本文是解读Tomcat的启动过程,从Bootstrap类开始解读整个的初始化组件和启动流程。 本系列的源码工程为:HowTomcatWorksSourceCode。
上一篇文章有作出Tomcat启动流程-初始化和start方法的简单序列图:
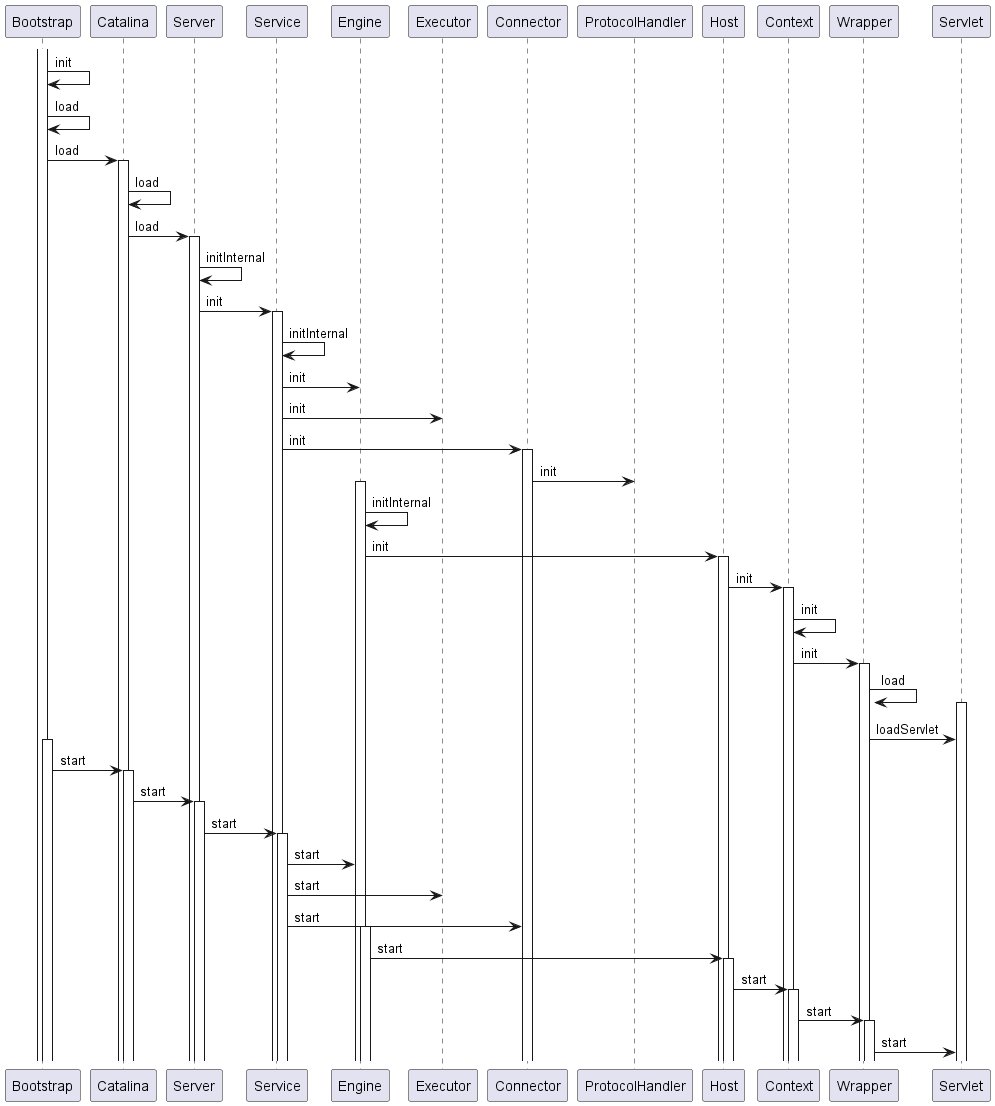
其实我们只要使用ps或者jps查看tomcat启动的进程,会得到类似如下的启动进程信息;
44740 org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap start
-Djava.util.logging.config.file=***\conf\logging.properties
-Djava.util.logging.manager=org.apache.juli.ClassLoaderLogManager
-Dfile.encoding=utf-8
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote= -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=1099
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.password.file=****\jmxremote.password
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.access.file=***\jmxremote.access
-Djava.rmi.server.hostname=127.0.0.1
-Djdk.tls.ephemeralDHKeySize=2048
-Djava.protocol.handler.pkgs=org.apache.catalina.webresources
--add-opens=java.base/java.lang=ALL-UNNAMED
--add-opens=java.base/java.io=ALL-UNNAMED
--add-opens=java.base/java.util=ALL-UNNAMED
--add-opens=java.base/java.ut
我们从Bootstrap这个类开始解读Tomcat启动流程中的初始化流程。
一、Catalina
虽然看进程信息启动类是Bootstrap,但实际执行的启动类是Catalina。
Bootstrap源码如下(有删减):
/**
* Bootstrap loader for Catalina. This application constructs a class loader
* for use in loading the Catalina internal classes (by accumulating all of the
* JAR files found in the "server" directory under "catalina.home"), and
* starts the regular execution of the container. The purpose of this
* roundabout approach is to keep the Catalina internal classes (and any
* other classes they depend on, such as an XML parser) out of the system
* class path and therefore not visible to application level classes.
*
* @author Craig R. McClanahan
* @author Remy Maucherat
*/
public final class Bootstrap {
/**
* Daemon reference.
*/
//实际启动的类型Catalina
private Object catalinaDaemon = null;
//三个类加载器
ClassLoader commonLoader = null;
ClassLoader catalinaLoader = null;
ClassLoader sharedLoader = null;
// -------------------------------------------------------- Private Methods
//初始化类加载器
private void initClassLoaders() {
try {
commonLoader = createClassLoader("common", null);
if (commonLoader == null) {
// no config file, default to this loader - we might be in a 'single' env.
commonLoader = this.getClass().getClassLoader();
}
catalinaLoader = createClassLoader("server", commonLoader);
sharedLoader = createClassLoader("shared", commonLoader);
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleThrowable(t);
log.error("Class loader creation threw exception", t);
System.exit(1);
}
}
//创建类加载器
private ClassLoader createClassLoader(String name, ClassLoader parent) throws Exception {
String value = CatalinaProperties.getProperty(name + ".loader");
if ((value == null) || (value.equals(""))) {
return parent;
}
value = replace(value);
List<Repository> repositories = new ArrayList<>();
String[] repositoryPaths = getPaths(value);
for (String repository : repositoryPaths) {
// Check for a JAR URL repository
try {
URI uri = new URI(repository);
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
URL url = uri.toURL();
repositories.add(new Repository(repository, RepositoryType.URL));
continue;
} catch (IllegalArgumentException | MalformedURLException | URISyntaxException e) {
// Ignore
}
// Local repository
if (repository.endsWith("*.jar")) {
repository = repository.substring
(0, repository.length() - "*.jar".length());
repositories.add(new Repository(repository, RepositoryType.GLOB));
} else if (repository.endsWith(".jar")) {
repositories.add(new Repository(repository, RepositoryType.JAR));
} else {
repositories.add(new Repository(repository, RepositoryType.DIR));
}
}
return ClassLoaderFactory.createClassLoader(repositories, parent);
}
/**
* Initialize daemon.
* @throws Exception Fatal initialization error
*/
//初始化Catalina实例
public void init() throws Exception {
initClassLoaders();
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(catalinaLoader);
SecurityClassLoad.securityClassLoad(catalinaLoader);
// Load our startup class and call its process() method
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Loading startup class");
}
Class<?> startupClass = catalinaLoader.loadClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");
Object startupInstance = startupClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
// Set the shared extensions class loader
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Setting startup class properties");
}
String methodName = "setParentClassLoader";
Class<?> paramTypes[] = new Class[1];
paramTypes[0] = Class.forName("java.lang.ClassLoader");
Object paramValues[] = new Object[1];
paramValues[0] = sharedLoader;
Method method =
startupInstance.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);
method.invoke(startupInstance, paramValues);
catalinaDaemon = startupInstance;
}
/**
* Load daemon.
