本文是SpringBoot源码阅读计划的第二篇文章,本文主要介绍一下SpringBoot的启动流程。
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MySpringBootApplication.class, args);
}
主类启动代码就这样一行,本文将简单解读一下SpringApplication的创建流程和run方法。 本文源码地址为:https://github.com/zouhuanli/MySpringBoot.git。
一、SpringApplication的创建流程
跟踪run方法来到:
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
和
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this(null, primarySources);
}
进入SpringApplication的构造器方法。
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
//资源加载器
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
//加载源,这里就是MySpringBootApplication.class
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
//判断APP应用的类型,类型有;NONE-无需WEB的jar应用,SERVLET、REACTIVE-两个类型的Web应用
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
//创建初始化器
this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = new ArrayList<>(
getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class));
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//设置监听器
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
//应用主类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
我们主要分析这几个方法。
1.确定webApplicationType
确定应用类型的方法deduceFromClasspath很简单,如下:
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
//REACTIVE栈
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
//尝试加载 SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES = { "jakarta.servlet.Servlet","org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" };
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
//加载Servlet和ConfigurableWebApplicationContext都成功,返回SERVLET
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
可以看到,不引入reactive栈时候,加载DispatcherServlet和ServletContainer都成功时候应用类型是WebApplicationType.SERVLET,否则是默认的jar应用。 可以通过SpringApplication#setWebApplicationType手动设置类型,引用了web模块也可以设置为NONE类型。
2.设置初始化器
初始化器是及其重要的,在后续的各流程中会使用到这些初始化器。初始化器简单说是SpringBoot内部创建的一系列组件,在各个流程使用。
我们回顾一下《DispatcherServlet的初始化流程》这篇文章,其中的initStrategies方法:
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
上面这里从DispatcherServlet.properties文件创建默认的九大组件。
而初始化器或者说工厂组件是通过spring.factories文件来配置的,如下:
# Logging Systems
org.springframework.boot.logging.LoggingSystemFactory=\
org.springframework.boot.logging.logback.LogbackLoggingSystem.Factory,\
org.springframework.boot.logging.log4j2.Log4J2LoggingSystem.Factory,\
org.springframework.boot.logging.java.JavaLoggingSystem.Factory
# PropertySource Loaders
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=\
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertiesPropertySourceLoader,\
org.springframework.boot.env.YamlPropertySourceLoader
# ConfigData Location Resolvers
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigDataLocationResolver=\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigTreeConfigDataLocationResolver,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.StandardConfigDataLocationResolver
# ConfigData Loaders
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigDataLoader=\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigTreeConfigDataLoader,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.StandardConfigDataLoader
