本文是SpringBoot源码阅读计划的第五篇文章,本文简单解读一下内置的Servlet容器(tomcat)执行流程的源代码。
本文源码地址为:https://github.com/zouhuanli/MySpringBoot.git。
在普通的SpringMVC应用中,在”web.xml”配置DispatcherServlet和各种监听器,过滤器等组件。再启动Tomcat,由servlet容器Tomcat创建DispatcherServlet。
而在SpringBoot中,这些配置和组件是自动创建和配置,然后通过内置的Servlet容器启动,支持Tomcat、jetty、Undertow。
在项目中引入starter-web模块,里面引入了tomcat、web、webmvc等模块。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<version>3.1.3</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>6.0.11</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>6.0.11</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
一、简单使用
引入starter-web模块后,boot会自动引入相关依赖项,并配置好默认的DispatcherServlet,我们直接使用即可。
这里写一个简单的controller,如下。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserController.class);
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/add", method = RequestMethod.POST, produces = "application/json")
public ResponseResult<User> add(@Valid @RequestBody User user, BindingResult bindingResult) {
LOGGER.info("add method:{}", user);
if (bindingResult.hasErrors()) {
List<ObjectError> errors = bindingResult.getAllErrors();
errors.forEach(p -> {
FieldError fieldError = (FieldError) p;
LOGGER.error("Invalid Parameter : object - {},field - {},errorMessage - {}", fieldError.getObjectName(), fieldError.getField(), fieldError.getDefaultMessage());
});
return ResponseResult.fail("invalid parameter");
}
userService.add(user);
return ResponseResult.success(user);
}
@GetMapping("/listAll")
public List<User> listAll() {
LOGGER.info("listAll method");
return userService.listAll();
}
@GetMapping("/get/{uid}")
public User getByUid(@PathVariable("uid") Integer uid) {
LOGGER.info("listAll method");
return userService.getByUid(uid);
}
}
然后设置tomcat的启动端口,’server.port’配置项在ServerProperties这个配置类。SpringBoot的配置一般是按前缀划分的,也就是说你随便写一个”aaa.cc.b’这样的配置boot框架自身是使用它没法自动配置的。
比如数据库配置的前缀’spring.datasource’,mybatis配置的前缀’mybatis.’,都是在对应的PropertiesBean内定义。
server:
port: 8888
spring:
config:
import:
- classpath:application-db.yml
直接启动应用,浏览器输入:http://localhost:8888/user/listAll 进行测试。返回:
[
{
"uid": -1909834037,
"uname": "zouhl",
"password": null,
"gender": "M",
"phone": "12345678901",
"email": "test@gmail.com",
"address": "阿巴阿巴",
"age": null
},
{
"uid": -1224581745,
"uname": "zouhl",
"password": null,
"gender": "M",
"phone": "12345678901",
"email": "test@gmail.com",
"address": "阿巴阿巴",
"age": null
},
{
"uid": -801153946,
"uname": "zouhl",
"password": null,
"gender": "M",
"phone": "12345678901",
"email": "test@gmail.com",
"address": "阿巴阿巴",
"age": null
},
{
"uid": -556398336,
"uname": "zouhl",
"password": null,
"gender": "M",
"phone": "12345678901",
"email": "test@gmail.com",
"address": "阿巴阿巴",
"age": null
},
{
"uid": 10000009,
"uname": "李四",
"password": null,
"gender": null,
"phone": null,
"email": null,
"address": null,
"age": null
}
]
可以看到通过SpringBoot集成Web功能启动Web项目是非常简单的,配置非常少,几乎没有XML配置。
WebMVC和tomcat的自动配置依然是通过XXXAutoConfiguration类来完成的。
二、自动配置
我们来到autoconfigure工程的web.servlet包内,可以看到主要有DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration、ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration、WebMvcAutoConfiguration。
这些自动配置类的实现原理请参考一下这篇文章:(自动配置实现原理)。
自动配置类的注册、创建和执行流程这里不做详细的解读,这里关注一下创建了哪些需要的组件。
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration源码如下。
@AutoConfiguration(after = SslAutoConfiguration.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRequest.class)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)
@Import({ ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedJetty.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedUndertow.class })
public class ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration {
//创建ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer,定制化ServletWebServerFactory,
// ServletWebServerFactory是用于创建Server(Tomcat、Jetty、Undertow)的工厂类
@Bean
public ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer servletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(ServerProperties serverProperties,
ObjectProvider<WebListenerRegistrar> webListenerRegistrars,
ObjectProvider<CookieSameSiteSupplier> cookieSameSiteSuppliers, ObjectProvider<SslBundles> sslBundles) {
return new ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(serverProperties, webListenerRegistrars.orderedStream().toList(),
cookieSameSiteSuppliers.orderedStream().toList(), sslBundles.getIfAvailable());
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnClass(name = "org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat")
public TomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer tomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(
ServerProperties serverProperties) {
return new TomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(serverProperties);
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "server.forward-headers-strategy", havingValue = "framework")
@ConditionalOnMissingFilterBean(ForwardedHeaderFilter.class)
static class ForwardedHeaderFilterConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnClass(name = "org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat")
ForwardedHeaderFilterCustomizer tomcatForwardedHeaderFilterCustomizer(ServerProperties serverProperties) {
return (filter) -> filter.setRelativeRedirects(serverProperties.getTomcat().isUseRelativeRedirects());
}
@Bean
FilterRegistrationBean<ForwardedHeaderFilter> forwardedHeaderFilter(
ObjectProvider<ForwardedHeaderFilterCustomizer> customizerProvider) {
ForwardedHeaderFilter filter = new ForwardedHeaderFilter();
customizerProvider.ifAvailable((customizer) -> customizer.customize(filter));
FilterRegistrationBean<ForwardedHeaderFilter> registration = new FilterRegistrationBean<>(filter);
registration.setDispatcherTypes(DispatcherType.REQUEST, DispatcherType.ASYNC, DispatcherType.ERROR);
registration.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
return registration;
}
}
interface ForwardedHeaderFilterCustomizer {
void customize(ForwardedHeaderFilter filter);
}
/**
* Registers a {@link WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor}. Registered via
* {@link ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar} for early registration.
