharset());
}
if (connector.getXpoweredBy()) {
response.addHeader("X-Powered-By", POWERED_BY);
}
boolean async = false;
boolean postParseSuccess = false;
req.setRequestThread();
try {
// Parse and set Catalina and configuration specific
// request parameters
postParseSuccess = postParseRequest(req, request, res, response);
if (postParseSuccess) {
// check valves if we support async
request.setAsyncSupported(connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
// Calling the container
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}
if (request.isAsync()) {
async = true;
ReadListener readListener = req.getReadListener();
if (readListener != null && request.isFinished()) {
// Possible the all data may have been read during service()
// method so this needs to be checked here
ClassLoader oldCL = null;
try {
oldCL = request.getContext().bind(null);
if (req.sendAllDataReadEvent()) {
req.getReadListener().onAllDataRead();
}
} finally {
request.getContext().unbind(oldCL);
}
}
Throwable throwable = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
// If an async request was started, is not going to end once
// this container thread finishes and an error occurred, trigger
// the async error process
if (!request.isAsyncCompleting() && throwable != null) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().setErrorState(throwable, true);
}
} else {
request.finishRequest();
response.finishResponse();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
} finally {
AtomicBoolean error = new AtomicBoolean(false);
res.action(ActionCode.IS_ERROR, error);
if (request.isAsyncCompleting() && error.get()) {
// Connection will be forcibly closed which will prevent
// completion happening at the usual point. Need to trigger
// call to onComplete() here.
res.action(ActionCode.ASYNC_POST_PROCESS, null);
async = false;
}
// Access log
if (!async && postParseSuccess) {
// Log only if processing was invoked.
// If postParseRequest() failed, it has already logged it.
Context context = request.getContext();
Host host = request.getHost();
// If the context is null, it is likely that the endpoint was
// shutdown, this connection closed and the request recycled in
// a different thread. That thread will have updated the access
// log so it is OK not to update the access log here in that
// case.
// The other possibility is that an error occurred early in
// processing and the request could not be mapped to a Context.
// Log via the host or engine in that case.
long time = System.nanoTime() - req.getStartTimeNanos();
if (context != null) {
context.logAccess(request, response, time, false);
} else if (response.isError()) {
if (host != null) {
host.logAccess(request, response, time, false);
} else {
connector.getService().getContainer().logAccess(request, response, time, false);
}
}
}
req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(null);
req.clearRequestThread();
// Recycle the wrapper request and response
if (!async) {
updateWrapperErrorCount(request, response);
request.recycle();
response.recycle();
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean prepare(org.apache.coyote.Request req, org.apache.coyote.Response res)
throws IOException, ServletException {
Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
return postParseRequest(req, request, res, response);
}
// ------------------------------------------------------ Protected Methods
//对Request和Response的处理
/**
* Perform the necessary processing after the HTTP headers have been parsed to enable the request/response pair to
* be passed to the start of the container pipeline for processing.
*
* @param req The coyote request object
* @param request The catalina request object
* @param res The coyote response object
* @param response The catalina response object
*
* @return <code>true</code> if the request should be passed on to the start of the container pipeline, otherwise
* <code>false</code>
*
* @throws IOException If there is insufficient space in a buffer while processing headers
* @throws ServletException If the supported methods of the target servlet cannot be determined
*/
protected boolean postParseRequest(org.apache.coyote.Request req, Request request, org.apache.coyote.Response res,
Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
// If the processor has set the scheme (AJP does this, HTTP does this if
// SSL is enabled) use this to set the secure flag as well. If the
// processor hasn't set it, use the settings from the connector
if (req.scheme().isNull()) {
// Use connector scheme and secure configuration, (defaults to
// "http" and false respectively)
req.scheme().setString(connector.getScheme());
request.setSecure(connector.getSecure());
} else {
// Use processor specified scheme to determine secure state
request.setSecure(req.scheme().equals("https"));
}
// At this point the Host header has been processed.