# Application Context Factories
org.springframework.boot.ApplicationContextFactory=\
org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.ReactiveWebServerApplicationContextFactory,\
org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContextFactory
# Run Listeners
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\
org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener
# Error Reporters
org.springframework.boot.SpringBootExceptionReporter=\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzers
# Application Context Initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.rsocket.context.RSocketPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer
# Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
org.springframework.boot.ClearCachesApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener
# Environment Post Processors
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\
org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.env.RandomValuePropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.env.SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.env.SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.reactor.DebugAgentEnvironmentPostProcessor
# Failure Analyzers
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigDataNotFoundFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.properties.IncompatibleConfigurationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.properties.NotConstructorBoundInjectionFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanCurrentlyInCreationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanDefinitionOverrideFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanNotOfRequiredTypeFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindValidationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.UnboundConfigurationPropertyFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.MutuallyExclusiveConfigurationPropertiesFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoSuchMethodFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.PortInUseFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ValidationExceptionFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyNameFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyValueFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.PatternParseFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseChangelogMissingFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.web.context.MissingWebServerFactoryBeanFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.ConnectorStartFailureAnalyzer
# Failure Analysis Reporters
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalysisReporter=\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.LoggingFailureAnalysisReporter
# Database Initializer Detectors
org.springframework.boot.sql.init.dependency.DatabaseInitializerDetector=\
org.springframework.boot.flyway.FlywayDatabaseInitializerDetector,\
org.springframework.boot.jdbc.init.DataSourceScriptDatabaseInitializerDetector,\