*/
//执行Catalina的load方法
private void load(String[] arguments) throws Exception {
// Call the load() method
String methodName = "load";
Object param[];
Class<?> paramTypes[];
if (arguments==null || arguments.length==0) {
paramTypes = null;
param = null;
} else {
paramTypes = new Class[1];
paramTypes[0] = arguments.getClass();
param = new Object[1];
param[0] = arguments;
}
Method method =
catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Calling startup class " + method);
}
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, param);
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------- Main Program
/**
* Load the Catalina daemon.
* @param arguments Initialization arguments
* @throws Exception Fatal initialization error
*/
//初始化Catalina实例
public void init(String[] arguments) throws Exception {
//初始化Catalina实例
init();
// 执行Catalina实例的load方法
load(arguments);
}
/**
* Start the Catalina daemon.
* @throws Exception Fatal start error
*/
//启动Catalina实例
public void start() throws Exception {
if (catalinaDaemon == null) {
init();
}
Method method = catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("start", (Class [])null);
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, (Object [])null);
}
/**
* Stop the Catalina Daemon.
* @throws Exception Fatal stop error
*/
//停止Catalina实例
public void stop() throws Exception {
Method method = catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("stop", (Class []) null);
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, (Object []) null);
}
/**
* Main method and entry point when starting Tomcat via the provided
* scripts.
*
* @param args Command line arguments to be processed
*/
//main,进程执行入口
public static void main(String args[]) {
synchronized (daemonLock) {
if (daemon == null) {
// Don't set daemon until init() has completed
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
try {
bootstrap.init();
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleThrowable(t);
t.printStackTrace();
return;
}
daemon = bootstrap;
} else {
// When running as a service the call to stop will be on a new
// thread so make sure the correct class loader is used to
// prevent a range of class not found exceptions.
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(daemon.catalinaLoader);
}
}
try {
String command = "start";
if (args.length > 0) {
command = args[args.length - 1];
}
if (command.equals("startd")) {
args[args.length - 1] = "start";
daemon.load(args);
daemon.start();
} else if (command.equals("stopd")) {
args[args.length - 1] = "stop";
daemon.stop();
} else if (command.equals("start")) {
//这里是start命令的执行代码
daemon.setAwait(true);
daemon.load(args);
daemon.start();
if (null == daemon.getServer()) {
System.exit(1);
}
} else if (command.equals("stop")) {
daemon.stopServer(args);
} else if (command.equals("configtest")) {
daemon.load(args);
if (null == daemon.getServer()) {
System.exit(1);
}
System.exit(0);
} else {
log.warn("Bootstrap: command \"" + command + "\" does not exist.");
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Unwrap the Exception for clearer error reporting
if (t instanceof InvocationTargetException &&
t.getCause() != null) {
t = t.getCause();
}
handleThrowable(t);
t.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
从源码可以看到Bootstrap通过反射创建Catalina、初始化Catalina、执行Catalina的load方法,然后执行Catalina的start方法,从而来启动tomcat的。
关闭Tomcat也是通过Catalina。
/**
* Stop the Catalina Daemon.
* @throws Exception Fatal stop error
*/
public void stop() throws Exception {
Method method = catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("stop", (Class []) null);
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, (Object []) null);
}
我们再继续进入Catalina类,看下load和start方法。
/**
* Startup/Shutdown shell program for Catalina. The following command line
* options are recognized:
* <ul>
* <li><b>-config {pathname}</b> - Set the pathname of the configuration file
* to be processed. If a relative path is specified, it will be
* interpreted as relative to the directory pathname specified by the
* "catalina.base" system property. [conf/server.xml]</li>
* <li><b>-help</b> - Display usage information.</li>
* <li><b>-nonaming</b> - Disable naming support.</li>
* <li><b>configtest</b> - Try to test the config</li>
* <li><b>start</b> - Start an instance of Catalina.</li>
* <li><b>stop</b> - Stop the currently running instance of Catalina.</li>
* </ul>
*
* @author Craig R. McClanahan
* @author Remy Maucherat
*/
public class Catalina {
//server的配置XML
public static final String SERVER_XML = "conf/server.xml";
/**
* Start a new server instance.
*/
//加载方法主要是创建Server服务器
public void load() {
if (loaded) {
return;
}
loaded = true;
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
// Before digester - it may be needed
initNaming();
// Parse main server.xml
parseServerXml(true);
Server s = getServer();
if (s == null) {
return;
}
getServer().setCatalina(this);
getServer().setCatalinaHome(Bootstrap.getCatalinaHomeFile());
getServer().setCatalinaBase(Bootstrap.getCatalinaBaseFile());
// Stream redirection
initStreams();
// Start the new server
try {
//初始化Server
getServer().init();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
if (throwOnInitFailure) {
throw new java.lang.Error(e);
} else {
log.error(sm.getString("catalina.initError"), e);
}
}
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(sm.getString("catalina.init", Long.toString(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - t1))));
}
}
/*
* Load using arguments
*/
//加载方法主要是创建Server服务器
public void load(String args[]) {
try {
if (arguments(args)) {
load();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
}
}
/**
* Start a new server instance.
*/
//启动Server服务器
public void start() {
if (getServer() == null) {
load();
}
if (getServer() == null) {
log.fatal(sm.getString("catalina.noServer"));
return;
}
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
// Start the new server
try {
getServer().start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.fatal(sm.getString("catalina.serverStartFail"), e);
try {
getServer().destroy();
} catch (LifecycleException e1) {
log.debug("destroy() failed for failed Server ", e1);
}
return;
}
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(sm.getString("catalina.startup", Long.toString(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - t1))));
}
if (generateCode) {
// Generate loader which will load all generated classes
generateLoader();
}
// Register shutdown hook
if (useShutdownHook) {
if (shutdownHook == null) {
shutdownHook = new CatalinaShutdownHook();
}
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(shutdownHook);
// If JULI is being used, disable JULI's shutdown hook since
// shutdown hooks run in parallel and log messages may be lost
// if JULI's hook completes before the CatalinaShutdownHook()
LogManager logManager = LogManager.getLogManager();
if (logManager instanceof ClassLoaderLogManager) {
((ClassLoaderLogManager) logManager).setUseShutdownHook(
false);
}
}
if (await) {
await();
stop();
}
}
/**
* Stop an existing server instance.
*/
//关闭Server服务器
public void stop() {
try {
// Remove the ShutdownHook first so that server.stop()
// doesn't get invoked twice
if (useShutdownHook) {
Runtime.getRuntime().removeShutdownHook(shutdownHook);
// If JULI is being used, re-enable JULI's shutdown to ensure
// log messages are not lost
LogManager logManager = LogManager.getLogManager();
if (logManager instanceof ClassLoaderLogManager) {
((ClassLoaderLogManager) logManager).setUseShutdownHook(
true);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
// This will fail on JDK 1.2. Ignoring, as Tomcat can run
// fine without the shutdown hook.
}
// Shut down the server
try {
Server s = getServer();
LifecycleState state = s.getState();
if (LifecycleState.STOPPING_PREP.compareTo(state) <= 0
&& LifecycleState.DESTROYED.compareTo(state) >= 0) {
// Nothing to do. stop() was already called
} else {
s.stop();
s.destroy();
}
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("catalina.stopError"), e);
}
}
}
从上面代码可以看出,这里Catalina主要是创建、初始化、启动、关闭Server(服务器)实例。
我们进入load方法看下Server是如何创建的?
/**
* Start a new server instance.
