本篇文章继续解读HTTP请求的处理过程。
本系列的源码工程为:HowTomcatWorksSourceCode。
本文目录为:
一、容器
上一篇文章讲到Adapter调用容器的阀来执行HTTP请求。
// Calling the container
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
这里的顶级Container是Engine,我们来到Engine和其Valve相关的代码。容器StandardEngine自身是没有invoke或者service方法,我们进入StandardEngineValve这个类。
1.1 Engine
Engine内部包含pipeline对象,存储设置的全部Valve;
/**
* The Pipeline object with which this Container is associated.
*/
protected final Pipeline pipeline = new StandardPipeline(this);
Pipeline类似于拦截器链,Valve就是内部的拦截器。容器的管道pipeline有一个基础阀。四类容器创建时候,会自带添加一个基础阀到对应的Pipeline内:
/**
* Create a new StandardEngine component with the default basic Valve.
*/
public StandardEngine() {
pipeline.setBasic(new StandardEngineValve());
// By default, the engine will hold the reloading thread
backgroundProcessorDelay = 10;
}
在HTTP请求处理过程中,某个容器的Pipeline链中,其基础阀是最后执行的。
@Override
public Valve getFirst() {
if (first != null) {
return first;
}
return basic;
}
非基础阀的invoke方法一般是执行自身逻辑后便调用链上的下一个阀,如AbstractAccessLogValve#invoke方法:
@Override
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
if (tlsAttributeRequired) {
// The log pattern uses TLS attributes. Ensure these are populated
// before the request is processed because with NIO2 it is possible
// for the connection to be closed (and the TLS info lost) before
// the access log requests the TLS info. Requesting it now causes it
// to be cached in the request.
request.getAttribute(Globals.CERTIFICATES_ATTR);
}
if (cachedElements != null) {
for (CachedElement element : cachedElements) {
element.cache(request);
}
}
getNext().invoke(request, response);
}
接下来继续来到StandardEngineValve,阅读其invoke方法:
/**
* Select the appropriate child Host to process this request, based on the requested server name. If no matching
* Host can be found, return an appropriate HTTP error.
*
* @param request Request to be processed
* @param response Response to be produced
*
* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurred
* @exception ServletException if a servlet error occurred
*/
@Override
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
// Select the Host to be used for this Request
Host host = request.getHost();
if (host == null) {
// HTTP 0.9 or HTTP 1.0 request without a host when no default host
// is defined.
// Don't overwrite an existing error
if (!response.isError()) {
response.sendError(404);
}
return;
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(host.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
// Ask this Host to process this request
host.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}
StandardEngineValve的invoke方法主要是交给Host的管道来处理请求。
1.2 Host
四种容器的Valve的处理过程是很类似的,StandardHostValve的invoke方法如下:
/**
* Select the appropriate child Context to process this request, based on the specified request URI. If no matching
* Context can be found, return an appropriate HTTP error.
*
* @param request Request to be processed
* @param response Response to be produced
*
* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurred
* @exception ServletException if a servlet error occurred
*/
@Override
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
// Select the Context to be used for this Request
Context context = request.getContext();
if (context == null) {
// Don't overwrite an existing error
if (!response.isError()) {
response.sendError(404);
}
return;
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(context.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
boolean asyncAtStart = request.isAsync();
try {
context.bind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, MY_CLASSLOADER);
if (!asyncAtStart && !context.fireRequestInitEvent(request.getRequest())) {
// Don't fire listeners during async processing (the listener
// fired for the request that called startAsync()).
// If a request init listener throws an exception, the request
// is aborted.
return;
}
// Ask this Context to process this request. Requests that are
// already in error must have been routed here to check for
// application defined error pages so DO NOT forward them to the
// application for processing.
try {
if (!response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
context.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
container.getLogger().error("Exception Processing " + request.getRequestURI(), t);
// If a new error occurred while trying to report a previous
// error allow the original error to be reported.
if (!response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, t);
throwable(request, response, t);
}
}
// Now that the request/response pair is back under container
// control lift the suspension so that the error handling can
// complete and/or the container can flush any remaining data
response.setSuspended(false);
Throwable t = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
// Protect against NPEs if the context was destroyed during a
// long running request.