org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseDatabaseInitializerDetector,\
org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.JpaDatabaseInitializerDetector,\
org.springframework.boot.r2dbc.init.R2dbcScriptDatabaseInitializerDetector
# Depends On Database Initialization Detectors
org.springframework.boot.sql.init.dependency.DependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector=\
org.springframework.boot.sql.init.dependency.AnnotationDependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector,\
org.springframework.boot.jdbc.SpringJdbcDependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector,\
org.springframework.boot.jooq.JooqDependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector,\
org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.JpaDependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector
这里创建初始化器/工厂组件与其相似,从“META-INF/spring.factories”读取初始化器/工厂组件的默认实现策略,在获取初始器时候进行实例化。
我们跟踪getSpringFactoriesInstances方法来到:
//FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION="META-INF/spring.factories"
public static SpringFactoriesLoader forDefaultResourceLocation(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
return forResourceLocation(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION, classLoader);
}
这里加载了spring.factories的所有配置。继续进入这两个方法:
public static SpringFactoriesLoader forResourceLocation(String resourceLocation, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.hasText(resourceLocation, "'resourceLocation' must not be empty");
ClassLoader resourceClassLoader = (classLoader != null ? classLoader :
SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader());
Map<String, SpringFactoriesLoader> loaders = cache.computeIfAbsent(
resourceClassLoader, key -> new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<>());
return loaders.computeIfAbsent(resourceLocation, key ->
new SpringFactoriesLoader(classLoader, loadFactoriesResource(resourceClassLoader, resourceLocation)));
}
protected static Map<String, List<String>> loadFactoriesResource(ClassLoader classLoader, String resourceLocation) {
Map<String, List<String>> result = new LinkedHashMap<>();
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(resourceLocation);
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(urls.nextElement());
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
properties.forEach((name, value) -> {
String[] factoryImplementationNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) value);
List<String> implementations = result.computeIfAbsent(((String) name).trim(),
key -> new ArrayList<>(factoryImplementationNames.length));
Arrays.stream(factoryImplementationNames).map(String::trim).forEach(implementations::add);
});
}
result.replaceAll(SpringFactoriesLoader::toDistinctUnmodifiableList);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" + resourceLocation + "]", ex);
}
return Collections.unmodifiableMap(result);
}
其解析的配置的类型列表如下:
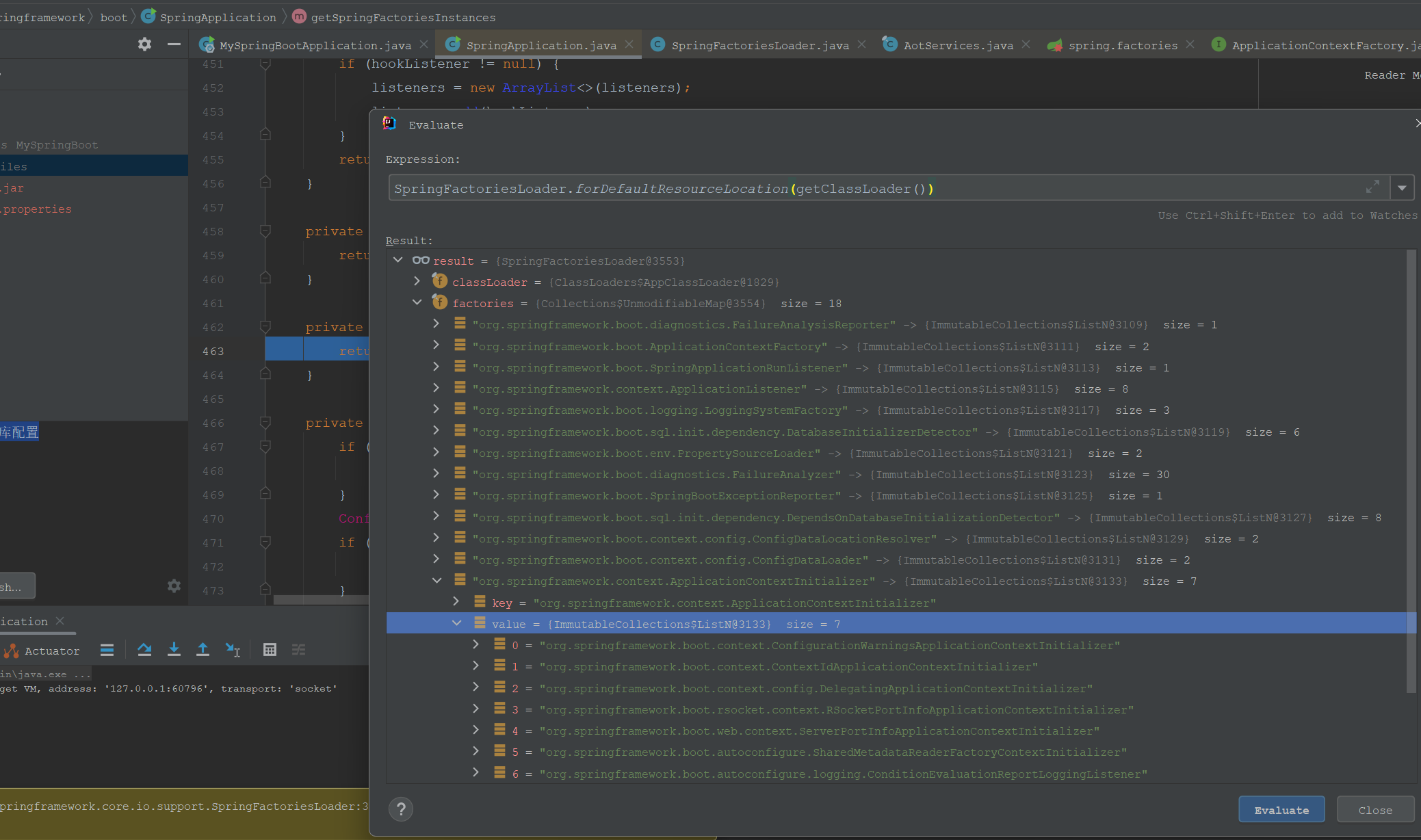
和spring.factories配置信息一致,这里只是加载了spring.factories配置信息,并没有真正创建某一个工厂类的实例。