*/
//通过BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar注册额外的Bean信息
public static class BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, BeanFactoryAware {
private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
if (beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory listableBeanFactory) {
this.beanFactory = listableBeanFactory;
}
}
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (this.beanFactory == null) {
return;
}
registerSyntheticBeanIfMissing(registry, "webServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor",
WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor.class);
registerSyntheticBeanIfMissing(registry, "errorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor",
ErrorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor.class);
}
private <T> void registerSyntheticBeanIfMissing(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, String name,
Class<T> beanClass) {
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(beanClass, true, false))) {
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(beanClass);
beanDefinition.setSynthetic(true);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(name, beanDefinition);
}
}
}
}
可以看到这里主要是创建ServletWebServerFactory的定制化器。
继续看下这个类ServletWebServerFactory的源码。
public class TomcatServletWebServerFactory extends AbstractServletWebServerFactory
implements ConfigurableTomcatWebServerFactory, ResourceLoaderAware {
//创建WebServer
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
Registry.disableRegistry();
}
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
for (LifecycleListener listener : this.serverLifecycleListeners) {
tomcat.getServer().addLifecycleListener(listener);
}
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
}
这里创建的WebServer有Tomcat、Jetty、Undertow三类。
我们继续进入ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration这个配置类。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
class ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Tomcat.class, UpgradeProtocol.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ServletWebServerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
static class EmbeddedTomcat {
//在这里创建TomcatServletWebServerFactory对象,用以创建TomcatWebServer
@Bean
TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcatServletWebServerFactory(
ObjectProvider<TomcatConnectorCustomizer> connectorCustomizers,
ObjectProvider<TomcatContextCustomizer> contextCustomizers,
ObjectProvider<TomcatProtocolHandlerCustomizer<?>> protocolHandlerCustomizers) {
TomcatServletWebServerFactory factory = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
factory.getTomcatConnectorCustomizers().addAll(connectorCustomizers.orderedStream().toList());
factory.getTomcatContextCustomizers().addAll(contextCustomizers.orderedStream().toList());
factory.getTomcatProtocolHandlerCustomizers().addAll(protocolHandlerCustomizers.orderedStream().toList());
return factory;
}
}
/**
* Nested configuration if Jetty is being used.
*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Server.class, Loader.class, WebAppContext.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ServletWebServerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
static class EmbeddedJetty {
@Bean
JettyServletWebServerFactory jettyServletWebServerFactory(
ObjectProvider<JettyServerCustomizer> serverCustomizers) {
JettyServletWebServerFactory factory = new JettyServletWebServerFactory();
factory.getServerCustomizers().addAll(serverCustomizers.orderedStream().toList());
return factory;
}
}
/**
* Nested configuration if Undertow is being used.
*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Undertow.class, SslClientAuthMode.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ServletWebServerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
static class EmbeddedUndertow {
@Bean
UndertowServletWebServerFactory undertowServletWebServerFactory(
ObjectProvider<UndertowDeploymentInfoCustomizer> deploymentInfoCustomizers,
ObjectProvider<UndertowBuilderCustomizer> builderCustomizers) {
UndertowServletWebServerFactory factory = new UndertowServletWebServerFactory();
factory.getDeploymentInfoCustomizers().addAll(deploymentInfoCustomizers.orderedStream().toList());
factory.getBuilderCustomizers().addAll(builderCustomizers.orderedStream().toList());
return factory;
}
@Bean
UndertowServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer undertowServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(
ServerProperties serverProperties) {
return new UndertowServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(serverProperties);
}
}
}
可以看到,三类WebServerFactory用到创建对应WebServer实例。
我们再来到EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration这个自动配置类。
@AutoConfiguration
@ConditionalOnNotWarDeployment
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)
public class EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration {
/**
* Nested configuration if Tomcat is being used.