if (!context.getState().isAvailable()) {
return;
}
// Look for (and render if found) an application level error page
if (response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
// If an error has occurred that prevents further I/O, don't waste time
// producing an error report that will never be read
AtomicBoolean result = new AtomicBoolean(false);
response.getCoyoteResponse().action(ActionCode.IS_IO_ALLOWED, result);
if (result.get()) {
if (t != null) {
throwable(request, response, t);
} else {
status(request, response);
}
}
}
if (!request.isAsync() && !asyncAtStart) {
context.fireRequestDestroyEvent(request.getRequest());
}
} finally {
// Access a session (if present) to update last accessed time, based
// on a strict interpretation of the specification
if (context.getAlwaysAccessSession()) {
request.getSession(false);
}
context.unbind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, MY_CLASSLOADER);
}
}
依然是转交给Context去处理。StandardHostValve处理之前也是先调用其他的Valve的invoke方法(若有配置Valve)。
我们继续来到Context的相关处理流程。
1.3 Context
StandardContextValve的invoke方法源码如下:
@Override
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
// Select the Context to be used for this Request
Context context = request.getContext();
if (context == null) {
// Don't overwrite an existing error
if (!response.isError()) {
response.sendError(404);
}
return;
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(context.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
boolean asyncAtStart = request.isAsync();
try {
context.bind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, MY_CLASSLOADER);
if (!asyncAtStart && !context.fireRequestInitEvent(request.getRequest())) {
// Don't fire listeners during async processing (the listener
// fired for the request that called startAsync()).
// If a request init listener throws an exception, the request
// is aborted.
return;
}
// Ask this Context to process this request. Requests that are
// already in error must have been routed here to check for
// application defined error pages so DO NOT forward them to the
// application for processing.
try {
if (!response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
context.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
container.getLogger().error("Exception Processing " + request.getRequestURI(), t);
// If a new error occurred while trying to report a previous
// error allow the original error to be reported.
if (!response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, t);
throwable(request, response, t);
}
}
// Now that the request/response pair is back under container
// control lift the suspension so that the error handling can
// complete and/or the container can flush any remaining data
response.setSuspended(false);
Throwable t = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
// Protect against NPEs if the context was destroyed during a
// long running request.
if (!context.getState().isAvailable()) {
return;
}
// Look for (and render if found) an application level error page
if (response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
// If an error has occurred that prevents further I/O, don't waste time
// producing an error report that will never be read
AtomicBoolean result = new AtomicBoolean(false);
response.getCoyoteResponse().action(ActionCode.IS_IO_ALLOWED, result);
if (result.get()) {
if (t != null) {