*/
public void load() {
if (loaded) {
return;
}
loaded = true;
// Before digester - it may be needed
initNaming();
// Parse main server.xml
//注意看这行代码,解析server,xml文件
parseServerXml(true);
Server s = getServer();
if (s == null) {
return;
}
getServer().setCatalina(this);
getServer().setCatalinaHome(Bootstrap.getCatalinaHomeFile());
getServer().setCatalinaBase(Bootstrap.getCatalinaBaseFile());
// Stream redirection
initStreams();
// Start the new server
try {
getServer().init();
}
}
我们继续来到parseServerXml方法(有删减):
protected void parseServerXml(boolean start) {
// Set configuration source
ConfigFileLoader.setSource(new CatalinaBaseConfigurationSource(Bootstrap.getCatalinaBaseFile(), getConfigFile()));
File file = configFile();
// Init source location
File serverXmlLocation = null;
String xmlClassName = null;
if (serverXml != null) {
serverXml.load(this);
} else {
try (ConfigurationSource.Resource resource = ConfigFileLoader.getSource().getServerXml()) {
// Create and execute our Digester
//注意看createStartDigester方法
Digester digester = start ? createStartDigester() : createStopDigester();
InputStream inputStream = resource.getInputStream();
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(resource.getURI().toURL().toString());
inputSource.setByteStream(inputStream);
digester.push(this);
//解析
digester.parse(inputSource);
}
}
}
}
注意看到这个方法createStartDigester:
/**
* Create and configure the Digester we will be using for startup.
* @return the main digester to parse server.xml
*/
protected Digester createStartDigester() {
// Initialize the digester
Digester digester = new Digester();
digester.setValidating(false);
digester.setRulesValidation(true);
Map<Class<?>, List<String>> fakeAttributes = new HashMap<>();
// Ignore className on all elements
List<String> objectAttrs = new ArrayList<>();
objectAttrs.add("className");
fakeAttributes.put(Object.class, objectAttrs);
// Ignore attribute added by Eclipse for its internal tracking
List<String> contextAttrs = new ArrayList<>();
contextAttrs.add("source");
fakeAttributes.put(StandardContext.class, contextAttrs);
// Ignore Connector attribute used internally but set on Server
List<String> connectorAttrs = new ArrayList<>();
connectorAttrs.add("portOffset");
fakeAttributes.put(Connector.class, connectorAttrs);
digester.setFakeAttributes(fakeAttributes);
digester.setUseContextClassLoader(true);
// Configure the actions we will be using
//这里解析了节点,并设置了对应的规则
digester.addObjectCreate("Server",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server");
digester.addSetNext("Server",
"setServer",
"org.apache.catalina.Server");
//......
digester.addRuleSet(new EngineRuleSet("Server/Service/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new HostRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new ContextRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/Host/"));
addClusterRuleSet(digester, "Server/Service/Engine/Host/Cluster/");
digester.addRuleSet(new NamingRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context/"));
// When the 'engine' is found, set the parentClassLoader.
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Engine",
new SetParentClassLoaderRule(parentClassLoader));
addClusterRuleSet(digester, "Server/Service/Engine/Cluster/");
return digester;
}
上面代码是解析server.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Server port="8005" shutdown="SHUTDOWN">
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.startup.VersionLoggerListener" />
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.AprLifecycleListener" SSLEngine="on" />
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.JreMemoryLeakPreventionListener" />
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.mbeans.GlobalResourcesLifecycleListener" />
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.ThreadLocalLeakPreventionListener" />
<GlobalNamingResources>
<Resource name="UserDatabase" auth="Container"
type="org.apache.catalina.UserDatabase"
description="User database that can be updated and saved"
factory="org.apache.catalina.users.MemoryUserDatabaseFactory"
pathname="conf/tomcat-users.xml" />
</GlobalNamingResources>
<Service name="Catalina">
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443"
maxParameterCount="1000"
URIEncoding="UTF-8"
/>
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost">
<Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.LockOutRealm">
<Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.UserDatabaseRealm"
resourceName="UserDatabase"/>
</Realm>
<Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps"
unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true">
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve" directory="logs"
prefix="localhost_access_log" suffix=".txt"
pattern="%h %l %u %t "%r" %s %b" />
</Host>
</Engine>
</Service>
</Server>
从上面代码可以看到createStartDigester方法解析server.xml不仅仅是解析了每个节点,还设置了对应规则。如ObjectCreateRule:
@Override
public void begin(String namespace, String name, Attributes attributes)
throws Exception {
String realClassName = getRealClassName(attributes);
if (realClassName == null) {
throw new NullPointerException(sm.getString("rule.noClassName", namespace, name));
}
// Instantiate the new object and push it on the context stack
Class<?> clazz = digester.getClassLoader().loadClass(realClassName);
Object instance = clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();
digester.push(instance);
StringBuilder code = digester.getGeneratedCode();
if (code != null) {
code.append(System.lineSeparator());
code.append(System.lineSeparator());
code.append(realClassName).append(' ').append(digester.toVariableName(instance)).append(" = new ");
code.append(realClassName).append("();").append(System.lineSeparator());
}
}
其规则是通过反射创建对象。那么这几行代码设置的规则就是创建StandardServer(Server)实例,并设置Catalina的server引用是该实例。
digester.addObjectCreate("Server",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server");
digester.addSetNext("Server",
"setServer",
"org.apache.catalina.Server");
下面我们继续来到Server的源码。
二、Server
上面源码已经确定了Server的具体类型是StandardServer。看下Server的类继承关系图:
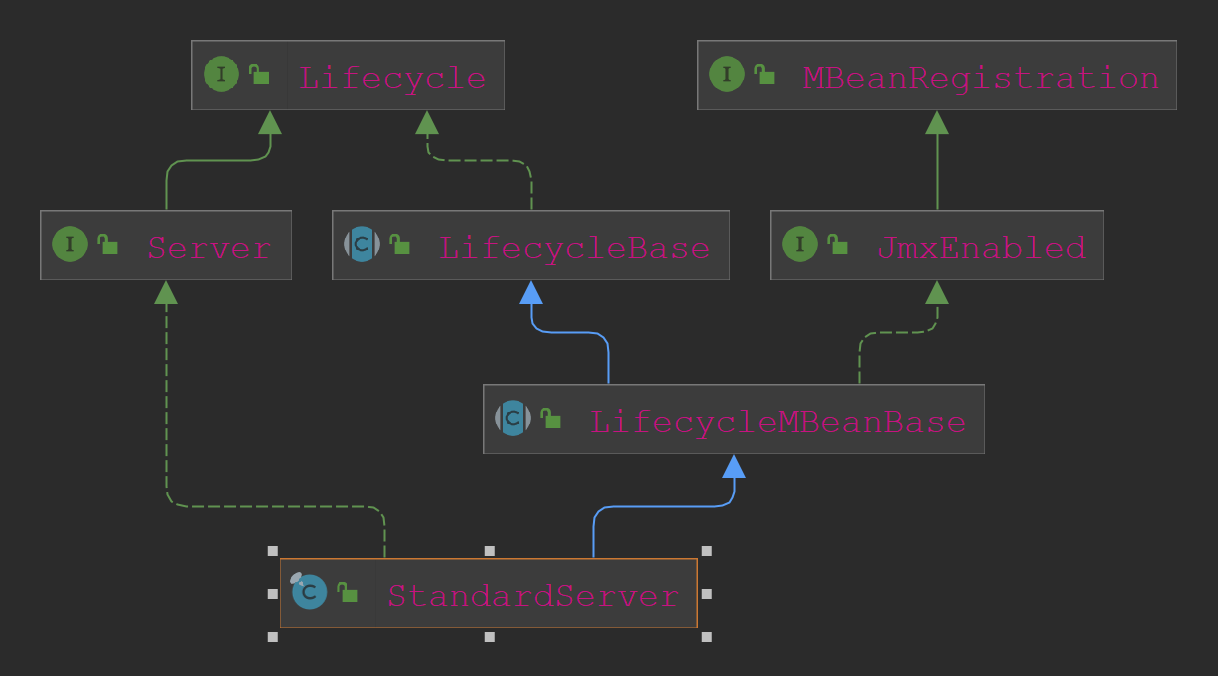
StandardServer实现了Lifecycle生命周期接口,其他的如Service、Container(四类)也都实现了Lifecycle生命周期接口。跟踪Catalina的这行代码:
getServer().init();
来到LifecycleBase的init方法如下:
@Override
public final synchronized void init() throws LifecycleException {
if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.NEW)) {
invalidTransition(Lifecycle.BEFORE_INIT_EVENT);
}
try {
//设置生命周期状态
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.INITIALIZING, null, false);
//实际某个组件的初始化
initInternal();
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.INITIALIZED, null, false);
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleSubClassException(t, "lifecycleBase.initFail", toString());
}
}
XXXInternal方法这里会议很多类似的,如stopInternal、startInternal,都是在一个操作的前与后设置生命周期状态。
下面来到StandardServer的init方法:
/**
* Invoke a pre-startup initialization. This is used to allow connectors to bind to restricted ports under Unix
* operating environments.