*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Tomcat.class, UpgradeProtocol.class })
public static class TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizerConfiguration {
//这里创建TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer,用于定制化TomcatWebServerFactory
@Bean
public TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer tomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer(Environment environment,
ServerProperties serverProperties) {
return new TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer(environment, serverProperties);
}
}
}
我们继续看下TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer#customize方法。
//定制化参数,从而作用于WebServer
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableTomcatWebServerFactory factory) {
ServerProperties.Tomcat properties = this.serverProperties.getTomcat();
PropertyMapper map = PropertyMapper.get().alwaysApplyingWhenNonNull();
map.from(properties::getBasedir).to(factory::setBaseDirectory);
map.from(properties::getBackgroundProcessorDelay)
.as(Duration::getSeconds)
.as(Long::intValue)
.to(factory::setBackgroundProcessorDelay);
customizeRemoteIpValve(factory);
ServerProperties.Tomcat.Threads threadProperties = properties.getThreads();
map.from(threadProperties::getMax)
.when(this::isPositive)
.to((maxThreads) -> customizeMaxThreads(factory, threadProperties.getMax()));
map.from(threadProperties::getMinSpare)
.when(this::isPositive)
.to((minSpareThreads) -> customizeMinThreads(factory, minSpareThreads));
map.from(this.serverProperties.getMaxHttpRequestHeaderSize())
.asInt(DataSize::toBytes)
.when(this::isPositive)
.to((maxHttpRequestHeaderSize) -> customizeMaxHttpRequestHeaderSize(factory, maxHttpRequestHeaderSize));
map.from(properties::getMaxHttpResponseHeaderSize)
.asInt(DataSize::toBytes)
.when(this::isPositive)
.to((maxHttpResponseHeaderSize) -> customizeMaxHttpResponseHeaderSize(factory, maxHttpResponseHeaderSize));
map.from(properties::getMaxSwallowSize)
.asInt(DataSize::toBytes)
.to((maxSwallowSize) -> customizeMaxSwallowSize(factory, maxSwallowSize));
map.from(properties::getMaxHttpFormPostSize)
.asInt(DataSize::toBytes)
.when((maxHttpFormPostSize) -> maxHttpFormPostSize != 0)
.to((maxHttpFormPostSize) -> customizeMaxHttpFormPostSize(factory, maxHttpFormPostSize));
map.from(properties::getAccesslog)
.when(ServerProperties.Tomcat.Accesslog::isEnabled)
.to((enabled) -> customizeAccessLog(factory));
map.from(properties::getUriEncoding).to(factory::setUriEncoding);
map.from(properties::getConnectionTimeout)
.to((connectionTimeout) -> customizeConnectionTimeout(factory, connectionTimeout));
map.from(properties::getMaxConnections)
.when(this::isPositive)
.to((maxConnections) -> customizeMaxConnections(factory, maxConnections));
map.from(properties::getAcceptCount)
.when(this::isPositive)
.to((acceptCount) -> customizeAcceptCount(factory, acceptCount));
map.from(properties::getProcessorCache)
.to((processorCache) -> customizeProcessorCache(factory, processorCache));
map.from(properties::getKeepAliveTimeout)
.to((keepAliveTimeout) -> customizeKeepAliveTimeout(factory, keepAliveTimeout));
map.from(properties::getMaxKeepAliveRequests)
.to((maxKeepAliveRequests) -> customizeMaxKeepAliveRequests(factory, maxKeepAliveRequests));
map.from(properties::getRelaxedPathChars)
.as(this::joinCharacters)
.whenHasText()
.to((relaxedChars) -> customizeRelaxedPathChars(factory, relaxedChars));
map.from(properties::getRelaxedQueryChars)
.as(this::joinCharacters)
.whenHasText()
.to((relaxedChars) -> customizeRelaxedQueryChars(factory, relaxedChars));
map.from(properties::isRejectIllegalHeader)
.to((rejectIllegalHeader) -> customizeRejectIllegalHeader(factory, rejectIllegalHeader));
customizeStaticResources(factory);
customizeErrorReportValve(this.serverProperties.getError(), factory);
}
这个方法用于定制化WebServer的参数。
最后来到DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration这个自动配置类。
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@AutoConfiguration(after = ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.class)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass(DispatcherServlet.class)
public class DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration {
/**
* The bean name for a DispatcherServlet that will be mapped to the root URL "/".
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME = "dispatcherServlet";
/**
* The bean name for a ServletRegistrationBean for the DispatcherServlet "/".