throwable(request, response, t);
} else {
status(request, response);
}
}
}
if (!request.isAsync() && !asyncAtStart) {
context.fireRequestDestroyEvent(request.getRequest());
}
} finally {
// Access a session (if present) to update last accessed time, based
// on a strict interpretation of the specification
if (context.getAlwaysAccessSession()) {
request.getSession(false);
}
context.unbind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, MY_CLASSLOADER);
}
}
可以看到这里依然是调用下一级容器的Pipeline去执行处理请求。
Context的Pipeline(Valve)信息追踪如下:
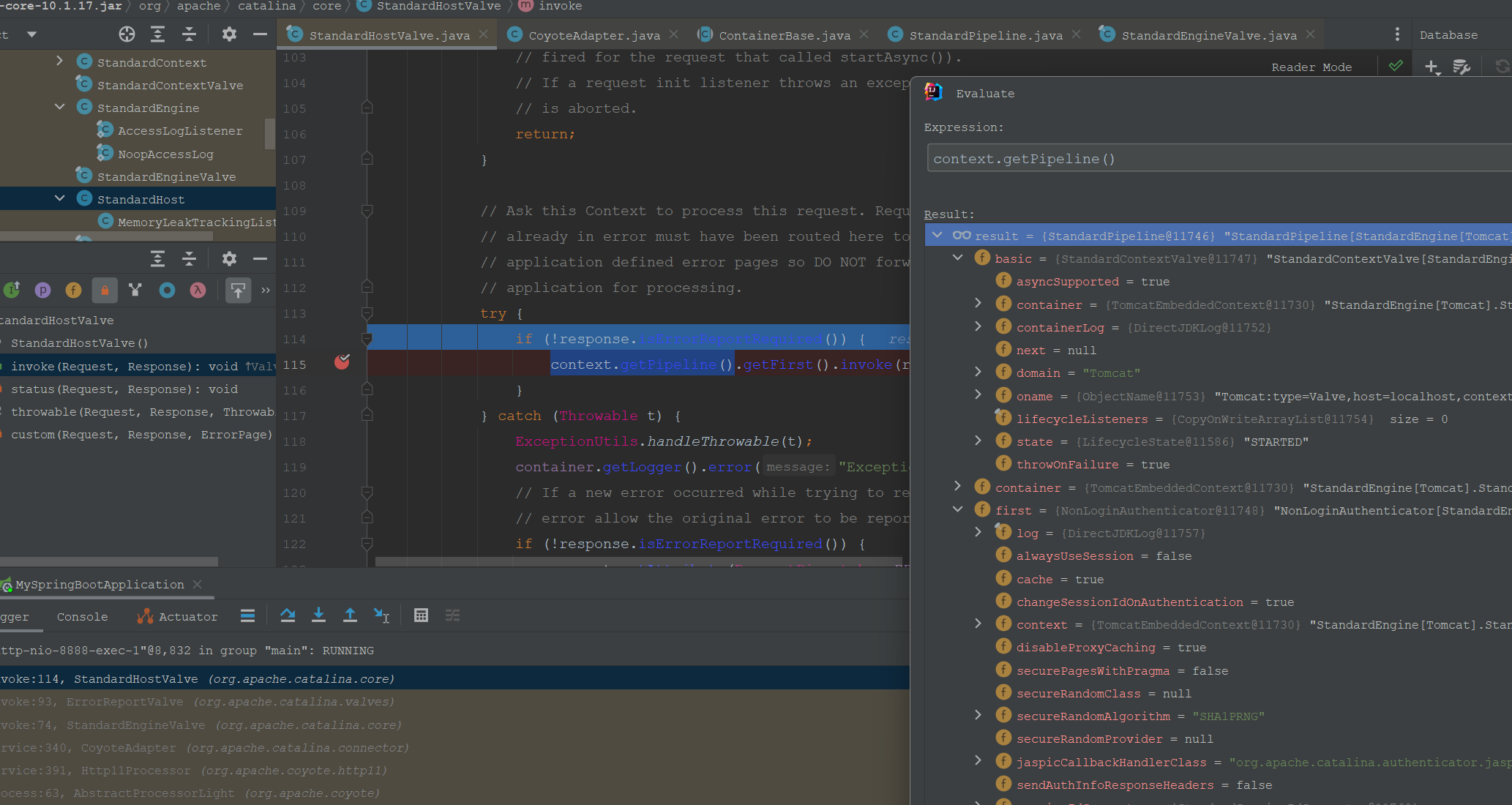
Context的Pipeline处理完成后则交给Wrapper的Pipeline去处理。
1.4 Wrapper
这里我们直接来到StandardWrapperValve,其invoke方法如下:
/**
* Invoke the servlet we are managing, respecting the rules regarding servlet lifecycle support.
*
* @param request Request to be processed
* @param response Response to be produced
*
* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurred
* @exception ServletException if a servlet error occurred
*/
@Override
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
// Initialize local variables we may need
boolean unavailable = false;
Throwable throwable = null;
// This should be a Request attribute...
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
requestCount.incrementAndGet();
StandardWrapper wrapper = (StandardWrapper) getContainer();
Servlet servlet = null;
Context context = (Context) wrapper.getParent();
// Check for the application being marked unavailable
if (!context.getState().isAvailable()) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,
sm.getString("standardContext.isUnavailable"));
unavailable = true;
}
// Check for the servlet being marked unavailable
if (!unavailable && wrapper.isUnavailable()) {
container.getLogger().info(sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable", wrapper.getName()));
checkWrapperAvailable(response, wrapper);
unavailable = true;
}
// Allocate a servlet instance to process this request
try {
if (!unavailable) {
servlet = wrapper.allocate();
}
} catch (UnavailableException e) {
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException", wrapper.getName()), e);
checkWrapperAvailable(response, wrapper);
} catch (ServletException e) {
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException", wrapper.getName()),
StandardWrapper.getRootCause(e));
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException", wrapper.getName()), e);
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
servlet = null;
}
MessageBytes requestPathMB = request.getRequestPathMB();
DispatcherType dispatcherType = DispatcherType.REQUEST;
if (request.getDispatcherType() == DispatcherType.ASYNC) {
dispatcherType = DispatcherType.ASYNC;
}
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_TYPE_ATTR, dispatcherType);
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_REQUEST_PATH_ATTR, requestPathMB);
// Create the filter chain for this request
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain = ApplicationFilterFactory.createFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet);
// Call the filter chain for this request
// NOTE: This also calls the servlet's service() method
Container container = this.container;
try {
if ((servlet != null) && (filterChain != null)) {
// Swallow output if needed
if (context.getSwallowOutput()) {
try {
SystemLogHandler.startCapture();
