本文是Spring源码阅读计划的第二十二篇文章,本文在上一篇文章的基础上解读Spring WebFlux的请求处理流程。
在上一篇文章中我们分析到WebFlux或者说Gateway底层使用Netty接受客户端请求连接,MainReactor是ServerChannel不断accept获得客户端连接,再将客户端连接注册到SubReactor,由SubReactor负责具体客户端连接Chanel的整个IO事件处理。
对上层开发者,Netty暴露的主要API就是ChannelHandler。本文也会从ChannelHandler作为分析起点分析整个请求的处理流程。
一、NettyWebServer和ChannelHandler
上一篇文章的NettyServer的Bind方法如下:
@Override
public Mono<? extends DisposableServer> bind(ServerBootstrap b) {
SslProvider ssl = SslProvider.findSslSupport(b);
if (ssl != null && ssl.getDefaultConfigurationType() == null) {
ssl = SslProvider.updateDefaultConfiguration(ssl, SslProvider.DefaultConfigurationType.TCP);
SslProvider.setBootstrap(b, ssl);
}
if (b.config()
.group() == null) {
TcpServerRunOn.configure(b, LoopResources.DEFAULT_NATIVE, TcpResources.get());
}
return Mono.create(sink -> {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = b.clone();
ConnectionObserver obs = BootstrapHandlers.connectionObserver(bootstrap);
ConnectionObserver childObs =
BootstrapHandlers.childConnectionObserver(bootstrap);
ChannelOperations.OnSetup ops =
BootstrapHandlers.channelOperationFactory(bootstrap);
convertLazyLocalAddress(bootstrap);
BootstrapHandlers.finalizeHandler(bootstrap, ops, new ChildObserver(childObs));
ChannelFuture f = bootstrap.bind();
DisposableBind disposableServer = new DisposableBind(sink, f, obs, bootstrap);
f.addListener(disposableServer);
sink.onCancel(disposableServer);
});
}
我们注意这行代码“BootstrapHandlers.finalizeHandler(bootstrap, ops, new ChildObserver(childObs));” 里面是添加了BootstrapInitializerHandler这样的初始的ChannelHandler。我们进入其方法。
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
static final class BootstrapInitializerHandler extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
//ChannelPipeline
final BootstrapPipelineHandler pipeline;
//监听器
final ConnectionObserver listener;
final ChannelOperations.OnSetup opsFactory;
BootstrapInitializerHandler(@Nullable BootstrapPipelineHandler pipeline,
ChannelOperations.OnSetup opsFactory,
ConnectionObserver listener) {
this.pipeline = pipeline;
this.opsFactory = opsFactory;
this.listener = listener;
}
//注意这个方法
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) {
if (pipeline != null) {
for (PipelineConfiguration pipelineConfiguration : pipeline) {
pipelineConfiguration.consumer.accept(listener, ch);
}
}
ChannelOperations.addReactiveBridge(ch, opsFactory, listener);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(format(ch, "Initialized pipeline {}"), ch.pipeline().toString());
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(cause);
}
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ctx.fireChannelInactive();
}
}
这里重点看这个initChannel方法,特别是这行“ChannelOperations.addReactiveBridge(ch, opsFactory, listener);”
/**
* Add {@link NettyPipeline#ReactiveBridge} handler at the end of {@link Channel}
* pipeline. The bridge will buffer outgoing write and pass along incoming read to
* the current {@link ChannelOperations#get(Channel)}.