// Override if the proxyPort/proxyHost are set
String proxyName = connector.getProxyName();
int proxyPort = connector.getProxyPort();
if (proxyPort != 0) {
req.setServerPort(proxyPort);
} else if (req.getServerPort() == -1) {
// Not explicitly set. Use default ports based on the scheme
if (req.scheme().equals("https")) {
req.setServerPort(443);
} else {
req.setServerPort(80);
}
}
if (proxyName != null) {
req.serverName().setString(proxyName);
}
MessageBytes undecodedURI = req.requestURI();
// Check for ping OPTIONS * request
if (undecodedURI.equals("*")) {
if (req.method().equalsIgnoreCase("OPTIONS")) {
StringBuilder allow = new StringBuilder();
allow.append("GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, DELETE, OPTIONS");
// Trace if allowed
if (connector.getAllowTrace()) {
allow.append(", TRACE");
}
res.setHeader("Allow", allow.toString());
// Access log entry as processing won't reach AccessLogValve
connector.getService().getContainer().logAccess(request, response, 0, true);
return false;
} else {
response.sendError(400, sm.getString("coyoteAdapter.invalidURI"));
}
}
MessageBytes decodedURI = req.decodedURI();
// Filter CONNECT method
if (req.method().equalsIgnoreCase("CONNECT")) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, sm.getString("coyoteAdapter.connect"));
} else {
// No URI for CONNECT requests
if (undecodedURI.getType() == MessageBytes.T_BYTES) {
if (connector.getRejectSuspiciousURIs()) {
if (checkSuspiciousURIs(undecodedURI.getByteChunk())) {
response.sendError(400, sm.getString("coyoteAdapter.invalidURI"));
}
}
// Copy the raw URI to the decodedURI
decodedURI.duplicate(undecodedURI);
// Parse (and strip out) the path parameters
parsePathParameters(req, request);
// URI decoding
// %xx decoding of the URL
try {
req.getURLDecoder().convert(decodedURI.getByteChunk(),
connector.getEncodedSolidusHandlingInternal());
} catch (IOException ioe) {
response.sendError(400, sm.getString("coyoteAdapter.invalidURIWithMessage", ioe.getMessage()));
}
// Normalization
if (normalize(req.decodedURI(), connector.getAllowBackslash())) {
// Character decoding
convertURI(decodedURI, request);
// URIEncoding values are limited to US-ASCII supersets.
// Therefore it is not necessary to check that the URI remains
// normalized after character decoding
} else {
response.sendError(400, sm.getString("coyoteAdapter.invalidURI"));
}
} else {
/*
* The URI is chars or String, and has been sent using an in-memory protocol handler. The following
* assumptions are made: - req.requestURI() has been set to the 'original' non-decoded, non-normalized
* URI - req.decodedURI() has been set to the decoded, normalized form of req.requestURI() -
* 'suspicious' URI filtering - if required - has already been performed
*/
decodedURI.toChars();
// Remove all path parameters; any needed path parameter should be set
// using the request object rather than passing it in the URL
CharChunk uriCC = decodedURI.getCharChunk();
int semicolon = uriCC.indexOf(';');
if (semicolon > 0) {
decodedURI.setChars(uriCC.getBuffer(), uriCC.getStart(), semicolon);
}
}
}
// Request mapping.
MessageBytes serverName;
if (connector.getUseIPVHosts()) {
serverName = req.localName();
if (serverName.isNull()) {
// well, they did ask for it
res.action(ActionCode.REQ_LOCAL_NAME_ATTRIBUTE, null);
}
} else {
serverName = req.serverName();
}
// Version for the second mapping loop and
// Context that we expect to get for that version
String version = null;
Context versionContext = null;
boolean mapRequired = true;
if (response.isError()) {
// An error this early means the URI is invalid. Ensure invalid data
// is not passed to the mapper. Note we still want the mapper to
// find the correct host.
decodedURI.recycle();
}
while (mapRequired) {
// This will map the the latest version by default
connector.getService().getMapper().map(serverName, decodedURI, version, request.getMappingData());
// If there is no context at this point, either this is a 404
// because no ROOT context has been deployed or the URI was invalid
// so no context could be mapped.
if (request.getContext() == null) {
// Allow processing to continue.
// If present, the rewrite Valve may rewrite this to a valid
// request.
// The StandardEngineValve will handle the case of a missing
// Host and the StandardHostValve the case of a missing Context.