创建工厂类的实例是通过load方法去懒加载来创建的,实际用到了哪个类型才创建,和Java SPI一样。
load方法如下:
//创建一个类型的,配置中的所有对应的实现类的实例
public <T> List<T> load(Class<T> factoryType, @Nullable ArgumentResolver argumentResolver,
@Nullable FailureHandler failureHandler) {
Assert.notNull(factoryType, "'factoryType' must not be null");
List<String> implementationNames = loadFactoryNames(factoryType);
logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Loaded [%s] names: %s", factoryType.getName(), implementationNames));
List<T> result = new ArrayList<>(implementationNames.size());
FailureHandler failureHandlerToUse = (failureHandler != null) ? failureHandler : THROWING_FAILURE_HANDLER;
for (String implementationName : implementationNames) {
T factory = instantiateFactory(implementationName, factoryType, argumentResolver, failureHandlerToUse);
if (factory != null) {
result.add(factory);
}
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(result);
return result;
}
继续阅读是使用反射创建对应对象的,不再深入解读。
而Java SPI是”Service Provider Interface”,是Java自带的服务拓展加载和发现机制,允许一个接口的实现类型从配置文件加载、解析,从而创建实现对象。
例如,定义一个接口:
/**
* 一个正常的接口
*/
public interface TestSpiInterface {
/**
* 测试方法
*/
void test();
}
以及三个实现类:
/**
* 实现类,可以是多个,可以不是本工程或者包,允许从第三方jar包中获取
*/
public class TestSpiInterfaceA implements TestSpiInterface {
@Override
public void test() {
System.out.println("TestSpiInterfaceA");
}
}
/**
* 实现类,可以是多个,可以不是本工程或者包,允许从第三方jar包中获取
*/
public class TestSpiInterfaceB implements TestSpiInterface {
@Override
public void test() {
System.out.println("TestSpiInterfaceB");
}
}
/**
* 实现类,可以是多个,可以不是本工程或者包,允许从第三方jar包中获取
*/
public class TestSpiInterfaceC implements TestSpiInterface {
@Override
public void test() {
System.out.println("TestSpiInterfaceC");
}
}
创建META-INF.services.com.homura.myspringboot.spi.TestSpiInterface文件,如下:
com.homura.myspringboot.spi.impl.TestSpiInterfaceA
com.homura.myspringboot.spi.impl.TestSpiInterfaceC
测试主类如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 通过ServiceLoader加载实现类
ServiceLoader<TestSpiInterface> serviceLoader = ServiceLoader.load(TestSpiInterface.class);
for (TestSpiInterface testSpiInterface : serviceLoader) {
testSpiInterface.test();
}
}
输出结果:
TestSpiInterfaceA
TestSpiInterfaceC
SPI机制允许第三方实现拓展然后加入配置文件,增加了获得拓展的动态性。
有的文章说到SpringFactoriesLoader也是SPI机制,这里不做过多比较和解读。
3.设置监听器
设置监听器和上面设置BootstrapRegistryInitializer、ApplicationContextInitializer是一样的,仅仅是加载拓展的类型不一样,也是SpringFactoriesLoader从spring.factories
加载ApplicationListener拓展的实现类型列表,要注意的是spring.factories整个配置列表只会加载一次,后续需要哪种拓展类型的实现类型直接进入load就行。
deduceMainApplicationClass是确定主类,这里mainApplicationClass=MySpringBootApplication.class。
现在SpringApplication创建完成了,接下来解读run方法,应用的启动方法。
二、SpringApplication#run方法
在解读run方法启动方法之前,我们简单回顾一下«AnnotationConfigApplicationContext初始化流程»和
«BeanFactoryPostProcessor解读»这两篇文章。
在AnnotationConfigApplicationContext初始化流程这里,我们知道ApplicationContext首先注册了应用启动的配置类AppConfig这个Bean,然后在refresh流程的中的invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors使用ConfigurationClassPostProcessor去解析和注册注解配置的bean,期间用到了ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader、AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader、ConfigurationClassParser、ComponentScanAnnotationParser、ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser等类去解析对应注解以及引入的注解配置的Bean。