if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch();
} else {
filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
}
} finally {
String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture();
if (log != null && log.length() > 0) {
context.getLogger().info(log);
}
}
} else {
if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch();
} else {
filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
}
}
}
} catch (BadRequestException e) {
if (container.getLogger().isDebugEnabled()) {
container.getLogger().debug(
sm.getString("standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName(), context.getName()), e);
}
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e, HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST);
} catch (CloseNowException e) {
if (container.getLogger().isDebugEnabled()) {
container.getLogger().debug(
sm.getString("standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName(), context.getName()), e);
}
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
} catch (IOException e) {
container.getLogger()
.error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName(), context.getName()), e);
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
} catch (UnavailableException e) {
container.getLogger()
.error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName(), context.getName()), e);
wrapper.unavailable(e);
checkWrapperAvailable(response, wrapper);
// Do not save exception in 'throwable', because we
// do not want to do exception(request, response, e) processing
} catch (ServletException e) {
Throwable rootCause = StandardWrapper.getRootCause(e);
if (!(rootCause instanceof BadRequestException)) {
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.serviceExceptionRoot", wrapper.getName(),
context.getName(), e.getMessage()), rootCause);
}
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
container.getLogger()
.error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName(), context.getName()), e);
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
} finally {
// Release the filter chain (if any) for this request
if (filterChain != null) {
filterChain.release();
}
// Deallocate the allocated servlet instance
try {
if (servlet != null) {
wrapper.deallocate(servlet);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.deallocateException", wrapper.getName()), e);
if (throwable == null) {
throwable = e;
exception(request, response, e);
}
}
// If this servlet has been marked permanently unavailable,
// unload it and release this instance
try {
if ((servlet != null) && (wrapper.getAvailable() == Long.MAX_VALUE)) {
wrapper.unload();
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.unloadException", wrapper.getName()), e);
if (throwable == null) {
exception(request, response, e);
}
}
long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
long time = t2 - t1;
processingTime.add(time);
if (time > maxTime) {
maxTime = time;
}
if (time < minTime) {
minTime = time;
}
}
}
其内部主要的处理流程是:
- 若未加载Servlet的实例,则进行加载,创建和初始化Servlet。
- 创建过滤器执行链(filterChain),执行每个过滤器的过滤(doFilter)方法。
- 执行完成过滤器链最后一个过滤器后,执行Servlet的service方法。
追踪调试的过滤器链信息如下:
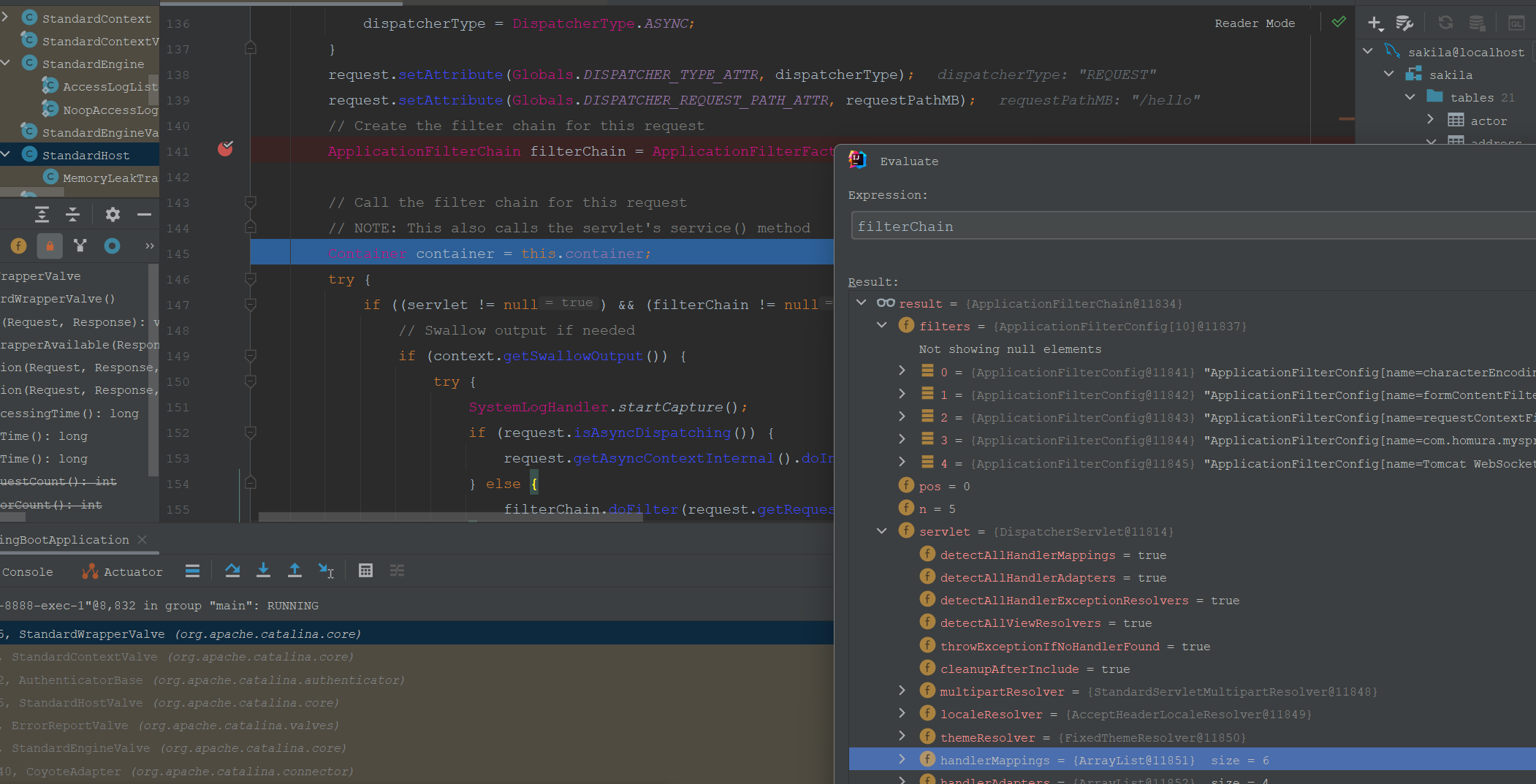
过滤器链内部执行的方法如下:
private void internalDoFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Call the next filter if there is one
if (pos < n) {
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = filters[pos++];
