本文是解读Tomcat的启动过程,从Bootstrap类开始解读整个的初始化组件和启动流程。 本系列的源码工程为:HowTomcatWorksSourceCode。
上一篇文章主要侧重于各项组件的创建和初始化流程,这篇文件我们从Bootstrap这个类开始解读Tomcat启动流程,也就是start方法的执行流程。
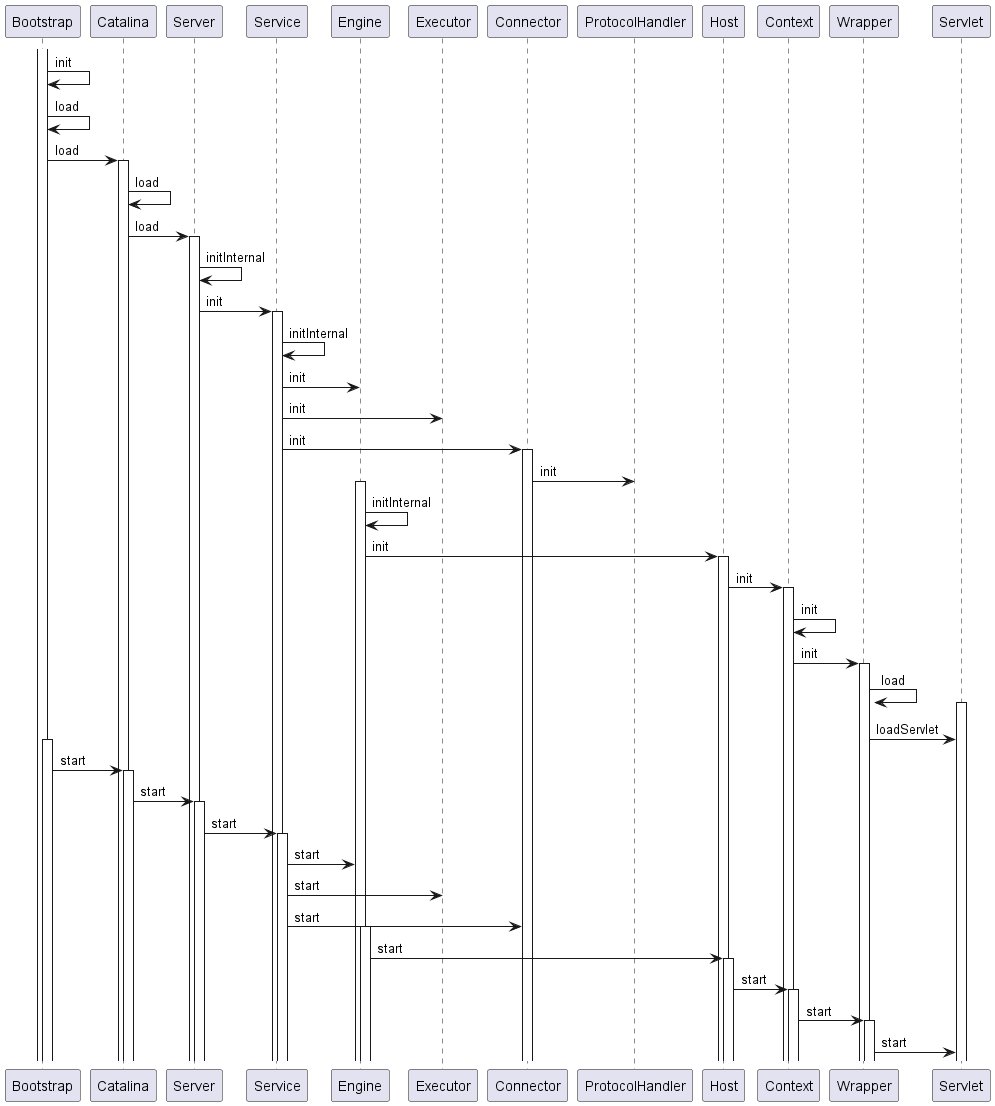
依旧是按照这个图的顺序进行流程解读:
本文目录为:
一、Catalina和Server
1.1 Catalina
Catalina的启动方法主要是启动Server:
/**
* Start a new server instance.