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME = "dispatcherServletRegistration";
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Conditional(DefaultDispatcherServletCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRegistration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(WebMvcProperties.class)
protected static class DispatcherServletConfiguration {
//这里创建了DispatcherServlet,依赖于WebMvcProperties这个PropertiesBean去读取WebMvc的配置
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet(WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties) {
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet = new DispatcherServlet();
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchOptionsRequest(webMvcProperties.isDispatchOptionsRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchTraceRequest(webMvcProperties.isDispatchTraceRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound(webMvcProperties.isThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound());
dispatcherServlet.setPublishEvents(webMvcProperties.isPublishRequestHandledEvents());
dispatcherServlet.setEnableLoggingRequestDetails(webMvcProperties.isLogRequestDetails());
return dispatcherServlet;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(MultipartResolver.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = DispatcherServlet.MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME)
public MultipartResolver multipartResolver(MultipartResolver resolver) {
// Detect if the user has created a MultipartResolver but named it incorrectly
return resolver;
}
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Conditional(DispatcherServletRegistrationCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRegistration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(WebMvcProperties.class)
@Import(DispatcherServletConfiguration.class)
protected static class DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration {
//这里创建DispatcherServletRegistrationBean 是DispatcherServlet的包装修饰类。
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME)
@ConditionalOnBean(value = DispatcherServlet.class, name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public DispatcherServletRegistrationBean dispatcherServletRegistration(DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet,
WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties, ObjectProvider<MultipartConfigElement> multipartConfig) {
DispatcherServletRegistrationBean registration = new DispatcherServletRegistrationBean(dispatcherServlet,
webMvcProperties.getServlet().getPath());
registration.setName(DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(webMvcProperties.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup());
multipartConfig.ifAvailable(registration::setMultipartConfig);
return registration;
}
}
到这里,主要的组件和配置都已经创建完成了。下面重点解读一下内置Servlet容器(Tomcat)的启动流程。
三、启动过程
3.1 SpringApplication的run方法
再次来到SpringApplication#run方法。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//创建ApplicationContext,这里是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext。不引入web时候一般是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//刷新容器,进入这个方法
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);
}
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof AbandonedRunException) {
throw ex;
}
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
if (context.isRunning()) {
Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof AbandonedRunException) {
throw ex;
}
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
refresh方法见过很多次了。
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
//钩子方法,进入这个方法
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
来到ServletWebServerApplicationContext#onrefresh方法。
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
//创建WebServer,默认是Tomcat的
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
3.2 创建Server
进入创建Server的方法。
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
StartupStep createWebServer = getApplicationStartup().start("spring.boot.webserver.create");
//创建ServletWebServerFactory的Bean,上面已经创建了TomcatServletWebServerFactory,这里直接就是getbean获取。
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
createWebServer.tag("factory", factory.getClass().toString());
// 执行ServletContextInitializer的onStartup这个监听方法。
//注意重点看这行代码.创建WebServer(Tomcat),启动Servlet容器,默认是Tomcat
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
createWebServer.end();
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerGracefulShutdown",
new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle(this.webServer));
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerStartStop",
new WebServerStartStopLifecycle(this, this.webServer));
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
而selfInitialize如下,允许在创建WebServer的时候执行onStartup监听方法,阅读ServletContextInitializer可以了解到:这个方法主要用于创建Servlet、Filter、Listener。
private void selfInitialize(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
prepareWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
registerApplicationScope(servletContext);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(getBeanFactory(), servletContext);
for (ServletContextInitializer beans : getServletContextInitializerBeans()) {
beans.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
再回到TomcatServletWebServerFactory#getWebServer方法。
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
Registry.disableRegistry();
}
//创建Tomcat
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
//添加监听器
for (LifecycleListener listener : this.serverLifecycleListeners) {
tomcat.getServer().addLifecycleListener(listener);
}
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
//注意此行代码
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
再进入TomcatWebServer的构造器。
public TomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat, boolean autoStart, Shutdown shutdown) {
Assert.notNull(tomcat, "Tomcat Server must not be null");
this.tomcat = tomcat;
this.autoStart = autoStart;
this.gracefulShutdown = (shutdown == Shutdown.GRACEFUL) ? new GracefulShutdown(tomcat) : null;
//初始化
initialize();
}
初始化方法内启动Tomcat。
private void initialize() throws WebServerException {
logger.info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + getPortsDescription(false));
synchronized (this.monitor) {
try {
addInstanceIdToEngineName();
Context context = findContext();
context.addLifecycleListener((event) -> {
if (context.equals(event.getSource()) && Lifecycle.START_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Remove service connectors so that protocol binding doesn't
// happen when the service is started.