*
* @param ch the channel to bridge
* @param opsFactory the operations factory to invoke on channel active
* @param listener the listener to forward connection events to
*/
public static void addReactiveBridge(Channel ch, OnSetup opsFactory, ConnectionObserver listener) {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast(NettyPipeline.ReactiveBridge, new ChannelOperationsHandler(opsFactory, listener));
}
这里在pipeline的尾部添加ChannelOperationsHandler,ChannelOperationsHandler里面包含了一个监听器。因为ChannelOperationsHandler是InBound的,所以是比管道里面的其他ChannelHandler最后之后才执行的。
然后这里需要特别注意的是监听器的类型,和其内部的handler。其内部的Handler处理请求,经过层层转派最终到DispatcherHandler去处理。
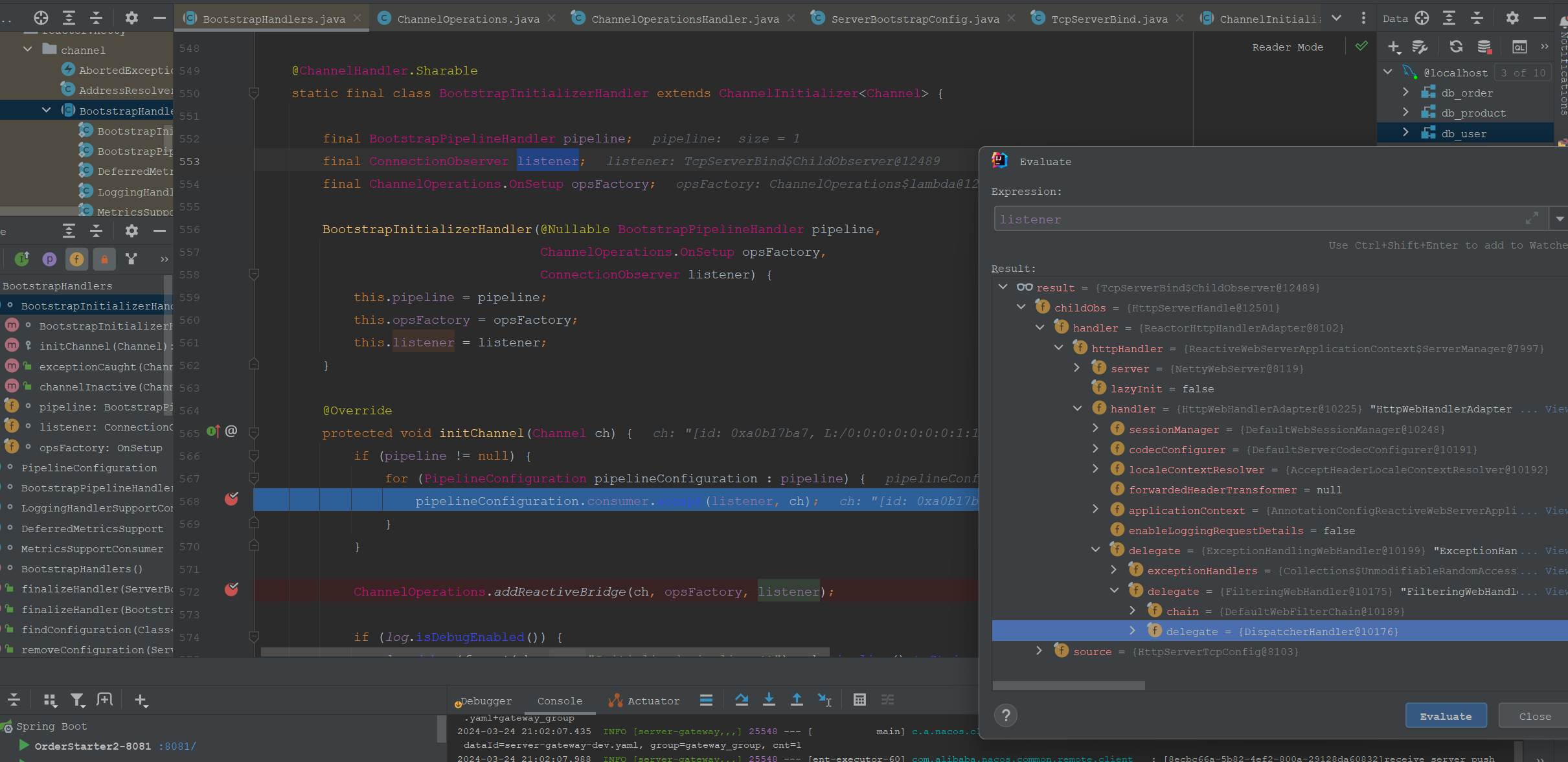
通过上面的源码分析,我们知道了请求会转发给listener监听器去处理。我们继续深入。
二、ReactiveServerHandler-响应式服务器处理器
2.1 ConnectionObserver-连接监听器
监听器主要是监听检测了连接的状态并进行相应的回调。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ConnectionObserver {
/**
* Return a noop connection listener
*
* @return a noop connection listener
*/
static ConnectionObserver emptyListener(){
return ReactorNetty.NOOP_LISTENER;
}
/**
* Connection listener {@link Context}
*
* @return current {@link Context} or {@link Context#empty()}
*/
default Context currentContext(){
return Context.empty();
}
/**
* React on connection fatal error, will request a disconnecting state
* change by default. It should only catch exceptions that can't be consumed by a
* {@link NettyInbound#receive} subscriber.
