本文简单解读Tomcat的Engine和Host组件。
本系列的源码工程为:HowTomcatWorksSourceCode。
本文目录为:
一、概述
Engine和Host都是属于Container容器的一类。一共由四类的容器:Engine、Host、Context、Wrapper。其基本概念如下:
Engine:表示整个Servlet的引擎。
Host:包含一个或者多个Context容器的虚拟主机。
Context:表示一个Web应用,可以有多个Wrapper。
Wrapper:表示一个独立的Servlet。
四种容器类的类关系图如下:
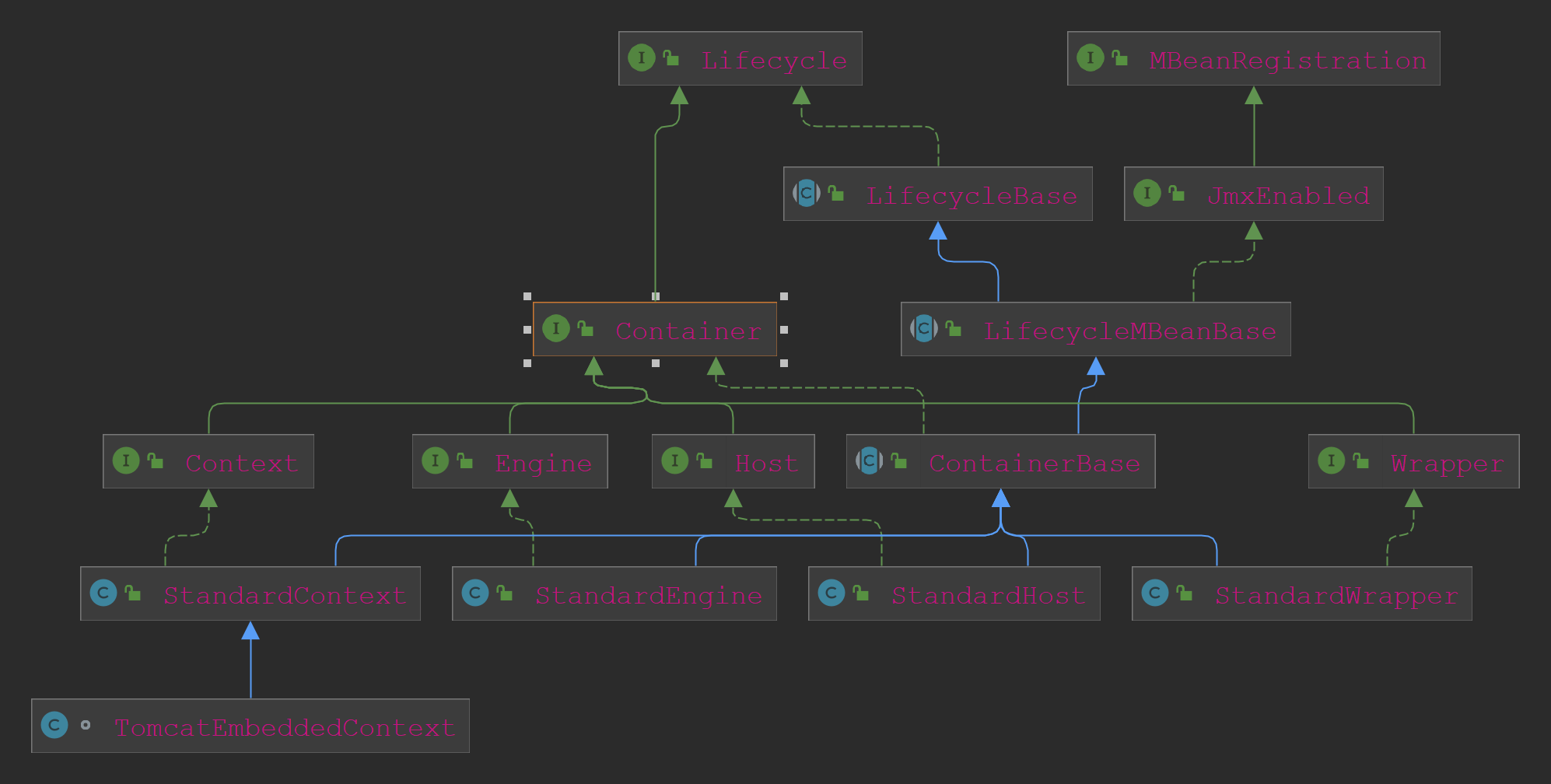
可以看到四种容器类都是实现了生命周期接口,方便统一关闭和启动;然后都继承自ContainerBase基类。
Engine是顶层容器,默认情况下Tomcat会使用Engine容器,并有一个Host作为子容器。
Host代表一个虚拟主机,其子容器就是Context了。
二、源码解读
2,1 StandardEngine
Engine的标准实现类StandardEngine的start和init方法如下:
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Ensure that a Realm is present before any attempt is made to start
// one. This will create the default NullRealm if necessary.