*/
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
// Register global String cache
// Note although the cache is global, if there are multiple Servers
// present in the JVM (may happen when embedding) then the same cache
// will be registered under multiple names
onameStringCache = register(new StringCache(), "type=StringCache");
// Register the MBeanFactory
MBeanFactory factory = new MBeanFactory();
factory.setContainer(this);
onameMBeanFactory = register(factory, "type=MBeanFactory");
// Register the naming resources
globalNamingResources.init();
// Initialize our defined Services
//初始化Service
for (Service service : services) {
service.init();
}
}
可以看到这里主要是初始化Service,在server.xml中默认的Service如下:
<Service name="Catalina">
<!--......-->
</Service>
同时也能确定Service是可以创建多个的,上面流程中的bootstrap、Catalina、Server是只创建了一个实例。如果使用boot启动这里可以调试到services的值
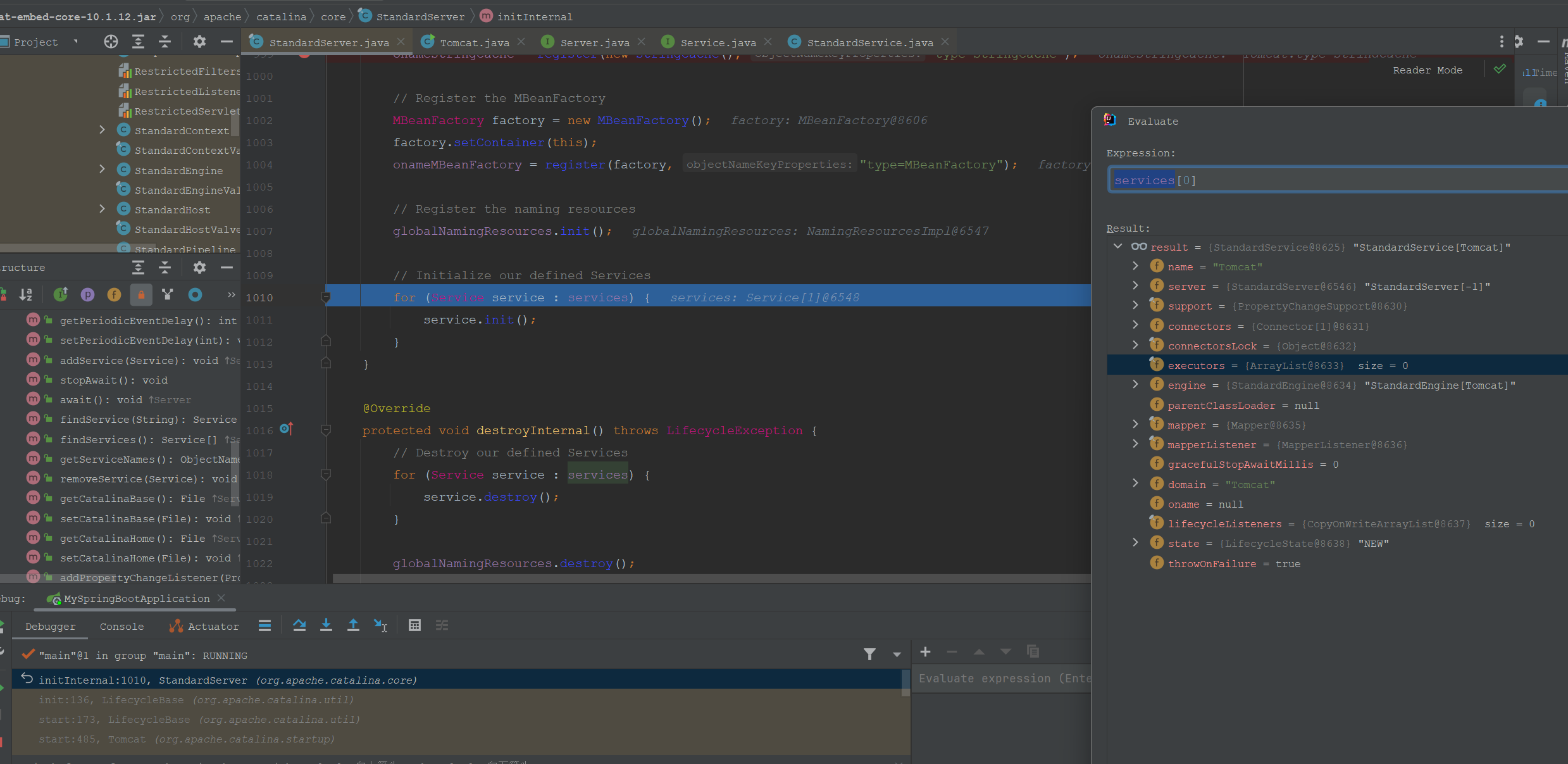
这个Service是在在Tomcat(内嵌的Tomcat启动器)这行代码创建的:
Service service = new StandardService();
service.setName("Tomcat");
server.addService(service);
return server;
如果是普通的Tomcat工程则是在这里Catalina类创建的:
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service",
"addService",
"org.apache.catalina.Service");
接下来,我们进入Service方法解读其init初始化方法。
三、Service
StandardService的类关系图如下:
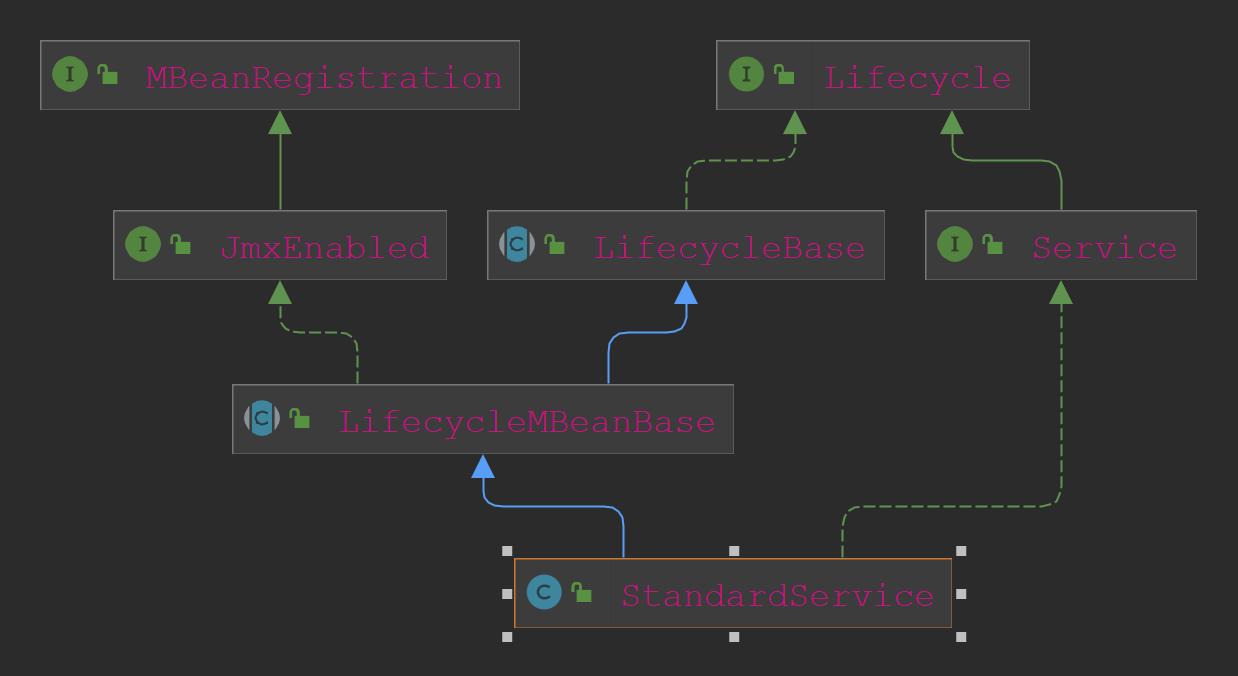
我们直接来到initInternal方法,如下:
/**
* Invoke a pre-startup initialization. This is used to allow connectors to bind to restricted ports under Unix
* operating environments.