*
* @param connection the remote connection
* @param error the failing cause
*/
default void onUncaughtException(Connection connection, Throwable error) {
onStateChange(connection, State.DISCONNECTING);
}
/**
* React on connection state change (e.g. http request or response)
*
* @param connection the connection reference
* @param newState the new State
*/
void onStateChange(Connection connection, State newState);
/**
* Chain together another {@link ConnectionObserver}
*
* @param other the next {@link ConnectionObserver}
*
* @return a new composite {@link ConnectionObserver}
*/
default ConnectionObserver then(ConnectionObserver other) {
return ReactorNetty.compositeConnectionObserver(this, other);
}
/**
* A marker interface for various state signals used in {@link #onStateChange(Connection, State)}
* <p>
* Specific protocol might implement more state type for instance
* request/response lifecycle.
*/
interface State {
/**
* Propagated when a connection has been established and is available
*/
State CONNECTED = ReactorNetty.CONNECTED;
/**
* Propagated when a connection is bound to a channelOperation and ready for
* user interaction
*/
State CONFIGURED = ReactorNetty.CONFIGURED;
/**
* Propagated when a connection has been reused / acquired
* (keep-alive or pooling)
*/
State ACQUIRED = ReactorNetty.ACQUIRED;
/**
* Propagated when a connection has been released but not fully closed
* (keep-alive or pooling)
*/
State RELEASED = ReactorNetty.RELEASED;
/**
* Propagated when a connection is being fully closed
*/
State DISCONNECTING = ReactorNetty.DISCONNECTING;
}
}
我们进入其中的一个实现类HttpServerHandle,其状态监听方法onStateChange如下:
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("FutureReturnValueIgnored")
public void onStateChange(Connection connection, State newState) {
if (newState == HttpServerState.REQUEST_RECEIVED) {
try {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(format(connection.channel(), "Handler is being applied: {}"), handler);
}
HttpServerOperations ops = (HttpServerOperations) connection;
Mono.fromDirect(handler.apply(ops, ops))
.subscribe(ops.disposeSubscriber());
}