removeServiceConnectors();
}
});
// Start the server to trigger initialization listeners
//启动tomcat
this.tomcat.start();
// We can re-throw failure exception directly in the main thread
rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions();
try {
ContextBindings.bindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(), getClass().getClassLoader());
}
catch (NamingException ex) {
// Naming is not enabled. Continue
}
// Unlike Jetty, all Tomcat threads are daemon threads. We create a
// blocking non-daemon to stop immediate shutdown
//创建等待线程
startDaemonAwaitThread();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
stopSilently();
destroySilently();
throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat", ex);
}
}
}
到这,TomcatServer就创建并启动了。
四、注册Servlet组件的相关注解(@ServletComponentScan、@WebServlet、@WebFilter以及@WebListener)的解读
4.1 简单使用
@ServletComponentScan、@WebServlet、@WebFilter以及@WebListener等注解用以添加Serlet、过滤器、监听器。
@WebServlet、@WebFilter以及@WebListener这三个注解并不是spring自身的,而是来自JakartaEE的,@ServletComponentScan用于扫描这三个注解注册的Servlet、过滤器、监听器。
先看个简单的示例:
自定义Servlet。
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/simple")
public class MySimpleServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MySimpleServlet.class);
public void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
LOGGER.info("MySimpleServlet.service()");
resp.getWriter().write("Hello,World!");
}
}
创建过滤器。
@WebFilter(urlPatterns = "/*")
public class MyFilter extends HttpFilter {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyFilter.class);
/**
* @param req a {@link ServletRequest} object that contains the request the client has made of the filter
* @param res a {@link ServletResponse} object that contains the response the filter sends to the client
* @param chain the <code>FilterChain</code> for invoking the next filter or the resource
* @throws IOException
* @throws ServletException
*/
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (!(req instanceof HttpServletRequest && res instanceof HttpServletResponse)) {
throw new ServletException("non-HTTP request or response");
}
beforeDo(req);
chain.doFilter(req, res);
afterDo(req, res);
}
/**
* 前置处理
* @param req
* @param res
*/
private void afterDo(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) {
LOGGER.info(")MyFilter.afterDo(");
}
/**
* 后置处理
* @param req
*/
private void beforeDo(ServletRequest req) {
LOGGER.info("MyFilter.beforeDo()");
}
}
创建监听器。
@WebListener(value = "MyListener")
public class MyListener implements ServletContextListener {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyListener.class);
/**
* * Notification that the web application initialization process is starting. All ServletContextListeners are
* notified of context initialization before any filter or servlet in the web application is initialized. The
* default implementation is a NO-OP.
*
* @param sce Information about the ServletContext that was initialized
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
LOGGER.info("MyListener.contextInitialized()");
}
/**
* * Notification that the servlet context is about to be shut down. All servlets and filters have been destroyed
* before any ServletContextListeners are notified of context destruction. The default implementation is a NO-OP.
*
* @param sce Information about the ServletContext that was destroyed
*/
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
LOGGER.info("MyListener.contextDestroyed()");
}
}
启动应用,执行测试。
POST http://localhost:8888/simple HTTP/1.1
content-type: text/plain;charset: utf-8
1233aabaaaaaa1123
执行结果:
2023-11-05 18:40:33,682|INFO | MyListener.java:22 |main|MyListener.contextInitialized()
2023-11-05 18:40:33,917|INFO | DirectJDKLog.java:173 |main|Starting ProtocolHandler ["http-nio-8888"]
2023-11-05 18:40:33,935|INFO | TomcatWebServer.java:220 |main|Tomcat started on port(s): 8888 (http) with context path ''
2023-11-05 18:40:33,940|INFO | StartupInfoLogger.java:57 |main|Started MySpringBootApplication in 0.962 seconds (process running for 1.36)
2023-11-05 18:40:43,631|INFO | MyFilter.java:52 |http-nio-8888-exec-1|MyFilter.beforeDo()
2023-11-05 18:40:43,631|INFO | MySimpleServlet.java:18 |http-nio-8888-exec-1|MySimpleServlet.service()
2023-11-05 18:40:43,632|INFO | MyFilter.java:44 |http-nio-8888-exec-1|)MyFilter.afterDo(
4.2 注册流程
4.2.1 Bean注册流程
首先ServletComponentScan注解引入了ServletComponentScanRegistrar,ServletComponentScanRegistrar内部注册了ServletComponentRegisteringPostProcessor。
@Import(ServletComponentScanRegistrar.class)
public @interface ServletComponentScan {
//......
}
ServletComponentScanRegistrar#addPostProcessor方法。
private void addPostProcessor(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Set<String> packagesToScan) {
ServletComponentRegisteringPostProcessorBeanDefinition definition = new ServletComponentRegisteringPostProcessorBeanDefinition(
packagesToScan);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(BEAN_NAME, definition);
}
static final class ServletComponentRegisteringPostProcessorBeanDefinition extends GenericBeanDefinition {
private final Set<String> packageNames = new LinkedHashSet<>();
ServletComponentRegisteringPostProcessorBeanDefinition(Collection<String> packageNames) {
setBeanClass(ServletComponentRegisteringPostProcessor.class);
setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
addPackageNames(packageNames);
}
@Override
public Supplier<?> getInstanceSupplier() {
return () -> new ServletComponentRegisteringPostProcessor(this.packageNames);
}
private void addPackageNames(Collection<String> additionalPackageNames) {
this.packageNames.addAll(additionalPackageNames);
}
}
ServletComponentRegisteringPostProcessor是一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,在AbstractApplicationContext#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors作为入口,注册额外的bean信息。
这里是扫描注册路径,把Servlet、过滤器、监听器的Bean信息注册到容器。
private void scanPackage(ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider componentProvider, String packageToScan) {
for (BeanDefinition candidate : componentProvider.findCandidateComponents(packageToScan)) {
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition annotatedBeanDefinition) {
for (ServletComponentHandler handler : HANDLERS) {
handler.handle(annotatedBeanDefinition, (BeanDefinitionRegistry) this.applicationContext);
}
}
}
}
如WebFilterHandler注册过滤器的Bean信息:
@Override
public void doHandle(Map<String, Object> attributes, AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.rootBeanDefinition(FilterRegistrationBean.class);
builder.addPropertyValue("asyncSupported", attributes.get("asyncSupported"));
builder.addPropertyValue("dispatcherTypes", extractDispatcherTypes(attributes));
builder.addPropertyValue("filter", beanDefinition);
builder.addPropertyValue("initParameters", extractInitParameters(attributes));
String name = determineName(attributes, beanDefinition);
builder.addPropertyValue("name", name);
builder.addPropertyValue("servletNames", attributes.get("servletNames"));
builder.addPropertyValue("urlPatterns", extractUrlPatterns(attributes));
registry.registerBeanDefinition(name, builder.getBeanDefinition());
}
到这里这三个注解注册的Bean信息就注册到容器中里了,由Spring容器创建对应的Bean实例。
4.2.2 注册为Servlet组件的注册流程
有了这三种组件的Bean实例,如何注册为Servlet组件呢?