*/
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
if (engine != null) {
//初始化Engine
engine.init();
}
// Initialize any Executors
for (Executor executor : findExecutors()) {
if (executor instanceof JmxEnabled) {
((JmxEnabled) executor).setDomain(getDomain());
}
//初始化线程池
executor.init();
}
// Initialize mapper listener
//初始化监听器
mapperListener.init();
// Initialize our defined Connectors
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
for (Connector connector : connectors) {
//初始化连接器
connector.init();
}
}
}
从源码可以看到Service的初始化方法主要是初始化Engine、Executor、Connector等组件。 Executor线程池拓展了原生的Java的Executor线程池接口,其类关系图如下:
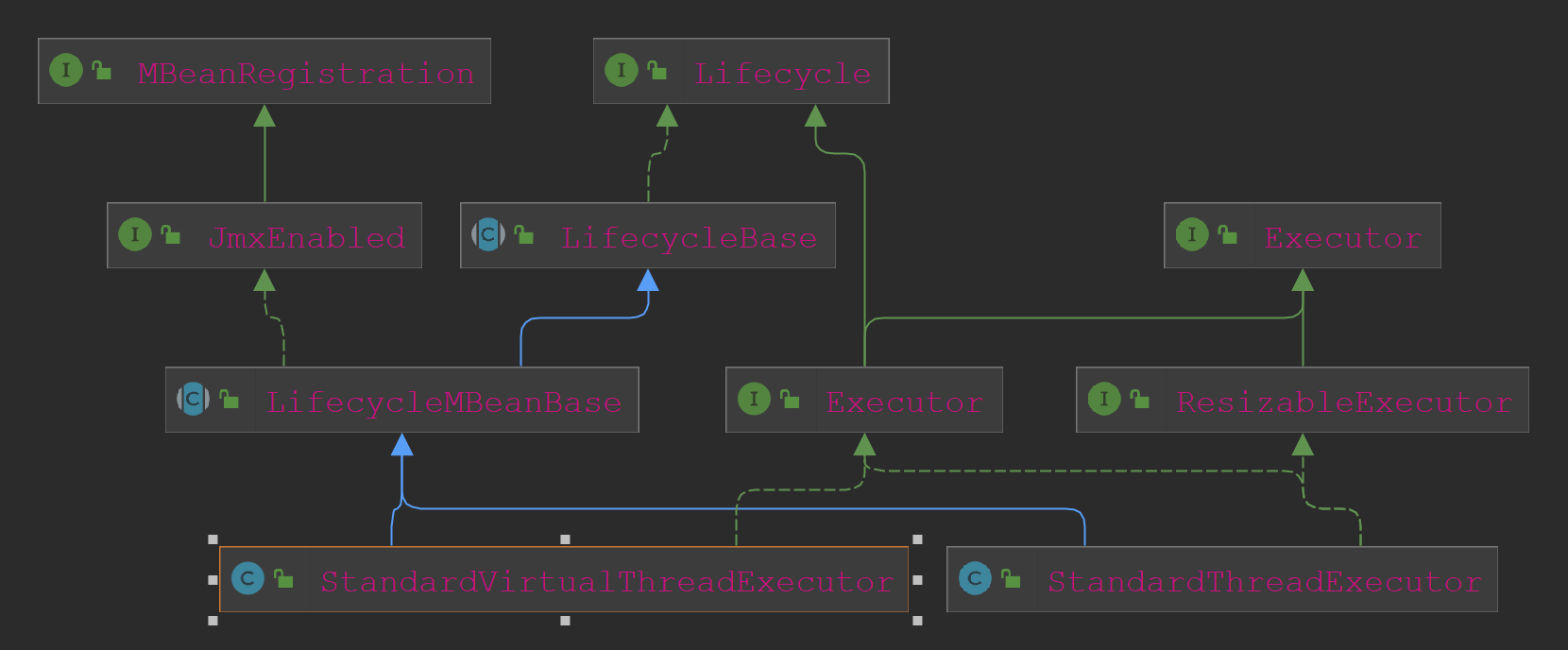
在Tomcat10居然就已有虚拟线程的实现了,官方的VirtualThread是JDK21(2023年9月)才发布。
连接器Connector源码如下:
public class Connector extends LifecycleMBeanBase {
public Connector(String protocol) {
configuredProtocol = protocol;
ProtocolHandler p = null;
try {
p = ProtocolHandler.create(protocol);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInstantiationFailed"), e);
}
if (p != null) {
protocolHandler = p;
protocolHandlerClassName = protocolHandler.getClass().getName();
} else {
protocolHandler = null;
protocolHandlerClassName = protocol;
}
// Default for Connector depends on this system property
setThrowOnFailure(Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE"));
}
public Connector(ProtocolHandler protocolHandler) {
protocolHandlerClassName = protocolHandler.getClass().getName();
configuredProtocol = protocolHandlerClassName;
this.protocolHandler = protocolHandler;
// Default for Connector depends on this system property
setThrowOnFailure(Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE"));
}
/**
* Pause the connector.
*/
public void pause() {
try {
if (protocolHandler != null) {
protocolHandler.pause();
}
}
}
/**
* Resume the connector.