catch (Throwable t) {
log.error(format(connection.channel(), ""), t);
//"FutureReturnValueIgnored" this is deliberate
connection.channel()
.close();
}
}
}
这里处理REQUEST_RECEIVED(已收到请求)状态。这里最核心的就是这行代码“Mono.fromDirect(handler.apply(ops, ops)).subscribe(ops.disposeSubscriber());”,这里是交给handler处理。
然后这里我们调试一下,可以看到HttpServerOperations这个对象是包含request和response的复合对象:
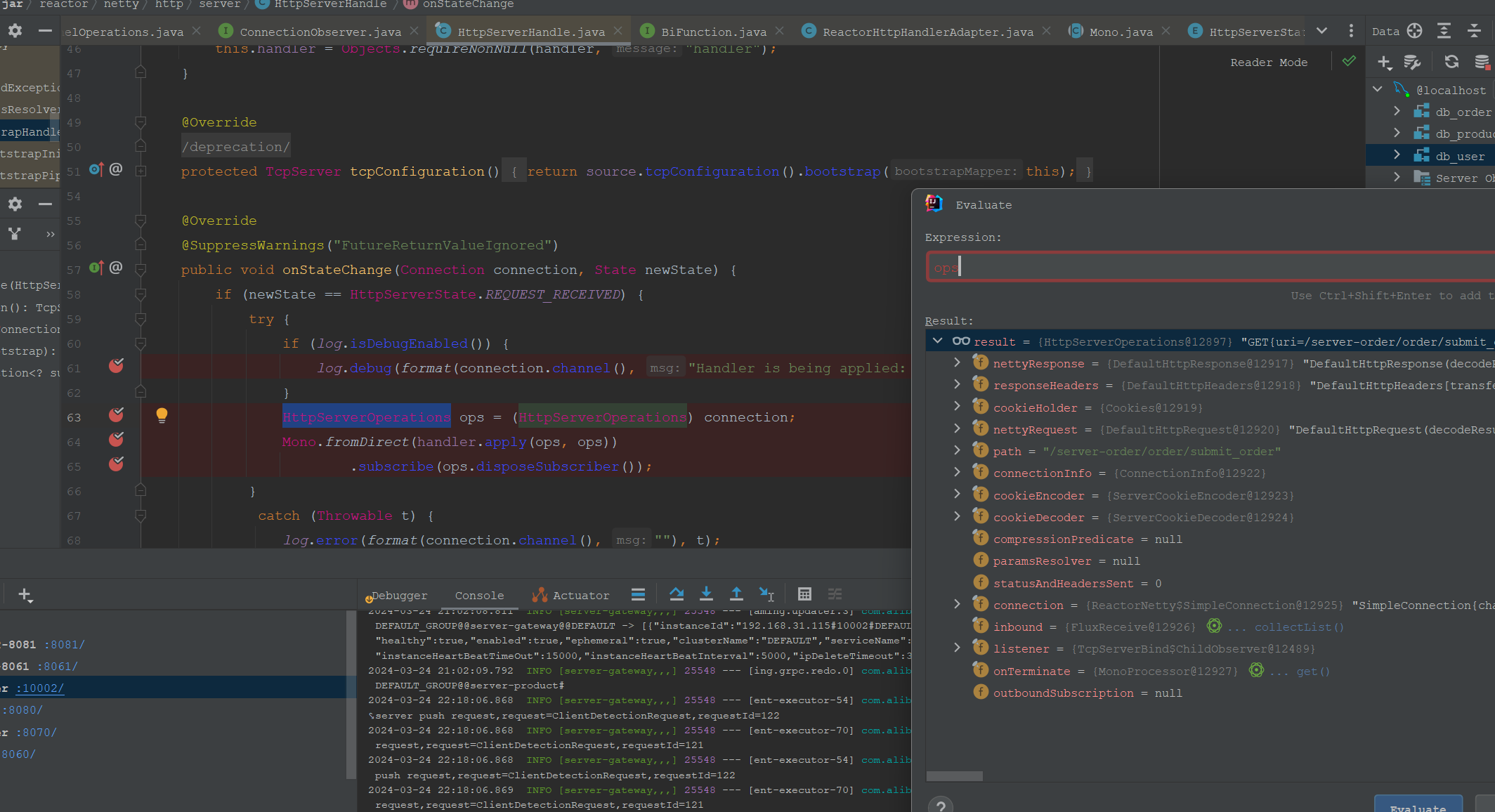
这和SpringMVC+tomcat由底层web容器tomcat创建request和response对象是很像的。然后需要注意的是这里request和response对象就不是Servlet标准的。
2.2 HttpHandler-Http处理器
上面的handler是ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter,我们继续来到这个类型。ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter的apply方法如下:
@Override
public Mono<Void> apply(HttpServerRequest reactorRequest, HttpServerResponse reactorResponse) {
NettyDataBufferFactory bufferFactory = new NettyDataBufferFactory(reactorResponse.alloc());
try {
ReactorServerHttpRequest request = new ReactorServerHttpRequest(reactorRequest, bufferFactory);
ServerHttpResponse response = new ReactorServerHttpResponse(reactorResponse, bufferFactory);
if (request.getMethod() == HttpMethod.HEAD) {
response = new HttpHeadResponseDecorator(response);
}
return this.httpHandler.handle(request, response)
.doOnError(ex -> logger.trace(request.getLogPrefix() + "Failed to complete: " + ex.getMessage()))
.doOnSuccess(aVoid -> logger.trace(request.getLogPrefix() + "Handling completed"));
}
}
这里还是主要将请求转派给HttpHandler处理。这里的handler是ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext$ServerManager这个内部类。
static final class ServerManager implements HttpHandler {
private final WebServer server;
private final boolean lazyInit;
private volatile HttpHandler handler;
private ServerManager(ReactiveWebServerFactory factory, boolean lazyInit) {
this.handler = this::handleUninitialized;
this.server = factory.getWebServer(this);
this.lazyInit = lazyInit;
}
private Mono<Void> handleUninitialized(ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The HttpHandler has not yet been initialized");
}
@Override
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) {
return this.handler.handle(request, response);
}
//......