*/
public void start() {
if (getServer() == null) {
load();
}
if (getServer() == null) {
log.fatal(sm.getString("catalina.noServer"));
return;
}
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
// Start the new server
try {
getServer().start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.fatal(sm.getString("catalina.serverStartFail"), e);
try {
getServer().destroy();
} catch (LifecycleException e1) {
log.debug("destroy() failed for failed Server ", e1);
}
return;
}
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(sm.getString("catalina.startup", Long.toString(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - t1))));
}
if (generateCode) {
// Generate loader which will load all generated classes
generateLoader();
}
// Register shutdown hook
if (useShutdownHook) {
if (shutdownHook == null) {
shutdownHook = new CatalinaShutdownHook();
}
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(shutdownHook);
// If JULI is being used, disable JULI's shutdown hook since
// shutdown hooks run in parallel and log messages may be lost
// if JULI's hook completes before the CatalinaShutdownHook()
LogManager logManager = LogManager.getLogManager();
if (logManager instanceof ClassLoaderLogManager) {
((ClassLoaderLogManager) logManager).setUseShutdownHook(
false);
}
}
if (await) {
await();
stop();
}
}
1.2 Server
Server的启动方法主要是启动多个Service:
/**
* Start nested components ({@link Service}s) and implement the requirements of
* {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error that prevents this component from being
* used
*/
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
fireLifecycleEvent(CONFIGURE_START_EVENT, null);
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Initialize utility executor
synchronized (utilityExecutorLock) {
reconfigureUtilityExecutor(getUtilityThreadsInternal(utilityThreads));
register(utilityExecutor, "type=UtilityExecutor");
}
globalNamingResources.start();
// Start our defined Services
synchronized (servicesLock) {
for (Service service : services) {
service.start();
}
}
if (periodicEventDelay > 0) {
monitorFuture = getUtilityExecutor().scheduleWithFixedDelay(this::startPeriodicLifecycleEvent, 0, 60,
TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
我们继续来到Service的启动方法。
二、Service
Service的启动方法启动了三类组件:engine,executor,connector.
/**
* Start nested components ({@link Executor}s, {@link Connector}s and {@link Container}s) and implement the
* requirements of {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error that prevents this component from being
* used
*/
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(sm.getString("standardService.start.name", this.name));
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Start our defined Container first
if (engine != null) {
synchronized (engine) {
engine.start();
}
}
synchronized (executors) {
for (Executor executor : executors) {
executor.start();
}
}
mapperListener.start();
// Start our defined Connectors second
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
for (Connector connector : connectors) {
// If it has already failed, don't try and start it
if (connector.getState() != LifecycleState.FAILED) {
connector.start();
}
}
}
}
其中Connector连接器的启动主要是启动protocolHandler协议处理器:
/**
* Begin processing requests via this Connector.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if a fatal startup error occurs
*/
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Validate settings before starting
String id = (protocolHandler != null) ? protocolHandler.getId() : null;
if (id == null && getPortWithOffset() < 0) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("coyoteConnector.invalidPort", Integer.valueOf(getPortWithOffset())));
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Configure the utility executor before starting the protocol handler
if (protocolHandler != null && service != null) {
protocolHandler.setUtilityExecutor(service.getServer().getUtilityExecutor());
}
try {
protocolHandler.start();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Includes NPE - protocolHandler will be null for invalid protocol if throwOnFailure is false
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerStartFailed"), e);
}
}
下面进入Container的启动方法。
三、Container容器
Container有四种:Engine、Host、Context、Wrapper。
3.1 Engine
Engine的start方法如下:
/**
* Start this component and implement the requirements of
* {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error that prevents this component from being
* used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Log our server identification information
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(sm.getString("standardEngine.start", ServerInfo.getServerInfo()));
}
// Standard container startup
super.startInternal();
}
再来到ContainerBase的start方法:
/**
* Start this component and implement the requirements of
* {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error that prevents this component from being
* used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
reconfigureStartStopExecutor(getStartStopThreads());
// Start our subordinate components, if any
logger = null;
getLogger();
Cluster cluster = getClusterInternal();
if (cluster instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) cluster).start();
}
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if (realm instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
}
// Start our child containers, if any
//获得子容器
Container[] children = findChildren();