try {
Filter filter = filterConfig.getFilter();
if (request.isAsyncSupported() &&
"false".equalsIgnoreCase(filterConfig.getFilterDef().getAsyncSupported())) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR, Boolean.FALSE);
}
if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
Principal principal = ((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal();
Object[] args = new Object[] { req, res, this };
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege("doFilter", filter, classType, args, principal);
} else {
filter.doFilter(request, response, this);
}
} catch (IOException | ServletException | RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
e = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(e);
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("filterChain.filter"), e);
}
return;
}
// We fell off the end of the chain -- call the servlet instance
try {
if (dispatcherWrapsSameObject) {
lastServicedRequest.set(request);
lastServicedResponse.set(response);
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported() && !servletSupportsAsync) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR, Boolean.FALSE);
}
// Use potentially wrapped request from this point
if ((request instanceof HttpServletRequest) && (response instanceof HttpServletResponse) &&
Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
Principal principal = ((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal();
Object[] args = new Object[] { req, res };
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege("service", servlet, classTypeUsedInService, args, principal);
} else {
servlet.service(request, response);
}
} catch (IOException | ServletException | RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
e = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(e);
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("filterChain.servlet"), e);
} finally {
if (dispatcherWrapsSameObject) {
lastServicedRequest.set(null);
lastServicedResponse.set(null);
}
}
}
里面首先执行过滤器的过滤方法。
filter.doFilter(request, response, this);
最后执行servlet的方法:
servlet.service(request, response);
到这里我们知道我们配置的拦截器(Filter)是由Tomcat创建并执行的。
接下来就是Servlet的方法。
二、Servlet
Servlet的定义是处理Web请求的顶层接口,是一套实现Web功能的规范。这里没有限定协议是Http,虽然Tomcat的Http协议的Servlet容器,但jakarta的标准并没有限定Http协议。
其核心方法处理Web请求的service方法如下:
void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException;
Servlet自身是一个顶层接口,在SpringMVC中一般是由DispatcherServlet实现该接口。
三、DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet实现Servlet接口,并最终将由doDispatch方法处理请求,内部做分派调用Handler处理请求返回结果。
其源码如下:
/**
* Process the actual dispatching to the handler.
* <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order.
* The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters
* to find the first that supports the handler class.
* <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers
* themselves to decide which methods are acceptable.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = HttpMethod.GET.matches(method);
if (isGet || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new ServletException("Handler dispatch failed: " + err, err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new ServletException("Handler processing failed: " + err, err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
这里处理请求的过程可以参考笔者的这篇文章: Spring源码阅读十五:DispatcherServlet的请求处理流程.