}
分析其源码,请求也是转派给内部的handler对象。而这个内部的handler对象是类型是HttpWebHandlerAdapter,我们进入这个类型,其handle方法如下:
@Override
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) {
if (this.forwardedHeaderTransformer != null) {
try {
request = this.forwardedHeaderTransformer.apply(request);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to apply forwarded headers to " + formatRequest(request), ex);
}
response.setStatusCode(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
return response.setComplete();
}
}
ServerWebExchange exchange = createExchange(request, response);
LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn ->
exchange.getLogPrefix() + formatRequest(exchange.getRequest()) +
(traceOn ? ", headers=" + formatHeaders(exchange.getRequest().getHeaders()) : ""));
return getDelegate().handle(exchange)
.doOnSuccess(aVoid -> logResponse(exchange))
.onErrorResume(ex -> handleUnresolvedError(exchange, ex))
.then(Mono.defer(response::setComplete));
}
可以看到这里首先是创建ServerWebExchange对象,然后还是转发给内部的handler去处理,这里的handler是WebHandler类型。并且提交handler处理后也注册了doOnSuccess、onErrorResume等回调。
HttpWebHandlerAdapter的父类型WebHandlerDecorator是WebHandler类型delegate的修饰对象,因此我们需要继续进入目标对象delegate。
public class WebHandlerDecorator implements WebHandler {
private final WebHandler delegate;
/**
* Create a {@code WebHandlerDecorator} for the given delegate.
* @param delegate the WebHandler delegate
*/
public WebHandlerDecorator(WebHandler delegate) {
Assert.notNull(delegate, "'delegate' must not be null");
this.delegate = delegate;
}
/**
* Return the wrapped delegate.
*/
public WebHandler getDelegate() {
return this.delegate;
}
@Override
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
return this.delegate.handle(exchange);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return getClass().getSimpleName() + " [delegate=" + this.delegate + "]";
}
}
2.3 WebHandler-Web处理器
delegate对象是类型是ExceptionHandlingWebHandler,其内部包含一组异常处理器WebExceptionHandler。其handle方法如下:
@Override
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
Mono<Void> completion;
try {
completion = super.handle(exchange);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
completion = Mono.error(ex);
}
for (WebExceptionHandler handler : this.exceptionHandlers) {
completion = completion.onErrorResume(ex -> handler.handle(exchange, ex));
}
return completion;
}
可以看到这里主要是在正常请求处理之后进行异常处理器的统一处理。
ExceptionHandlingWebHandler其内部也包含一个委派类,其委派类delegate是FilteringWebHandler 。
FilteringWebHandler继承WebHandlerDecorator,那内部也应该持有一个目标类型的委派类,然后看名字应该持有一个过滤器链表。
FilteringWebHandler源码如下,其内部的handle方法是通过过滤器链来链式调用过滤器的handle方法层层过滤的。
public class FilteringWebHandler extends WebHandlerDecorator {
private final DefaultWebFilterChain chain;
/**
* Constructor.