getRealm();
super.initInternal();
}
/**
* Start this component and implement the requirements of
* {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error that prevents this component from being
* used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Log our server identification information
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(sm.getString("standardEngine.start", ServerInfo.getServerInfo()));
}
// Standard container startup
super.startInternal();
}
可以看到StandardEngine的init、start、stop方法都是ContainerBase的基础方法,本身未做任何拓展。
我们在来到StandardEngineValve的invoke方法:
/**
* Select the appropriate child Host to process this request, based on the requested server name. If no matching
* Host can be found, return an appropriate HTTP error.
*
* @param request Request to be processed
* @param response Response to be produced
*
* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurred
* @exception ServletException if a servlet error occurred
*/
@Override
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
// Select the Host to be used for this Request
Host host = request.getHost();
//如果Engine的Host是null,直接返回。而不是交给下一个host去
if (host == null) {
// HTTP 0.9 or HTTP 1.0 request without a host when no default host
// is defined.
// Don't overwrite an existing error
if (!response.isError()) {
response.sendError(404);
}
return;
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(host.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
// Ask this Host to process this request
host.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}
这里的管道(列表)是类似链表的结构,其存储的Valve是一个组件的任务处理器,最主要的方法就是invoke方法,类似于Servlet的Filter过滤器。管道则类似于FilterChain过滤器链。
获取添加的阀的列表的代码如下,这里就是一个简单的链表的遍历:
/**
* Return the set of Valves in the pipeline associated with this Container, including the basic Valve (if any). If
* there are no such Valves, a zero-length array is returned.
*/
@Override
public Valve[] getValves() {
List<Valve> valveList = new ArrayList<>();
Valve current = first;
if (current == null) {
current = basic;
}
while (current != null) {
valveList.add(current);
current = current.getNext();
}
return valveList.toArray(new Valve[0]);
}
而StandardEngineValve的invoke方法如下:
/**
* Select the appropriate child Host to process this request, based on the requested server name. If no matching
* Host can be found, return an appropriate HTTP error.
*
* @param request Request to be processed
* @param response Response to be produced
*
* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurred
* @exception ServletException if a servlet error occurred
*/
@Override
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
// Select the Host to be used for this Request
Host host = request.getHost();
if (host == null) {
// HTTP 0.9 or HTTP 1.0 request without a host when no default host
// is defined.
// Don't overwrite an existing error
if (!response.isError()) {
response.sendError(404);
}
return;
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(host.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
// Ask this Host to process this request
host.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}
可以看到这里的阀是需要一个Host的。
下面我们再来到StandardHost的源码。
2.2 StandardHost
StandardHost的源码如下(有删减):
public class StandardHost extends ContainerBase implements Host {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(StandardHost.class);
// ----------------------------------------------------------- Constructors
/**
* Create a new StandardHost component with the default basic Valve.
*/
public StandardHost() {
super();
//添加基础阀
pipeline.setBasic(new StandardHostValve());
}
}
/**
* Start this component and implement the requirements of
* {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error that prevents this component from being
* used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Set error report valve
String errorValve = getErrorReportValveClass();
//设置和添加错误报告的valve
if ((errorValve != null) && (!errorValve.equals(""))) {
try {
boolean found = false;
Valve[] valves = getPipeline().getValves();
for (Valve valve : valves) {
if (errorValve.equals(valve.getClass().getName())) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
if (!found) {
Valve valve = ErrorReportValve.class.getName().equals(errorValve) ? new ErrorReportValve() :
(Valve) Class.forName(errorValve).getConstructor().newInstance();
getPipeline().addValve(valve);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString("standardHost.invalidErrorReportValveClass", errorValve), t);
}
}
super.startInternal();
}
可以看到StandardHost的init、start、stop等方法也是ContainerBase基类的方法。
而StandardHostValve的invoke方法如下:
// --------------------------------------------------------- Public Methods
/**
* Select the appropriate child Context to process this request, based on the specified request URI. If no matching
* Context can be found, return an appropriate HTTP error.