*/
public void resume() {
if (protocolHandler != null) {
protocolHandler.resume();
}
}
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
// Initialize adapter
adapter = new CoyoteAdapter(this);
protocolHandler.setAdapter(adapter);
protocolHandler.init();
}
/**
* Begin processing requests via this Connector.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if a fatal startup error occurs
*/
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Configure the utility executor before starting the protocol handler
if (protocolHandler != null && service != null) {
protocolHandler.setUtilityExecutor(service.getServer().getUtilityExecutor());
}
protocolHandler.start();
}
@Override
protected void stopInternal() throws LifecycleException {
setState(LifecycleState.STOPPING);
try {
if (protocolHandler != null) {
protocolHandler.stop();
}
}
}
@Override
protected void destroyInternal() throws LifecycleException {
if (protocolHandler != null) {
protocolHandler.destroy();
super.destroyInternal();
}
}
Connector的init方法主要是创建CoyoteAdapter适配器和执行protocolHandler协议处理器的初始化。connectors如下,其内部的协议处理器是Http11NioProtocol:
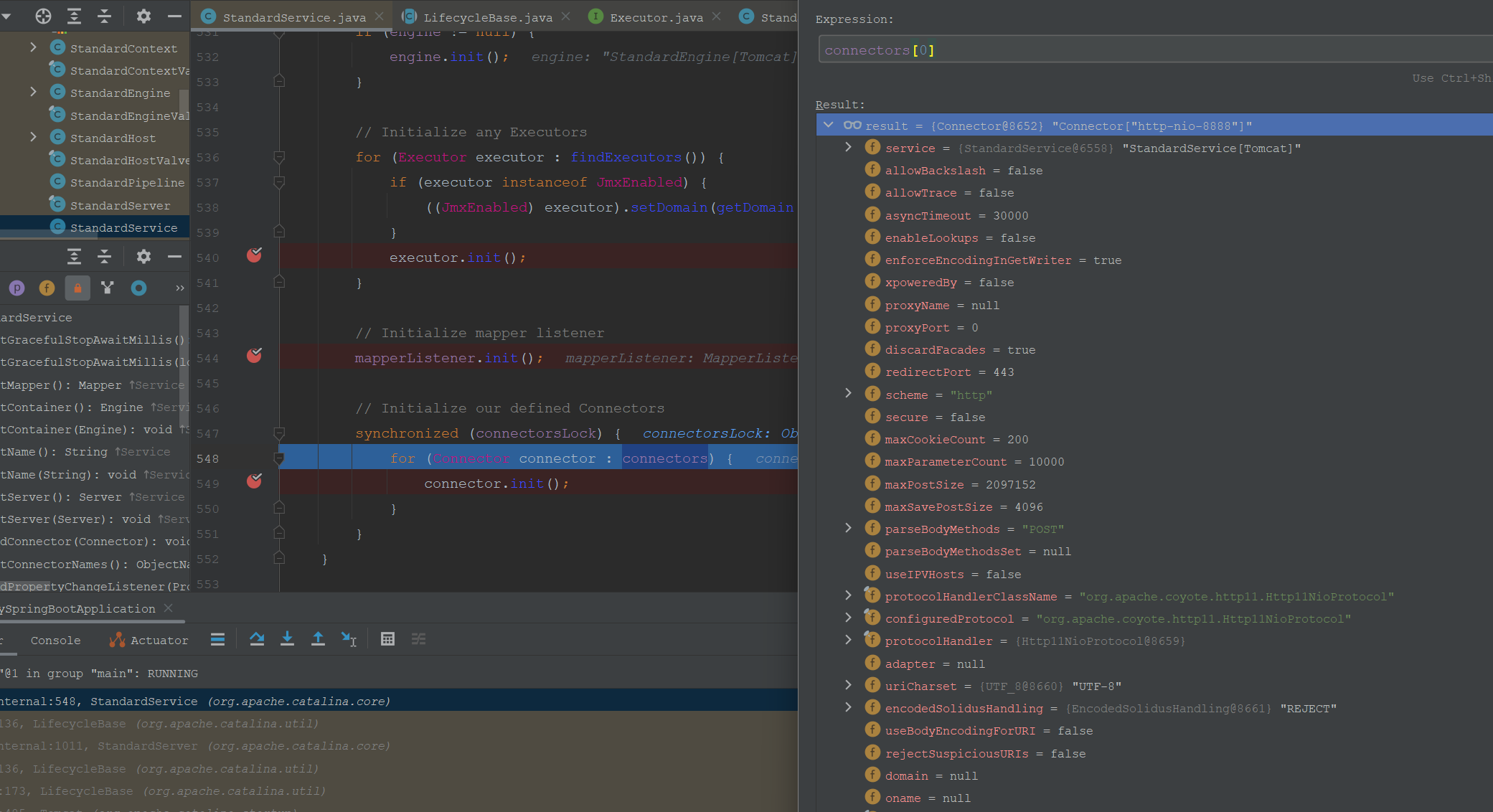
下面来到容器组件的初始化流程。
四、Container容器(Engine、Host、Context)
默认的四类容器组件有Engine、Host、Context、Wrapper四类。类继承关系图如下:
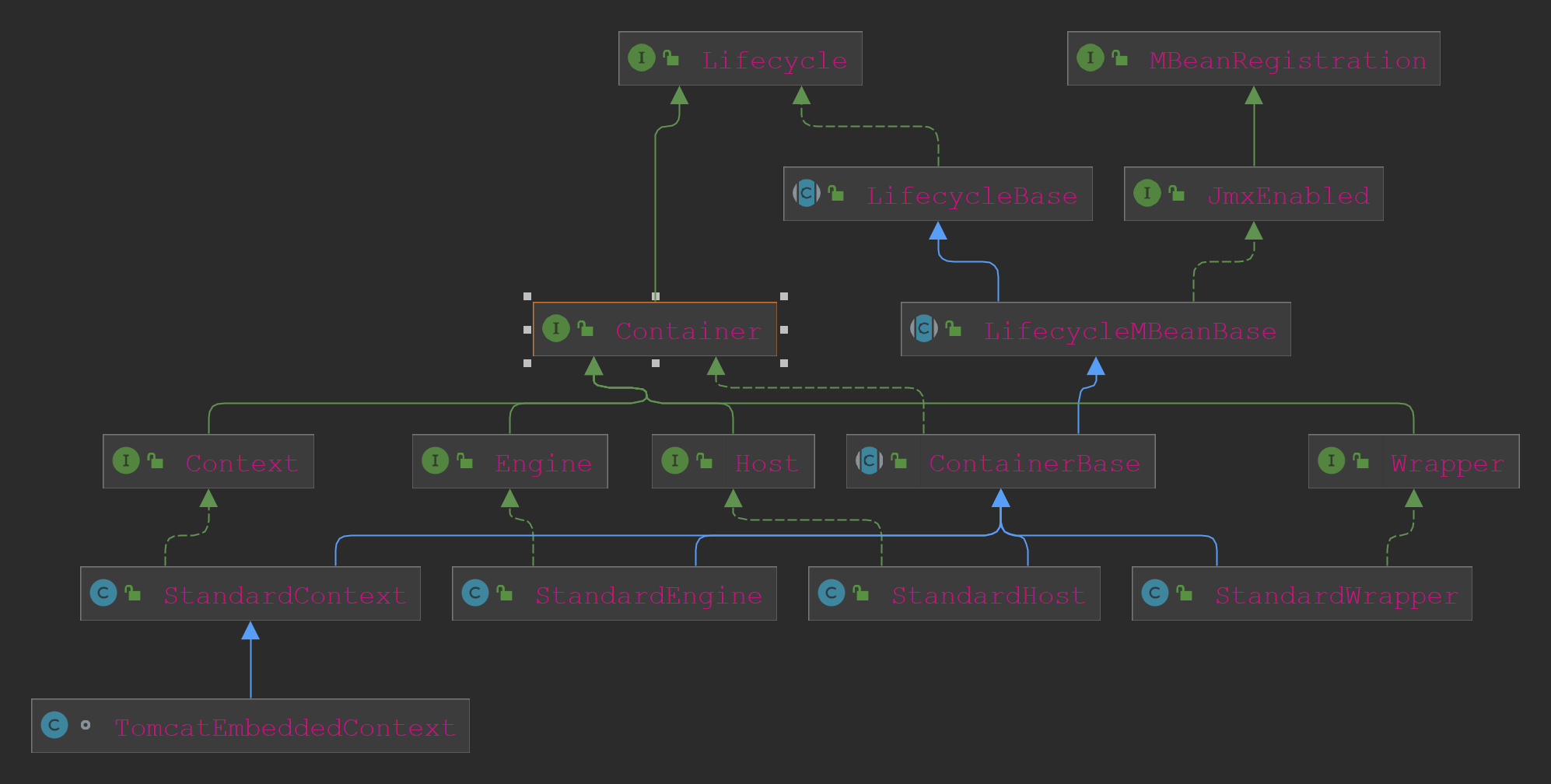
默认的容器组件实现类是StandardXXX,下面先解读一下StandardEngine的源码。
4.1 Engine
StandardEngine的源码如下:
/**
* Standard implementation of the <b>Engine</b> interface. Each child container must be a Host implementation to process
* the specific fully qualified host name of that virtual host.
*
* @author Craig R. McClanahan
*/
public class StandardEngine extends ContainerBase implements Engine {
/**
* Return the default host.