* @param filters the chain of filters
*/
public FilteringWebHandler(WebHandler handler, List<WebFilter> filters) {
super(handler);
this.chain = new DefaultWebFilterChain(handler, filters);
}
/**
* Return a read-only list of the configured filters.
*/
public List<WebFilter> getFilters() {
return this.chain.getFilters();
}
@Override
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
return this.chain.filter(exchange);
}
}
过滤器链的源码如下:
public class DefaultWebFilterChain implements WebFilterChain {
private final List<WebFilter> allFilters;
private final WebHandler handler;
@Nullable
private final WebFilter currentFilter;
@Nullable
private final DefaultWebFilterChain chain;
/**
* Public constructor with the list of filters and the target handler to use.
* @param handler the target handler
* @param filters the filters ahead of the handler
* @since 5.1
*/
public DefaultWebFilterChain(WebHandler handler, List<WebFilter> filters) {
Assert.notNull(handler, "WebHandler is required");
this.allFilters = Collections.unmodifiableList(filters);
this.handler = handler;
DefaultWebFilterChain chain = initChain(filters, handler);
this.currentFilter = chain.currentFilter;
this.chain = chain.chain;
}
private static DefaultWebFilterChain initChain(List<WebFilter> filters, WebHandler handler) {
DefaultWebFilterChain chain = new DefaultWebFilterChain(filters, handler, null, null);
ListIterator<? extends WebFilter> iterator = filters.listIterator(filters.size());
while (iterator.hasPrevious()) {
chain = new DefaultWebFilterChain(filters, handler, iterator.previous(), chain);
}
return chain;
}
/**
* Private constructor to represent one link in the chain.
*/
private DefaultWebFilterChain(List<WebFilter> allFilters, WebHandler handler,
@Nullable WebFilter currentFilter, @Nullable DefaultWebFilterChain chain) {
this.allFilters = allFilters;
this.currentFilter = currentFilter;
this.handler = handler;
this.chain = chain;
}
/**