在«SpringBoot启动流程»这篇文章中,跟踪SpringBoot启动流程中来到这行代码:
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
然后来到ServletContextInitializer初始化器起作用的这个方法。
private void selfInitialize(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
prepareWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
registerApplicationScope(servletContext);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(getBeanFactory(), servletContext);
for (ServletContextInitializer beans : getServletContextInitializerBeans()) {
beans.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
先看一下ServletContextInitializer的类关系图。
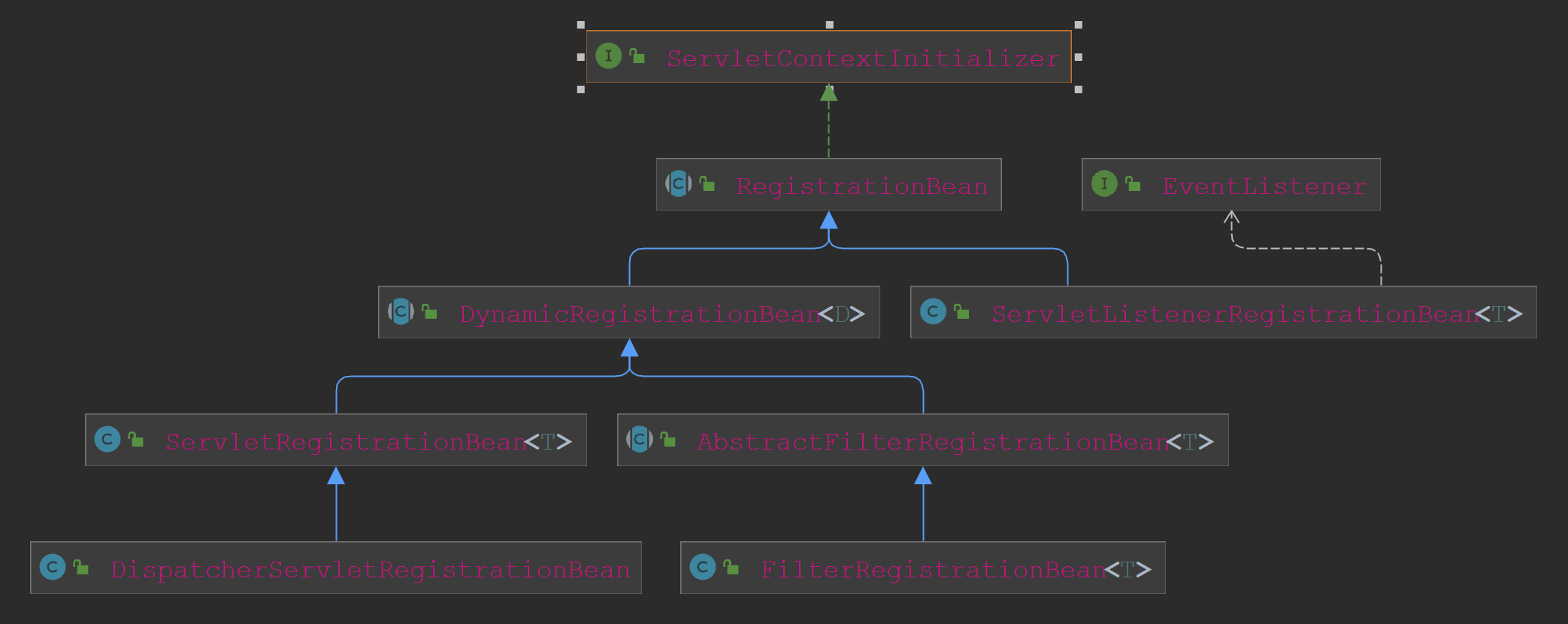
看这个图应该可以了解到这个接口主要用以注册Servlet、Filter、Listener这三类组件。
首先ServletContextInitializerBeans这边把Servlet、Filter、Listener的Bean实例转换为RegistrationBean.