// If present, the error reporting valve will provide a response
// body.
return true;
}
// Now we have the context, we can parse the session ID from the URL
// (if any). Need to do this before we redirect in case we need to
// include the session id in the redirect
String sessionID;
if (request.getServletContext().getEffectiveSessionTrackingModes().contains(SessionTrackingMode.URL)) {
// Get the session ID if there was one
sessionID = request.getPathParameter(SessionConfig.getSessionUriParamName(request.getContext()));
if (sessionID != null) {
request.setRequestedSessionId(sessionID);
request.setRequestedSessionURL(true);
}
}
// Look for session ID in cookies and SSL session
try {
parseSessionCookiesId(request);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// Too many cookies
if (!response.isError()) {
response.setError();
response.sendError(400, e.getMessage());
}
return true;
}
parseSessionSslId(request);
sessionID = request.getRequestedSessionId();
mapRequired = false;
if (version != null && request.getContext() == versionContext) {
// We got the version that we asked for. That is it.
} else {
version = null;
versionContext = null;
Context[] contexts = request.getMappingData().contexts;
// Single contextVersion means no need to remap
// No session ID means no possibility of remap
if (contexts != null && sessionID != null) {
// Find the context associated with the session
for (int i = contexts.length; i > 0; i--) {
Context ctxt = contexts[i - 1];
if (ctxt.getManager().findSession(sessionID) != null) {
// We found a context. Is it the one that has
// already been mapped?
if (!ctxt.equals(request.getMappingData().context)) {
// Set version so second time through mapping
// the correct context is found
version = ctxt.getWebappVersion();
versionContext = ctxt;
// Reset mapping
request.getMappingData().recycle();
mapRequired = true;
// Recycle cookies and session info in case the
// correct context is configured with different
// settings
request.recycleSessionInfo();
request.recycleCookieInfo(true);
}
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!mapRequired && request.getContext().getPaused()) {
// Found a matching context but it is paused. Mapping data will
// be wrong since some Wrappers may not be registered at this
// point.
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Should never happen
}
// Reset mapping
request.getMappingData().recycle();
mapRequired = true;
}
}
// Possible redirect
MessageBytes redirectPathMB = request.getMappingData().redirectPath;
if (!redirectPathMB.isNull()) {
String redirectPath = URLEncoder.DEFAULT.encode(redirectPathMB.toString(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
String query = request.getQueryString();
if (request.isRequestedSessionIdFromURL()) {
// This is not optimal, but as this is not very common, it
// shouldn't matter
redirectPath = redirectPath + ";" + SessionConfig.getSessionUriParamName(request.getContext()) + "=" +
request.getRequestedSessionId();
}
if (query != null) {
// This is not optimal, but as this is not very common, it
// shouldn't matter
redirectPath = redirectPath + "?" + query;
}
response.sendRedirect(redirectPath);
request.getContext().logAccess(request, response, 0, true);
return false;
}
// Filter TRACE method
if (!connector.getAllowTrace() && req.method().equalsIgnoreCase("TRACE")) {
Wrapper wrapper = request.getWrapper();
String header = null;
if (wrapper != null) {
String[] methods = wrapper.getServletMethods();
if (methods != null) {
for (String method : methods) {
if ("TRACE".equals(method)) {
continue;
}
if (header == null) {
header = method;
} else {
header += ", " + method;
}
}
}
}
if (header != null) {
res.addHeader("Allow", header);
}
response.sendError(405, sm.getString("coyoteAdapter.trace"));
// Safe to skip the remainder of this method.