*
* @param request Request to be processed
* @param response Response to be produced
*
* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurred
* @exception ServletException if a servlet error occurred
*/
@Override
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
// Select the Context to be used for this Request
Context context = request.getContext();
if (context == null) {
// Don't overwrite an existing error
if (!response.isError()) {
response.sendError(404);
}
return;
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(context.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
boolean asyncAtStart = request.isAsync();
try {
context.bind(MY_CLASSLOADER);
if (!asyncAtStart && !context.fireRequestInitEvent(request.getRequest())) {
// Don't fire listeners during async processing (the listener
// fired for the request that called startAsync()).
// If a request init listener throws an exception, the request
// is aborted.
return;
}
// Ask this Context to process this request. Requests that are
// already in error must have been routed here to check for
// application defined error pages so DO NOT forward them to the
// application for processing.
try {
if (!response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
context.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
container.getLogger().error("Exception Processing " + request.getRequestURI(), t);
// If a new error occurred while trying to report a previous
// error allow the original error to be reported.
if (!response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, t);
throwable(request, response, t);
}
}
// Now that the request/response pair is back under container
// control lift the suspension so that the error handling can
// complete and/or the container can flush any remaining data
response.setSuspended(false);
Throwable t = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
// Protect against NPEs if the context was destroyed during a
// long running request.
if (!context.getState().isAvailable()) {
return;
}
// Look for (and render if found) an application level error page
if (response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
// If an error has occurred that prevents further I/O, don't waste time
// producing an error report that will never be read
AtomicBoolean result = new AtomicBoolean(false);
response.getCoyoteResponse().action(ActionCode.IS_IO_ALLOWED, result);
if (result.get()) {
if (t != null) {
throwable(request, response, t);
} else {
status(request, response);
}
}
}
if (!request.isAsync() && !asyncAtStart) {
context.fireRequestDestroyEvent(request.getRequest());
}
} finally {
// Access a session (if present) to update last accessed time, based
// on a strict interpretation of the specification
if (context.getAlwaysAccessSession()) {
request.getSession(false);
}
context.unbind(MY_CLASSLOADER);
}
}
这行代码“ context.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);” 主要是调用COntext的管道进行处理请求和响应。
三、简单测试
这里以原书第13章的Bootstrap1这个类为例.
public final class Bootstrap1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//invoke: http://localhost:8080/app1/Primitive or http://localhost:8080/app1/Modern
System.setProperty("catalina.base", System.getProperty("user.dir"));
Connector connector = new HttpConnector();
Wrapper wrapper1 = new StandardWrapper();
wrapper1.setName("Primitive");
wrapper1.setServletClass("PrimitiveServlet");
Wrapper wrapper2 = new StandardWrapper();
wrapper2.setName("Modern");
wrapper2.setServletClass("ModernServlet");
Context context = new StandardContext();
// StandardContext's start method adds a default mapper
context.setPath("/app1");
context.setDocBase("app1");
context.addChild(wrapper1);
context.addChild(wrapper2);
LifecycleListener listener = new SimpleContextConfig();
((Lifecycle) context).addLifecycleListener(listener);
Host host = new StandardHost();
host.addChild(context);
host.setName("localhost");
host.setAppBase("webapps");
Loader loader = new WebappLoader();
context.setLoader(loader);
// context.addServletMapping(pattern, name);
context.addServletMapping("/Primitive", "Primitive");
context.addServletMapping("/Modern", "Modern");
connector.setContainer(host);
try {
connector.initialize();
((Lifecycle) connector).start();
//启动Host
((Lifecycle) host).start();
// make the application wait until we press a key.
System.in.read();
//关闭Host
((Lifecycle) host).stop();
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
正常启动应用,浏览器输入:http://localhost:8080/app1/Primitive
结果响应:
HTTP/1.1 200 ok
Content-Type: text/html
<html><h1></h1><body><p>Hello. Roses are red.</p></body></html>
四、参数资料
1.《深入剖析Tomcat》