*/
@Override
public String getDefaultHost() {
return defaultHost;
}
/**
* Set the default host.
*
* @param host The new default host
*/
//设置Host
@Override
public void setDefaultHost(String host) {
String oldDefaultHost = this.defaultHost;
if (host == null) {
this.defaultHost = null;
} else {
this.defaultHost = host.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
}
if (getState().isAvailable()) {
service.getMapper().setDefaultHostName(host);
}
support.firePropertyChange("defaultHost", oldDefaultHost, this.defaultHost);
}
/**
* Add a child Container, only if the proposed child is an implementation of Host.
*
* @param child Child container to be added
*/
//添加子容器Host
@Override
public void addChild(Container child) {
if (!(child instanceof Host)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("standardEngine.notHost"));
}
super.addChild(child);
}
//初始化
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Ensure that a Realm is present before any attempt is made to start
// one. This will create the default NullRealm if necessary.
getRealm();
super.initInternal();
}
/**
* Start this component and implement the requirements of
* {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error that prevents this component from being
* used
*/
@Override
//启动方法
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Log our server identification information
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(sm.getString("standardEngine.start", ServerInfo.getServerInfo()));
}
// Standard container startup
super.startInternal();
}
}
4.2 Host
继续来到Host的源码:
/**
* Standard implementation of the <b>Host</b> interface. Each child container must be a Context implementation to
* process the requests directed to a particular web application.
*
* @author Craig R. McClanahan
* @author Remy Maucherat
*/
public class StandardHost extends ContainerBase implements Host {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(StandardHost.class);
/**
* The application root for this Host.
*/
private String appBase = "webapps";
private volatile File appBaseFile = null;
/**
* Add a child Container, only if the proposed child is an implementation of Context.
*
* @param child Child container to be added
*/
//添加子容器
@Override
public void addChild(Container child) {
if (!(child instanceof Context)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("standardHost.notContext"));
}
child.addLifecycleListener(new MemoryLeakTrackingListener());
// Avoid NPE for case where Context is defined in server.xml with only a
// docBase
Context context = (Context) child;
if (context.getPath() == null) {
ContextName cn = new ContextName(context.getDocBase(), true);
context.setPath(cn.getPath());
}
super.addChild(child);
}
/**
* Start this component and implement the requirements of
* {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error that prevents this component from being
* used
*/
//启动方法
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Set error report valve
String errorValve = getErrorReportValveClass();
if ((errorValve != null) && (!errorValve.equals(""))) {
try {
boolean found = false;
Valve[] valves = getPipeline().getValves();
for (Valve valve : valves) {
if (errorValve.equals(valve.getClass().getName())) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
if (!found) {
Valve valve = ErrorReportValve.class.getName().equals(errorValve) ? new ErrorReportValve() :
(Valve) Class.forName(errorValve).getConstructor().newInstance();
getPipeline().addValve(valve);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString("standardHost.invalidErrorReportValveClass", errorValve), t);
}
}
super.startInternal();
}
}
4.3 Context
默认的Context的实现类是StandardContext,Boot的TomcatEmbeddedContext拓展了StandardContext。StandardContext的部分源码如下:
/**
* Standard implementation of the <b>Context</b> interface. Each child container must be a Wrapper implementation to
* process the requests directed to a particular servlet.
*
* @author Craig R. McClanahan
* @author Remy Maucherat
*/
public class StandardContext extends ContainerBase implements Context, NotificationEmitter {
//添加子容器
@Override
public void addChild(Container child) {
if (!(child instanceof Wrapper)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("standardContext.notWrapper"));
}
super.addChild(child);
}
//启动方法
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Post work directory
postWorkDirectory();
if (getLoader() == null) {
WebappLoader webappLoader = new WebappLoader();
webappLoader.setDelegate(getDelegate());
setLoader(webappLoader);
}
// Binding thread
ClassLoader oldCCL = bindThread();
try {
// Start our child containers, if not already started
for (Container child : findChildren()) {
if (!child.getState().isAvailable()) {
child.start();
}
}
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic),
// if any
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
}
}
// Set up the context init params
mergeParameters();
// Call ServletContainerInitializers
for (Map.Entry<ServletContainerInitializer,Set<Class<?>>> entry : initializers.entrySet()) {
try {
entry.getKey().onStartup(entry.getValue(), getServletContext());
}
}
// Load and initialize all "load on startup" servlets
if (ok) {
if (!loadOnStartup(findChildren())) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.servletFail"));
ok = false;
}
}
// Start ContainerBackgroundProcessor thread
super.threadStart();
}
}
//初始化方法
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
// Register the naming resources
if (namingResources != null) {
namingResources.init();
}
// Send j2ee.object.created notification
if (this.getObjectName() != null) {
Notification notification =
new Notification("j2ee.object.created", this.getObjectName(), sequenceNumber.getAndIncrement());
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
}
Context的官方解释是“A Context is a Container that represents a servlet context, and therefore an individual web application, in the Catalina servlet engine”。 这里官方的说明是指Context的一个servletContext,表示一个单独的Web Application。
五、Wrapper和Servlet
StandardWrapper指的是一个单独的servlet,没有子容器,是一个Servlet的修饰器:
/**
* The (single) possibly uninitialized instance of this servlet.
*/
protected volatile Servlet instance = null;
StandardWrapper源码如下(有删减):
public class StandardWrapper extends ContainerBase implements ServletConfig, Wrapper, NotificationEmitter {
/**
* The (single) possibly uninitialized instance of this servlet.
*/
protected volatile Servlet instance = null;
/**
* Flag that indicates if this instance has been initialized
*/
protected volatile boolean instanceInitialized = false;
/**
* The load-on-startup order value (negative value means load on first call) for this servlet.
*/
protected int loadOnStartup = -1;
/**
* Mappings associated with the wrapper.
*/
protected final ArrayList<String> mappings = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* The initialization parameters for this servlet, keyed by parameter name.
*/
protected HashMap<String,String> parameters = new HashMap<>();
/**
* The fully qualified servlet class name for this servlet.
*/
protected String servletClass = null;
/**
* @return the associated servlet instance.
*/
@Override
public Servlet getServlet() {
return instance;
}
/**
* Set the associated servlet instance.
*/
@Override
public void setServlet(Servlet servlet) {
instance = servlet;
}
/**
* Add a mapping associated with the Wrapper.
*
* @param mapping The new wrapper mapping
*/
@Override
public void addMapping(String mapping) {
mappingsLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
mappings.add(mapping);
} finally {
mappingsLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
if (parent.getState().equals(LifecycleState.STARTED)) {
fireContainerEvent(ADD_MAPPING_EVENT, mapping);
}
}
//装载Servlet
@Override
public synchronized void load() throws ServletException {
instance = loadServlet();
if (!instanceInitialized) {
initServlet(instance);
}
}
//装载Servlet
public synchronized Servlet loadServlet() throws ServletException {
Servlet servlet;
try {
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Complain if no servlet class has been specified
if (servletClass == null) {
unavailable(null);
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("standardWrapper.notClass", getName()));
}
InstanceManager instanceManager = ((StandardContext) getParent()).getInstanceManager();
try {
servlet = (Servlet) instanceManager.newInstance(servletClass);
}
initServlet(servlet);
fireContainerEvent("load", this);
loadTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - t1;
}
return servlet;
}
//Servlet初始化
private synchronized void initServlet(Servlet servlet) throws ServletException {
if (instanceInitialized) {
return;
}
// Call the initialization method of this servlet
try {
servlet.init(facade);
instanceInitialized = true;
}
}
/**
* @return the servlet context with which this servlet is associated.