因此,可以这里推断SpringBoot启动的ApplicationContext也是类似AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,也应是在invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法内通过ConfigurationClassPostProcessor实现注解配置的Bean的注册流程。
此外,因为WEB项目是默认创建内嵌的tomcat容器,run方法启动代码中也应该创建tomcat容器。
下面开始解读run方法。
1.创建BootstrapContext
创建启动上下文这个方法很简单,就是启动注册的bootstrapRegistryInitializers的初始化方法。
private DefaultBootstrapContext createBootstrapContext() {
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = new DefaultBootstrapContext();
this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers.forEach((initializer) -> initializer.initialize(bootstrapContext));
return bootstrapContext;
}
2.获得监听器和启动监听器
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
ArgumentResolver argumentResolver = ArgumentResolver.of(SpringApplication.class, this);
argumentResolver = argumentResolver.and(String[].class, args);
List<SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class,
argumentResolver);
SpringApplicationHook hook = applicationHook.get();
SpringApplicationRunListener hookListener = (hook != null) ? hook.getRunListener(this) : null;
if (hookListener != null) {
listeners = new ArrayList<>(listeners);
listeners.add(hookListener);
}
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger, listeners, this.applicationStartup);
}
这里的监听器依赖是从SpringFactoriesLoader读取到spring.factories去实例化,这里默认注册的监听器是EventPublishingRunListener。
然后是调用监听器的starting方法:
void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, Class<?> mainApplicationClass) {
doWithListeners("spring.boot.application.starting", (listener) -> listener.starting(bootstrapContext),
(step) -> {
if (mainApplicationClass != null) {
step.tag("mainApplicationClass", mainApplicationClass.getName());
}
});
}
3.准备环境
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
//创建环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
//配置环境
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
//发布监听事件:环境已准备好
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
Assert.state(!environment.containsProperty("spring.main.environment-prefix"),
"Environment prefix cannot be set via properties.");
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
EnvironmentConverter environmentConverter = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader());
environment = environmentConverter.convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
跟踪environmentPrepared方法,来到下面代码:
@Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
multicastInitialEvent(
new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(bootstrapContext, this.application, this.args, environment));
}
这里发布了ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent这个事件,我们继续查找一下使用了这个事件的监听器,来到EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener,来到下面方法:
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent environmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(environmentPreparedEvent);