return true;
}
doConnectorAuthenticationAuthorization(req, request);
return true;
}
}
这里最重要的就是service方法,可以作为分析Tomcat处理http请求的代码入口。跟踪引用,service方法是由Processor(Http处理器)来调用的。
三、协议处理器ProtocolHandler
我们先看下ProtocolHandler的实现类,如下:
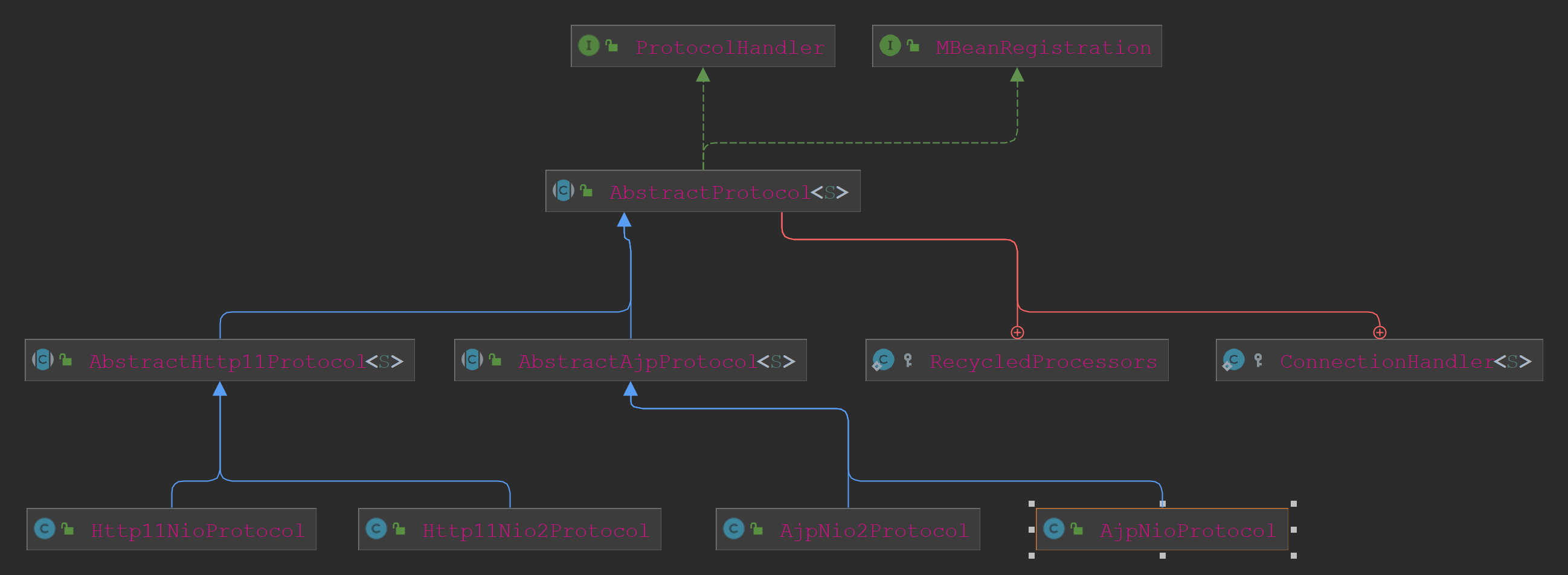
图片中有Tomcat默认的Http 1.1的NIO的协议处理器Http11NioProtocol。ProtocolHandler的典型方法有:init、start、pause、resume、stop、destroy和create等方法。
其中实现基类AbstractProtocol有这四个需要重点关注的内部对象:
/**
* Endpoint that provides low-level network I/O - must be matched to the ProtocolHandler implementation
* (ProtocolHandler using NIO, requires NIO Endpoint etc.).
*/
private final AbstractEndpoint<S, ?> endpoint;
private Handler<S> handler;
private final Set<Processor> waitingProcessors = ConcurrentHashMap.newKeySet();
/**
* The adapter provides the link between the ProtocolHandler and the connector.
*/
protected Adapter adapter;
AbstractProtocol组合了四个对象:一个NIO的端点,一个ConnectionHandler,一个Adapter(连接器的适配器)和一组连接(Socket)的处理器。
其中处理器Processor最主要的方法就是process方法,处理一个具体Socket的事件。
public interface Processor {
/**
* Process a connection. This is called whenever an event occurs (e.g. more data arrives) that allows processing to
* continue for a connection that is not currently being processed.
*
* @param socketWrapper The connection to process
* @param status The status of the connection that triggered this additional processing
*
* @return The state the caller should put the socket in when this method returns
*
* @throws IOException If an I/O error occurs during the processing of the request
*/
SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper, SocketEvent status) throws IOException;
//......
}
而NioEndpoint(EndPoint)内部最重要的内部对象就是:acceptor,SocketProcessor,Poller这三个。
/**
* Thread used to accept new connections and pass them to worker threads.