本文就不作过多解读。需要注意的是我们说DispatcherServlet是SpringMVC、SpringBoot的默认的Servlet是基于约定配置,开发者自己也可以实现Servlet来处理Http请求。
四、总结
结合上一篇文章和这篇文章,笔者这里总结一下Http请求的处理过程。
- 首先是连接器的处理过程,特别是NioEndpoint内部Acceptor+Poller+Workers的模型,然后是协议处理器Http11Processor和适配器。
- 适配器将请求转交给容器及其管道(Pipeline和Valve)处理。
- 容器处理之后,请求交给Servlet处理。
- Servlet则由具体的实现类去处理,SpringMVC默认是DispatcherServlet,最终由Handler(Controller)处理。也可以自己实现Servlet定义来处理。
Http请求的处理流程图如下:
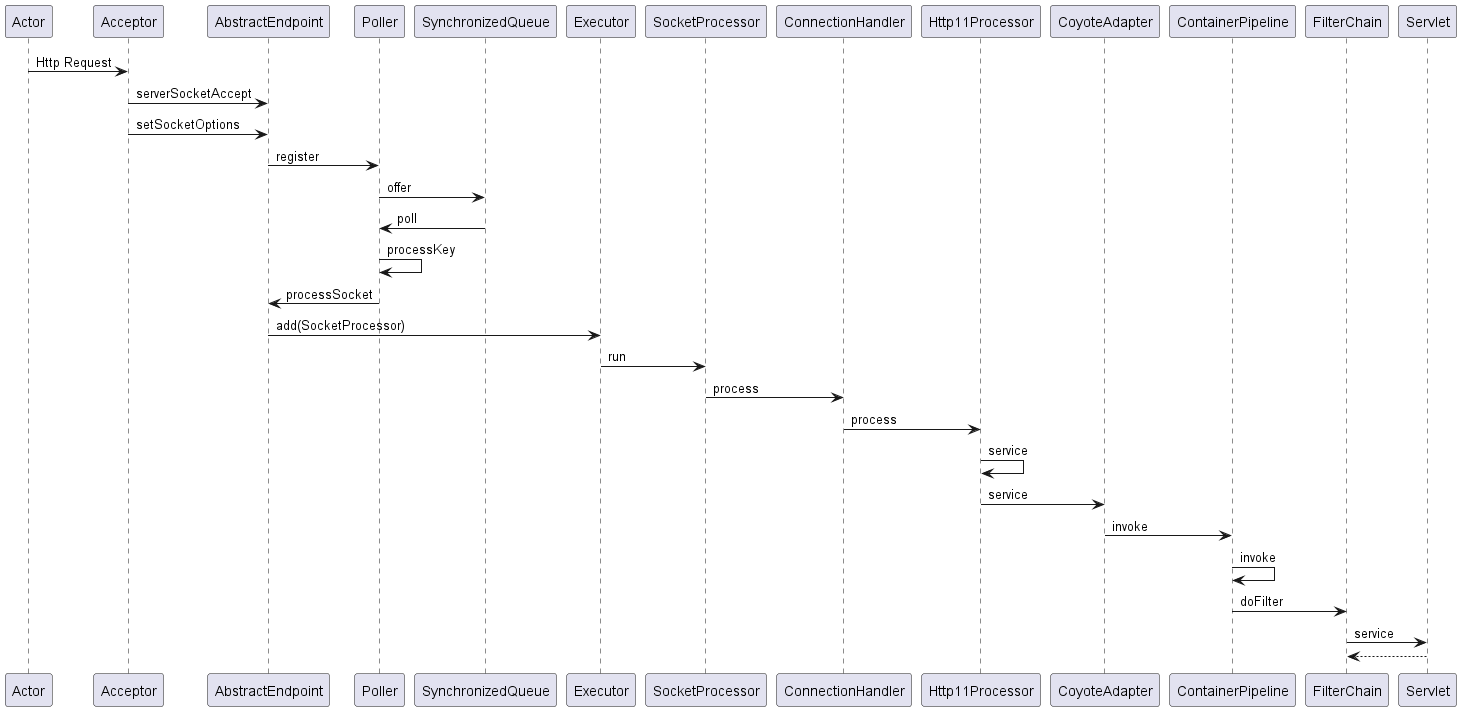
这里注意一点是管道Pipeline内必包含容器的基础阀,基础阀在该容器阀链表的最后一个执行。
五、参考材料
1.《深入剖析Tomcat》