List<Future<Void>> results = new ArrayList<>(children.length);
for (Container child : children) {
//异步启动子容器
results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(child)));
}
MultiThrowable multiThrowable = null;
for (Future<Void> result : results) {
try {
//获得异步启动的结果
result.get();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"), e);
if (multiThrowable == null) {
multiThrowable = new MultiThrowable();
}
multiThrowable.add(e);
}
}
if (multiThrowable != null) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"),
multiThrowable.getThrowable());
}
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Start our thread
if (backgroundProcessorDelay > 0) {
monitorFuture = Container.getService(ContainerBase.this).getServer().getUtilityExecutor()
.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new ContainerBackgroundProcessorMonitor(), 0, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
Engine的子容器是Host,我们继续来到Host的start方法。
3.2 Host
Host的start方法主要也是启动子容器:
/**
* Start this component and implement the requirements of
* {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error that prevents this component from being
* used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Set error report valve
String errorValve = getErrorReportValveClass();
if ((errorValve != null) && (!errorValve.equals(""))) {
try {
boolean found = false;
Valve[] valves = getPipeline().getValves();
for (Valve valve : valves) {
if (errorValve.equals(valve.getClass().getName())) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
if (!found) {
Valve valve = ErrorReportValve.class.getName().equals(errorValve) ? new ErrorReportValve() :
(Valve) Class.forName(errorValve).getConstructor().newInstance();
getPipeline().addValve(valve);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString("standardHost.invalidErrorReportValveClass", errorValve), t);
}
}
super.startInternal();
}
3.3 Context
Context的启动方法较长:
/**
* Start this component and implement the requirements of
* {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error that prevents this component from being
* used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Starting " + getBaseName());
}
// Send j2ee.state.starting notification
if (this.getObjectName() != null) {
Notification notification =
new Notification("j2ee.state.starting", this.getObjectName(), sequenceNumber.getAndIncrement());
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
setConfigured(false);
boolean ok = true;
// Currently this is effectively a NO-OP but needs to be called to
// ensure the NamingResources follows the correct lifecycle
if (namingResources != null) {
namingResources.start();
}
// Post work directory
postWorkDirectory();
// Add missing components as necessary
if (getResources() == null) { // (1) Required by Loader
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Configuring default Resources");
}
try {
setResources(new StandardRoot(this));
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.resourcesInit"), e);
ok = false;
}
}
if (ok) {
resourcesStart();
}
if (getLoader() == null) {
WebappLoader webappLoader = new WebappLoader();
webappLoader.setDelegate(getDelegate());
setLoader(webappLoader);
}
// An explicit cookie processor hasn't been specified; use the default
if (cookieProcessor == null) {
cookieProcessor = new Rfc6265CookieProcessor();
}
// Initialize character set mapper
getCharsetMapper();
// Reading the "catalina.useNaming" environment variable
String useNamingProperty = System.getProperty("catalina.useNaming");
if ((useNamingProperty != null) && (useNamingProperty.equals("false"))) {
useNaming = false;
}
if (ok && isUseNaming()) {
if (getNamingContextListener() == null) {
NamingContextListener ncl = new NamingContextListener();
ncl.setName(getNamingContextName());
ncl.setExceptionOnFailedWrite(getJndiExceptionOnFailedWrite());
addLifecycleListener(ncl);
setNamingContextListener(ncl);
}
}
// Standard container startup
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Processing standard container startup");
}
// Binding thread
ClassLoader oldCCL = bindThread();
try {
if (ok) {
// Start our subordinate components, if any
Loader loader = getLoader();
if (loader instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) loader).start();
}
// since the loader just started, the webapp classloader is now
// created.
if (loader.getClassLoader() instanceof WebappClassLoaderBase) {
WebappClassLoaderBase cl = (WebappClassLoaderBase) loader.getClassLoader();
cl.setClearReferencesRmiTargets(getClearReferencesRmiTargets());
cl.setClearReferencesStopThreads(getClearReferencesStopThreads());
cl.setClearReferencesStopTimerThreads(getClearReferencesStopTimerThreads());
cl.setClearReferencesHttpClientKeepAliveThread(getClearReferencesHttpClientKeepAliveThread());
cl.setClearReferencesThreadLocals(getClearReferencesThreadLocals());
cl.setSkipMemoryLeakChecksOnJvmShutdown(getSkipMemoryLeakChecksOnJvmShutdown());
}
// By calling unbindThread and bindThread in a row, we setup the
// current Thread CCL to be the webapp classloader
unbindThread(oldCCL);
oldCCL = bindThread();
// Initialize logger again. Other components might have used it
// too early, so it should be reset.
logger = null;
getLogger();
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if (null != realm) {
if (realm instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
}
// Place the CredentialHandler into the ServletContext so
// applications can have access to it. Wrap it in a "safe"
// handler so application's can't modify it.