*/
protected Acceptor<U> acceptor;
这些对象之间的关系是:
- ProtocolHandler(Http11NioProtocol)内部包含NioEndpoint、ConnectionHandler、Processor(Http11Processor)、Adapter。NioEndpoint内包含Acceptor、Poller、SocketProcessor(Worker)。
- Acceptor是一个轮询线程(死循环),接受连接的Socket,并包装为NioSocketWrapper,然后转换为PollerEvent,注册到Poller的事件队列中。
- Poller轮询器获取PollerEvent,将Socket封装为SocketProcessor(Worker),提交给线程池(Worker线程池)执行。SocketProcessor由Http11Processor处理,并最终来到Http11Processor的service方法。
- Http11Processor调用连接器的适配器Adapter处理,Adapter(连接器)连接Servlet容器,service方法最终调用Container(及其Pipeline和Valve)的处理方法。
</strong> 具体的执行流程和调试过程,笔者会在后面文章做详细的解读。本文对ProtocolHandler的解读主要是旨在理解连接器相关组件的关系。
四、简单测试
这里使用原书第3章的源码,只为演示简单的连接器功能。 连接器:
public class HttpConnector implements Runnable {
boolean stopped;
private String scheme = "http";
public String getScheme() {
return scheme;
}
public void run() {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
int port = 8080;
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port, 1, InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"));
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
while (!stopped) {
// Accept the next incoming connection from the server socket
Socket socket = null;
try {
socket = serverSocket.accept();
}
catch (Exception e) {
continue;
}
// Hand this socket off to an HttpProcessor
HttpProcessor processor = new HttpProcessor(this);
processor.process(socket);
}
}
public void start() {
Thread thread = new Thread(this);
thread.start();
}
}
Http的Socket的处理器:
public class HttpProcessor {
public HttpProcessor(HttpConnector connector) {
this.connector = connector;
}
/**
* The HttpConnector with which this processor is associated.
*/
private HttpConnector connector = null;
private HttpRequest request;
private HttpRequestLine requestLine = new HttpRequestLine();
private HttpResponse response;
protected String method = null;
protected String queryString = null;
/**
* The string manager for this package.
*/
protected StringManager sm =
StringManager.getManager("ex03.pyrmont.connector.http");
public void process(Socket socket) {
SocketInputStream input = null;
OutputStream output = null;
try {
input = new SocketInputStream(socket.getInputStream(), 2048);
output = socket.getOutputStream();
// create HttpRequest object and parse
request = new HttpRequest(input);
// create HttpResponse object
response = new HttpResponse(output);
response.setRequest(request);
response.setHeader("Server", "Pyrmont Servlet Container");
parseRequest(input, output);
parseHeaders(input);
//check if this is a request for a servlet or a static resource
//a request for a servlet begins with "/servlet/"
if (request.getRequestURI().startsWith("/servlet/")) {
ServletProcessor processor = new ServletProcessor();
processor.process(request, response);
} else {
StaticResourceProcessor processor = new StaticResourceProcessor();
processor.process(request, response);
}
// Close the socket
socket.close();
// no shutdown for this application
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Servlet的处理器(简化版的Container):
public class ServletProcessor {
public void process(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response) {
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
String servletName = uri.substring(uri.lastIndexOf("/") + 1);
URLClassLoader loader = null;
try {
// create a URLClassLoader
URL[] urls = new URL[1];
URLStreamHandler streamHandler = null;
File classPath = new File(Constants.WEB_ROOT);
String repository = (new URL("file", null, classPath.getCanonicalPath() + File.separator)).toString() ;
urls[0] = new URL(null, repository, streamHandler);
loader = new URLClassLoader(urls);
}
catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e.toString() );
}
Class myClass = null;
try {
myClass = loader.loadClass(servletName);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
Servlet servlet = null;
try {
servlet = (Servlet) myClass.newInstance();
HttpRequestFacade requestFacade = new HttpRequestFacade(request);
HttpResponseFacade responseFacade = new HttpResponseFacade(response);
servlet.service(requestFacade, responseFacade);
((HttpResponse) response).finishResponse();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
}
执行测试:浏览器输入http://localhost:8080//servlet/PrimitiveServlet。
结果返回:
Hello. Roses are red.
五、参数资料
1.《深入剖析Tomcat》