public ServletContextInitializerBeans(ListableBeanFactory beanFactory,
Class<? extends ServletContextInitializer>... initializerTypes) {
this.initializers = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
this.initializerTypes = (initializerTypes.length != 0) ? Arrays.asList(initializerTypes)
: Collections.singletonList(ServletContextInitializer.class);
addServletContextInitializerBeans(beanFactory);
addAdaptableBeans(beanFactory);
this.sortedList = this.initializers.values()
.stream()
.flatMap((value) -> value.stream().sorted(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE))
.toList();
logMappings(this.initializers);
}
转换为RegistrationBean。
protected void addAdaptableBeans(ListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
MultipartConfigElement multipartConfig = getMultipartConfig(beanFactory);
addAsRegistrationBean(beanFactory, Servlet.class, new ServletRegistrationBeanAdapter(multipartConfig));
addAsRegistrationBean(beanFactory, Filter.class, new FilterRegistrationBeanAdapter());
for (Class<?> listenerType : ServletListenerRegistrationBean.getSupportedTypes()) {
addAsRegistrationBean(beanFactory, EventListener.class, (Class<EventListener>) listenerType,
new ServletListenerRegistrationBeanAdapter());
}
}
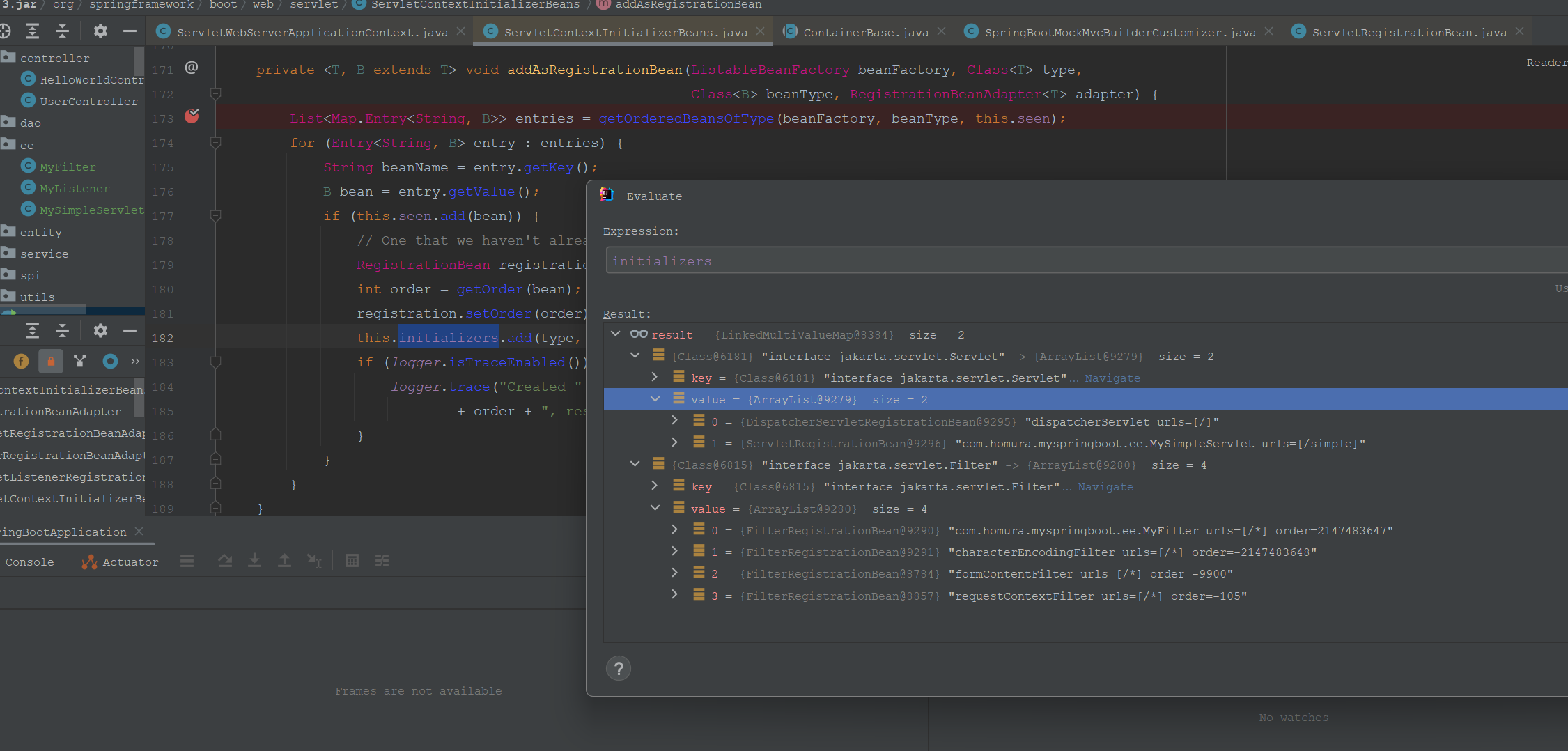
然后就是执行ServletContextInitializer#onStartup方法。
ServletContextInitializer源码如下:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ServletContextInitializer {
/**
* Configure the given {@link ServletContext} with any servlets, filters, listeners
* context-params and attributes necessary for initialization.