CredentialHandler safeHandler = new CredentialHandler() {
@Override
public boolean matches(String inputCredentials, String storedCredentials) {
return getRealmInternal().getCredentialHandler().matches(inputCredentials,
storedCredentials);
}
@Override
public String mutate(String inputCredentials) {
return getRealmInternal().getCredentialHandler().mutate(inputCredentials);
}
};
context.setAttribute(Globals.CREDENTIAL_HANDLER, safeHandler);
}
// Notify our interested LifecycleListeners
fireLifecycleEvent(CONFIGURE_START_EVENT, null);
// Start our child containers, if not already started
for (Container child : findChildren()) {
if (!child.getState().isAvailable()) {
child.start();
}
}
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic),
// if any
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
}
// Acquire clustered manager
Manager contextManager = null;
Manager manager = getManager();
if (manager == null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("standardContext.cluster.noManager",
Boolean.valueOf((getCluster() != null)), Boolean.valueOf(distributable)));
}
if ((getCluster() != null) && distributable) {
try {
contextManager = getCluster().createManager(getName());
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.cluster.managerError"), ex);
ok = false;
}
} else {
contextManager = new StandardManager();
}
}
// Configure default manager if none was specified
if (contextManager != null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("standardContext.manager", contextManager.getClass().getName()));
}
setManager(contextManager);
}
if (manager != null && (getCluster() != null) && distributable) {
// let the cluster know that there is a context that is distributable
// and that it has its own manager
getCluster().registerManager(manager);
}
}
if (!getConfigured()) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.configurationFail"));
ok = false;
}
// We put the resources into the servlet context
if (ok) {
getServletContext().setAttribute(Globals.RESOURCES_ATTR, getResources());
if (getInstanceManager() == null) {
setInstanceManager(createInstanceManager());
}
getServletContext().setAttribute(InstanceManager.class.getName(), getInstanceManager());
InstanceManagerBindings.bind(getLoader().getClassLoader(), getInstanceManager());
// Create context attributes that will be required
getServletContext().setAttribute(JarScanner.class.getName(), getJarScanner());
// Make the version info available
getServletContext().setAttribute(Globals.WEBAPP_VERSION, getWebappVersion());
// Make the utility executor available
getServletContext().setAttribute(ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor.class.getName(),
Container.getService(this).getServer().getUtilityExecutor());
}
// Set up the context init params
mergeParameters();
// Call ServletContainerInitializers
for (Map.Entry<ServletContainerInitializer,Set<Class<?>>> entry : initializers.entrySet()) {
try {
entry.getKey().onStartup(entry.getValue(), getServletContext());
} catch (ServletException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.sciFail"), e);
ok = false;
break;
}
}
// Configure and call application event listeners
if (ok) {
if (!listenerStart()) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.listenerFail"));
ok = false;
}
}
// Check constraints for uncovered HTTP methods
// Needs to be after SCIs and listeners as they may programmatically
// change constraints
if (ok) {
checkConstraintsForUncoveredMethods(findConstraints());
}
try {
// Start manager
Manager manager = getManager();
if (manager instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) manager).start();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.managerFail"), e);
ok = false;
}
// Configure and call application filters
if (ok) {
if (!filterStart()) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.filterFail"));
ok = false;
}
}
// Load and initialize all "load on startup" servlets
if (ok) {
if (!loadOnStartup(findChildren())) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.servletFail"));
ok = false;
}
}
// Start ContainerBackgroundProcessor thread
super.threadStart();
} finally {
// Unbinding thread
unbindThread(oldCCL);
}
// Set available status depending upon startup success
if (ok) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Starting completed");
}
} else {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.startFailed", getName()));
}
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Send j2ee.state.running notification
if (ok && (this.getObjectName() != null)) {
Notification notification =
new Notification("j2ee.state.running", this.getObjectName(), sequenceNumber.getAndIncrement());
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
// The WebResources implementation caches references to JAR files. On
// some platforms these references may lock the JAR files. Since web
// application start is likely to have read from lots of JARs, trigger
// a clean-up now.
getResources().gc();
// Reinitializing if something went wrong
if (!ok) {
setState(LifecycleState.FAILED);
// Send j2ee.object.failed notification
if (this.getObjectName() != null) {
Notification notification =
new Notification("j2ee.object.failed", this.getObjectName(), sequenceNumber.getAndIncrement());
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
} else {
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
}
}
我们可以看到主要是启动子容器、ServletContainerInitializers、监听器等。
for (Container child : findChildren()) {
if (!child.getState().isAvailable()) {
child.start();
}
}
for (Map.Entry<ServletContainerInitializer,Set<Class<?>>> entry : initializers.entrySet()) {
try {
entry.getKey().onStartup(entry.getValue(), getServletContext());
} catch (ServletException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.sciFail"), e);
ok = false;
break;
}
}
3.4 Wrapper
StandardWrapper在初始化中已经加载Servlet和初始化Servlet,其启动方法就是默认的ContainerBase#startInternal,因为没有子容器,所以不涉及子容器启动。
/**
* Start this component and implement the requirements of
* {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error that prevents this component from being
* used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Send j2ee.state.starting notification
if (this.getObjectName() != null) {
Notification notification = new Notification("j2ee.state.starting", this.getObjectName(), sequenceNumber++);
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
// Start up this component
super.startInternal();
setAvailable(0L);
// Send j2ee.state.running notification
if (this.getObjectName() != null) {
Notification notification = new Notification("j2ee.state.running", this.getObjectName(), sequenceNumber++);
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
}
有在上一篇文章的基础上,结合启动流程图来看,Tomcat的start方法也是按照这个流程来解读会很清晰。
四、参考材料
- 《深入剖析Tomcat》