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent();
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationFailedEvent) {
onApplicationFailedEvent();
}
}
继续进入onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent方法:
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = event.getEnvironment();
SpringApplication application = event.getSpringApplication();
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : getEnvironmentPostProcessors(application.getResourceLoader(),
event.getBootstrapContext())) {
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(environment, application);
}
}
在来到ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor#postProcessEnvironment方法
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
postProcessEnvironment(environment, application.getResourceLoader(), application.getAdditionalProfiles());
}
继续进入发现创建了ConfigDataEnvironment这个对象,这个类型是项目配置的类,其在下面代码设置了默认扫描配置文件的路径。
static {
List<ConfigDataLocation> locations = new ArrayList<>();
locations.add(ConfigDataLocation.of("optional:classpath:/;optional:classpath:/config/"));
locations.add(ConfigDataLocation.of("optional:file:./;optional:file:./config/;optional:file:./config/*/"));
DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS = locations.toArray(new ConfigDataLocation[0]);
}
4.createApplicationContext创建容器和上下文
createApplicationContext方法只是按照应用类型创建ApplicationContext上下文对象。 在解读ApplicationContext整体结构的文章中有提及到主要有两类的上下文,一类是refreshable的可以刷新的,一类是generic不刷新的。而示例工程是一个Web项目因此创建的ApplicationContext应该是generic的子类,应该是基于注解的AnnotationWebXXXContext这样的。 跟踪测试流程发现这里创建的是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext(名字好长啊),其类关系图如下:
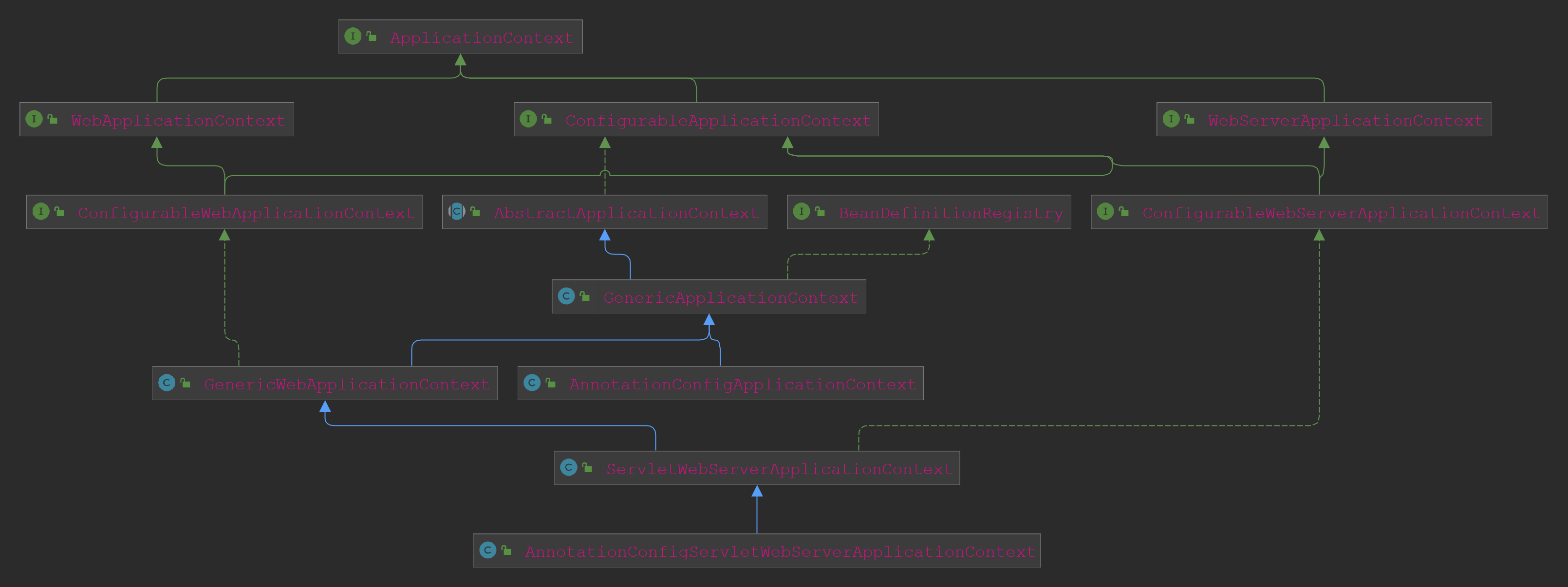
可以看到这里boot对标准Spring的ApplicationContext做了一些拓展和定制化。而手动设置应用类型为NONE,普通的标准Java应用自然是上下文对象是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。
5.prepareContext准备上下文
准备上下文是在context的刷新方法之前做一下前置处理。
private void prepareContext(DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
//设置环境
context.setEnvironment(environment);
//一些后置处理
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
//aot相关
addAotGeneratedInitializerIfNecessary(this.initializers);
//初始化器的初始化方法
applyInitializers(context);
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
bootstrapContext.close(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
//注册相关Bean
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory autowireCapableBeanFactory) {
autowireCapableBeanFactory.setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences);
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory listableBeanFactory) {
listableBeanFactory.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new PropertySourceOrderingBeanFactoryPostProcessor(context));
if (!AotDetector.useGeneratedArtifacts()) {
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
//注意看这行代码,注册启动类,也就是MySpringBootApplication这个类,和AnnotationConfigApplicationContext注册启动主配置类一样。
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
}
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
我们继续跟踪BeanDefinitionLoader#load方法,如下:
private void load(Object source) {
Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null");
if (source instanceof Class<?> clazz) {
load(clazz);
return;
}
if (source instanceof Resource resource) {
load(resource);
return;
}
if (source instanceof Package pack) {
load(pack);
return;
}
if (source instanceof CharSequence sequence) {
load(sequence);
return;
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid source type " + source.getClass());
}
BeanDefinitionLoader是融合读取XML的bean配置,注解的Bean配置(Component、@Configuration、@Bean等),以及groovy配置这三种的综合型的读取器。
然后进入AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader的注册方法,注册主配置类MySpringBootApplication到容器BeanFactory中,存入beanDefinitionMap。
这里只注册了主配置类和一些框架本身的基础设施类,尚未没有开始注册应用的全部的bean ,如下。
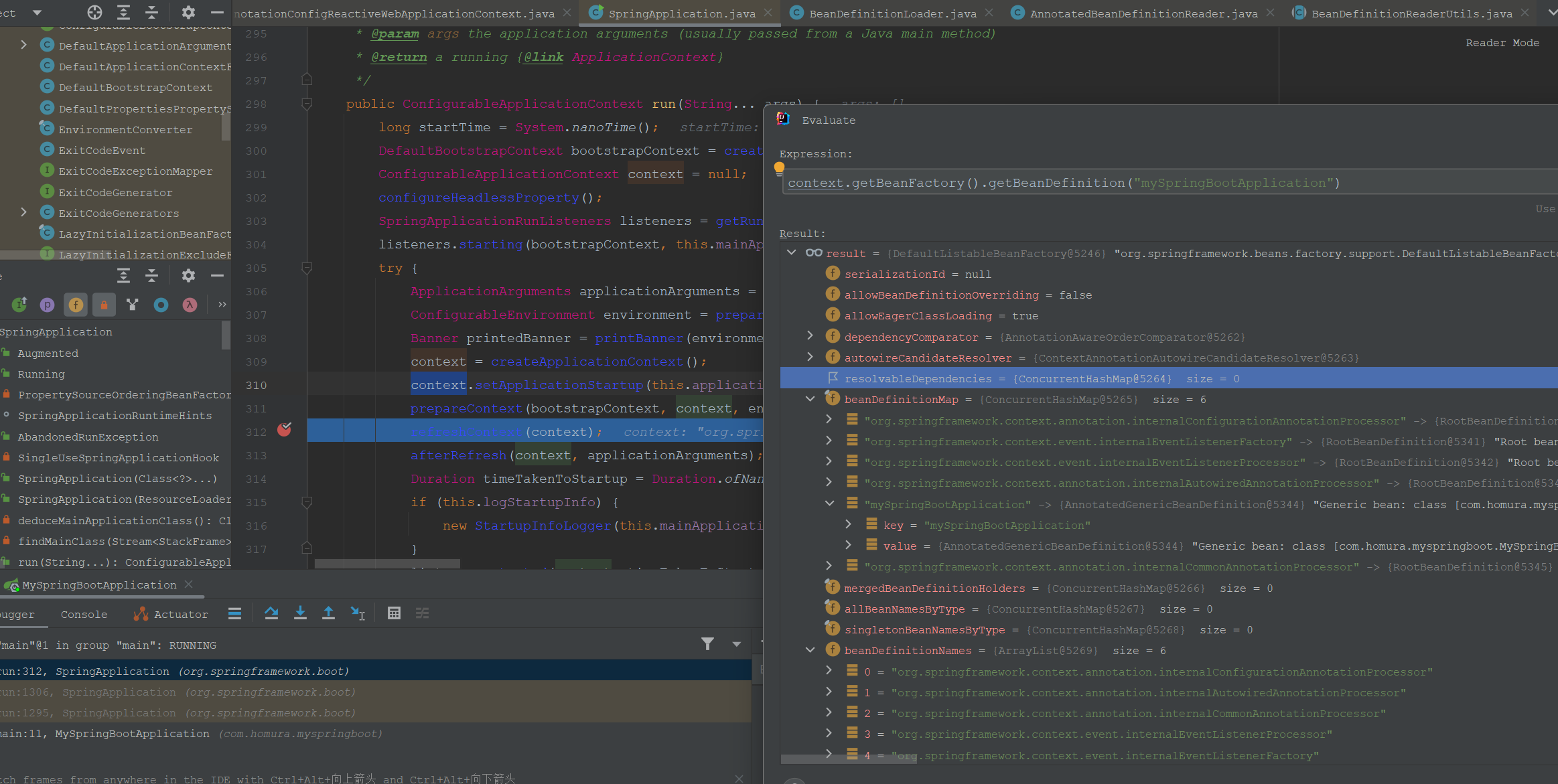
应用内其他的Bean是在refresh方法内部的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法通过ConfigurationClassPostProcessor去注册的。
6.refresh刷新容器
refresh方法就是AbstractApplicationContext的刷新方法,是销毁旧容器、创建和配置新容器,刷新整个应用下文的方法。这里额外注册了关闭钩子。
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
shutdownHook.registerApplicationContext(context);
}
refresh(context);
}
refresh方法这里不再过多解读,其基本方法如下:
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
refresh方法是创建上下文和容器及其核心的方法,笔者的多个文章有涉及这个方法。读者可以参考阅读一下这篇文章“Spring IoC容器初始化流程”。 下面笔者解读一下和boot有关联的两个方法。
6.1 特别点1:onRefresh方法
默认的onRefresh方法是一个空方法。
/**
* Template method which can be overridden to add context-specific refresh work.
* Called on initialization of special beans, before instantiation of singletons.
* <p>This implementation is empty.
* @throws BeansException in case of errors
* @see #refresh()
*/
protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException {
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
}
我们进入AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext的父类ServletWebServerApplicationContext,有重写这个方法:
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
这里创建了内嵌的WebServer。
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
StartupStep createWebServer = getApplicationStartup().start("spring.boot.webserver.create");
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
createWebServer.tag("factory", factory.getClass().toString());
//创建WebServer
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
createWebServer.end();
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerGracefulShutdown",
new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle(this.webServer));
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerStartStop",
new WebServerStartStopLifecycle(this, this.webServer));
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
框架提供的Sever类型有JettyWebServer、NettyWebServer、TomcatWebServer、UndertowServletWebServer、UndertowWebServer,示例工程的Server是TomcatWebServer。
6.2 特别点2:invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法
这个方法invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors笔者提及到多次了,方法内使用BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)完成了注解配置Bean的解析和注册。
/**
* Build and validate a configuration model based on the registry of
* {@link Configuration} classes.