* @param servletContext the {@code ServletContext} to initialize
* @throws ServletException if any call against the given {@code ServletContext}
* throws a {@code ServletException}
*/
void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException;
}
继续进入RegistrationBean#onStartup方法。
@Override
public final void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
String description = getDescription();
if (!isEnabled()) {
logger.info(StringUtils.capitalize(description) + " was not registered (disabled)");
return;
}
register(description, servletContext);
}
再解读一下register方法。
@Override
protected final void register(String description, ServletContext servletContext) {
D registration = addRegistration(description, servletContext);
if (registration == null) {
if (this.ignoreRegistrationFailure) {
logger.info(StringUtils.capitalize(description) + " was not registered (possibly already registered?)");
return;
}
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Failed to register '%s' on the servlet context. Possibly already registered?"
.formatted(description));
}
configure(registration);
}
这里分为两步,注册到ServletContext和进行配置。
注册到ServletContext就是简单的servletContext.addXXX方法。
@Override
protected Dynamic addRegistration(String description, ServletContext servletContext) {
Filter filter = getFilter();
return servletContext.addFilter(getOrDeduceName(filter), filter);
}
配置组件的方法则是配置Servlet和Filter的相关属性。例如配置Filter的方法,如下:
@Override
protected void configure(FilterRegistration.Dynamic registration) {
super.configure(registration);
EnumSet<DispatcherType> dispatcherTypes = this.dispatcherTypes;
if (dispatcherTypes == null) {
T filter = getFilter();
if (ClassUtils.isPresent("org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter",
filter.getClass().getClassLoader()) && filter instanceof OncePerRequestFilter) {
dispatcherTypes = EnumSet.allOf(DispatcherType.class);
}
else {
dispatcherTypes = EnumSet.of(DispatcherType.REQUEST);
}
}
Set<String> servletNames = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (ServletRegistrationBean<?> servletRegistrationBean : this.servletRegistrationBeans) {
servletNames.add(servletRegistrationBean.getServletName());
}
servletNames.addAll(this.servletNames);
if (servletNames.isEmpty() && this.urlPatterns.isEmpty()) {
registration.addMappingForUrlPatterns(dispatcherTypes, this.matchAfter, DEFAULT_URL_MAPPINGS);
}
else {
if (!servletNames.isEmpty()) {
registration.addMappingForServletNames(dispatcherTypes, this.matchAfter,
StringUtils.toStringArray(servletNames));
}
if (!this.urlPatterns.isEmpty()) {
registration.addMappingForUrlPatterns(dispatcherTypes, this.matchAfter,
StringUtils.toStringArray(this.urlPatterns));
}
}
}
这样Filter、Dispatcher就创建成功并注册到ServletContext里。
在示例工程执行过程中,这里并没有找到MyListener这个监听器的注册流程。最后在StandardContext#listenerStart这个方法找到注册MyListener的源码。
// Instantiate the required listeners
//com.homura.myspringboot.ee.MyListener
String listeners[] = findApplicationListeners();
Object results[] = new Object[listeners.length];
boolean ok = true;
for (int i = 0; i < results.length; i++) {
if (getLogger().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLogger().debug(" Configuring event listener class '" + listeners[i] + "'");
}
try {
String listener = listeners[i];
results[i] = getInstanceManager().newInstance(listener);
} catch (Throwable t) {
t = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(t);
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardContext.applicationListener", listeners[i]), t);
ok = false;
}
}
if (!ok) {
getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardContext.applicationSkipped"));
return false;
}
// Sort listeners in two arrays
List<Object> eventListeners = new ArrayList<>();
List<Object> lifecycleListeners = new ArrayList<>();
for (Object result : results) {
if ((result instanceof ServletContextAttributeListener) ||
(result instanceof ServletRequestAttributeListener) || (result instanceof ServletRequestListener) ||
(result instanceof HttpSessionIdListener) || (result instanceof HttpSessionAttributeListener)) {
eventListeners.add(result);
}
if ((result instanceof ServletContextListener) || (result instanceof HttpSessionListener)) {
lifecycleListeners.add(result);
}
}
而findApplicationListeners()内applicationListeners监听器列表,由在创建TomcatServer配置Tomcat的Context时候的这个TomcatServletWebServerFactory#configureContext方法内注冊到Context的。 代码如下:
for (String webListenerClassName : getWebListenerClassNames()) {
context.addApplicationListener(webListenerClassName);
}
简单总结一下注册这三类组件的流程:
- ServletComponentScan注解引入的ServletComponentScanRegistrar注册了ServletComponentRegisteringPostProcessor,由ServletComponentRegisteringPostProcessor注册
WebFilter、WebListener、WebServlet注解标识的Bean。
- ServletContextInitializerBeans将其适配为XXXRegistrationBean,RegistrationBean实现了ServletContextInitializer接口。
- 创建WebServer过程中调用ServletContextInitializer的onStartup方法注册和配置Filter、Listener、Servlet等组件。
五、参考材料
1.《Spring Boot Reference Documentation》(version 3.1.5)
2.SpringBoot源码(版本3.1.3)