*/
@Override
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
if (parent == null) {
return null;
} else if (!(parent instanceof Context)) {
return null;
} else {
return ((Context) parent).getServletContext();
}
}
// ------------------------------------------------------ Lifecycle Methods
/**
* Start this component and implement the requirements of
* {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error that prevents this component from being
* used
*/
//启动方法
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Send j2ee.state.starting notification
if (this.getObjectName() != null) {
Notification notification = new Notification("j2ee.state.starting", this.getObjectName(), sequenceNumber++);
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
// Start up this component
super.startInternal();
setAvailable(0L);
// Send j2ee.state.running notification
if (this.getObjectName() != null) {
Notification notification = new Notification("j2ee.state.running", this.getObjectName(), sequenceNumber++);
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
}
/**
* Stop this component and implement the requirements of
* {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#stopInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error that prevents this component from being
* used
*/
//关闭方法
@Override
protected synchronized void stopInternal() throws LifecycleException {
setAvailable(Long.MAX_VALUE);
// Send j2ee.state.stopping notification
if (this.getObjectName() != null) {
Notification notification = new Notification("j2ee.state.stopping", this.getObjectName(), sequenceNumber++);
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
// Shut down our servlet instance (if it has been initialized)
try {
unload();
} catch (ServletException e) {
getServletContext().log(sm.getString("standardWrapper.unloadException", getName()), e);
}
// Shut down this component
super.stopInternal();
// Send j2ee.state.stopped notification
if (this.getObjectName() != null) {
Notification notification = new Notification("j2ee.state.stopped", this.getObjectName(), sequenceNumber++);
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
// Send j2ee.object.deleted notification
Notification notification = new Notification("j2ee.object.deleted", this.getObjectName(), sequenceNumber++);
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
}
一个Wrapper对应的是一个Servlet:
2023-12-06 22:37:42,148|DEBUG| DirectJDKLog.java:173 |main|Add child StandardWrapper[dispatcherServlet] StandardEngine[Tomcat].StandardHost[localhost].TomcatEmbeddedContext[]
2023-12-06 22:37:42,148|DEBUG| DirectJDKLog.java:173 |main|Setting state for [StandardEngine[Tomcat].StandardHost[localhost].TomcatEmbeddedContext[].StandardWrapper[dispatcherServlet]] to [INITIALIZING]
2023-12-06 22:37:42,148|DEBUG| DirectJDKLog.java:173 |main|Setting state for [StandardEngine[Tomcat].StandardHost[localhost].TomcatEmbeddedContext[].StandardWrapper[dispatcherServlet]] to [INITIALIZED]
2023-12-06 22:37:42,148|DEBUG| DirectJDKLog.java:173 |main|Setting state for [StandardEngine[Tomcat].StandardHost[localhost].TomcatEmbeddedContext[].StandardWrapper[dispatcherServlet]] to [STARTING_PREP
在StandardContext这个方法中会执行Wrapper的load方法,从而通过loadServlet方法装载Servlet。
public boolean loadOnStartup(Container children[]) {
// Collect "load on startup" servlets that need to be initialized
TreeMap<Integer,ArrayList<Wrapper>> map = new TreeMap<>();
for (Container child : children) {
Wrapper wrapper = (Wrapper) child;
int loadOnStartup = wrapper.getLoadOnStartup();
if (loadOnStartup < 0) {
continue;
}
Integer key = Integer.valueOf(loadOnStartup);
map.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(wrapper);
}
// Load the collected "load on startup" servlets
for (ArrayList<Wrapper> list : map.values()) {
for (Wrapper wrapper : list) {
try {
wrapper.load();
} catch (ServletException e) {
getLogger().error(
sm.getString("standardContext.loadOnStartup.loadException", getName(), wrapper.getName()),
StandardWrapper.getRootCause(e));
// NOTE: load errors (including a servlet that throws
// UnavailableException from the init() method) are NOT
// fatal to application startup
// unless failCtxIfServletStartFails="true" is specified
if (getComputedFailCtxIfServletStartFails()) {
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
StandardWrapper是一个Servlet的包装类,比如DispatcherServlet的StandardWrapper如下:
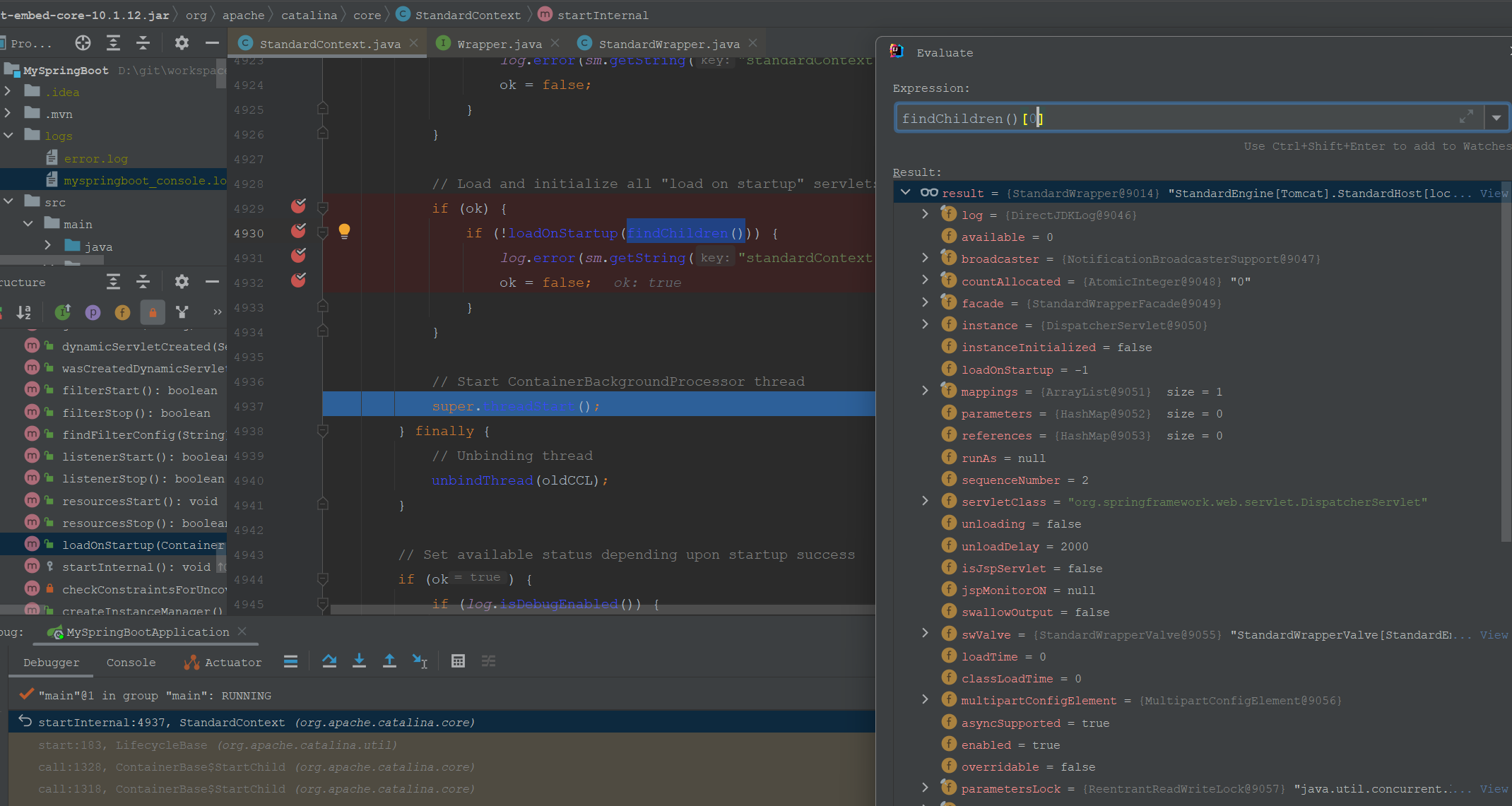
到这里Tomcat相关组件的初始化过程就解读完成了,下一篇文件解读启动过程,也就是start方法。
六、参考材料
- 《深入剖析Tomcat》
- 《HTTP权威指南》