*/
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (beanDef.getAttribute(ConfigurationClassUtils.CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);
}
}
else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));
}
}
// Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found
if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// Sort by previously determined @Order value, if applicable
configCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> {
int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition());
int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition());
return Integer.compare(i1, i2);
});
// Detect any custom bean name generation strategy supplied through the enclosing application context
SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null;
if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry _sbr) {
sbr = _sbr;
if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) {
BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(
AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR);
if (generator != null) {
this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator;
this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator;
}
}
}
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
}
// Parse each @Configuration class
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
//配置类候选集,在上面checkConfigurationClassCandidate通过@Configuration注解去判断,@SpringBootApplication内含了@Configuration注解
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);
Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());
do {
StartupStep processConfig = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.config-classes.parse");
//注意这行代码。从一个配置类解析相关的所有Bean信息。
parser.parse(candidates);
parser.validate();
Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);
// Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content
if (this.reader == null) {
this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
processConfig.tag("classCount", () -> String.valueOf(configClasses.size())).end();
candidates.clear();
if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {
String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Set<String> oldCandidateNames = Set.of(candidateNames);
Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();
for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {
BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
!alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {
candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));
}
}
}
candidateNames = newCandidateNames;
}
}
while (!candidates.isEmpty());
// Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classes
if (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) {
sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
// Store the PropertySourceDescriptors to contribute them Ahead-of-time if necessary
this.propertySourceDescriptors = parser.getPropertySourceDescriptors();
if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory cachingMetadataReaderFactory) {
// Clear cache in externally provided MetadataReaderFactory; this is a no-op
// for a shared cache since it'll be cleared by the ApplicationContext.
cachingMetadataReaderFactory.clearCache();
}
}
然后来到这个方法,这里解析了各种注解引入的Bean信息,也包含ComponentScan路径扫描的:
/**
* Apply processing and build a complete {@link ConfigurationClass} by reading the
* annotations, members and methods from the source class. This method can be called
* multiple times as relevant sources are discovered.
* @param configClass the configuration class being build
* @param sourceClass a source class
* @return the superclass, or {@code null} if none found or previously processed
*/
@Nullable
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass, Predicate<String> filter)
throws IOException {
if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) {
// Recursively process any member (nested) classes first
processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
}
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {
if (this.propertySourceRegistry != null) {
this.propertySourceRegistry.processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
else {
logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() +
"]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");
}
}
// Process any @ComponentScan annotations
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
}
// Process any @Import annotations
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), filter, true);
// Process any @ImportResource annotations
AnnotationAttributes importResource =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class);
if (importResource != null) {
String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations");
Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader> readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader");
for (String resource : resources) {
String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource);
configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass);
}
}
// Process individual @Bean methods
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
// Process default methods on interfaces
processInterfaces(configClass, sourceClass);
// Process superclass, if any
if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) {
String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName();
if (superclass != null && !superclass.startsWith("java") &&
!this.knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) {
this.knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass);
// Superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recurse
return sourceClass.getSuperClass();
}
}
// No superclass -> processing is complete
return null;
}
7.afterRefresh钩子方法
afterRefresh方法是一个空方法,作为拓展点。
/**
* Called after the context has been refreshed.
* @param context the application context
* @param args the application arguments
*/
protected void afterRefresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
}
8.started监听事件
这里是发布监听事件,执行监听器对应的监听方法。
void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Duration timeTaken) {
doWithListeners("spring.boot.application.started", (listener) -> listener.started(context, timeTaken));
}
9.执行runners
执行注册过的runner,有ApplicationRunner、CommandLineRunner两类。
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner applicationRunner) {
callRunner(applicationRunner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner) {
callRunner(commandLineRunner, args);
}
}
}
至此,启动流程基本分析一遍,要重关注spring.factories这里面的工厂类注册信息和作用、SpringBoot的ApplicationContext对基本ApplicationContext的拓展,以及refresh刷新容器的方法。
四、参考材料
1.《Spring Boot Reference Documentation》(version 3.1.5)
2.SpringBoot源码(版本3.1.3)