* Public constructor with the list of filters and the target handler to use.
* @param handler the target handler
* @param filters the filters ahead of the handler
* @deprecated as of 5.1 this constructor is deprecated in favor of
* {@link #DefaultWebFilterChain(WebHandler, List)}.
*/
@Deprecated
public DefaultWebFilterChain(WebHandler handler, WebFilter... filters) {
this(handler, Arrays.asList(filters));
}
public List<WebFilter> getFilters() {
return this.allFilters;
}
public WebHandler getHandler() {
return this.handler;
}
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
return Mono.defer(() ->
this.currentFilter != null && this.chain != null ?
invokeFilter(this.currentFilter, this.chain, exchange) :
this.handler.handle(exchange));
}
private Mono<Void> invokeFilter(WebFilter current, DefaultWebFilterChain chain, ServerWebExchange exchange) {
String currentName = current.getClass().getName();
return current.filter(exchange, chain).checkpoint(currentName + " [DefaultWebFilterChain]");
}
}
经过过滤器链调用,最终调用的handler是DispatcherHandler。
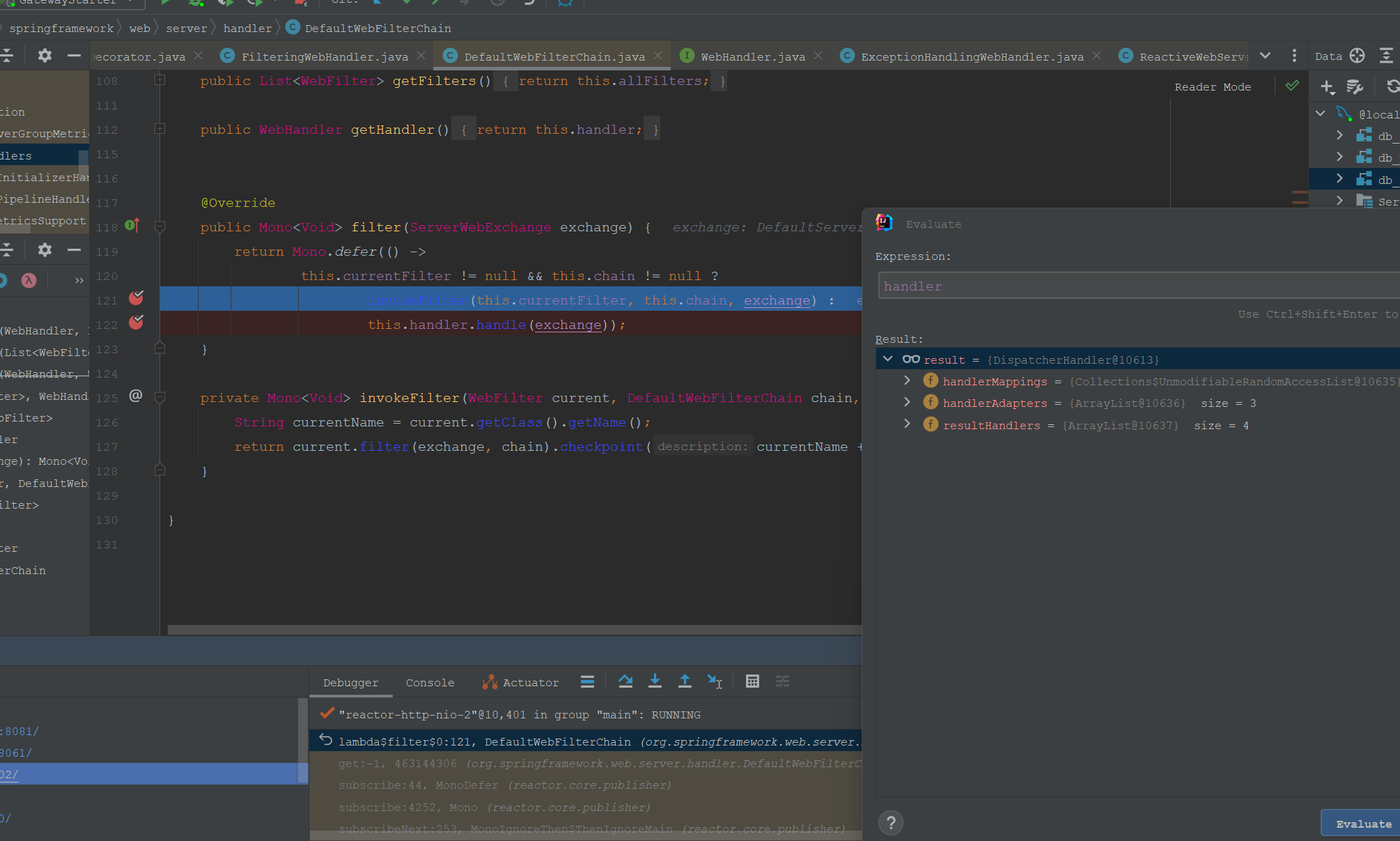
到这里,我们分析源码流程了解到了NettySever经过层层转发,最终将请求转派到了DispatcherHandler处理。而DispatcherHandler是webflux内的类,上面分析的流程涉及的类主要是Reactor和netty的。这样到这,底层的nettySever作为Web容器就和DispatcherHandler连接到一起了。
Tomcat Web容器经过层层请求转发最终请求到DispatcherServlet,Reactor和NettyServer的Web容器经过层层请求转发最终请求到DispatcherHandler。流程还是有很多相似之处的。
三、DispatcherHandler分派处理器
DispatcherHandler类似于DispatcherServlet,核心是请求分派,分派给具体的Handler处理。所以推断首先应该也要做路由映射,类似于HandlerMapping的功能。
首先看下DispatcherHandler的核心属性
@Nullable
private List<HandlerMapping> handlerMappings;
@Nullable
private List<HandlerAdapter> handlerAdapters;
@Nullable
private List<HandlerResultHandler> resultHandlers;
这三者分别是映射器,适配器,结果处理器。这三个组件是在策略集初始化方法内部创建的:
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
Map<String, HandlerMapping> mappingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(
context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
ArrayList<HandlerMapping> mappings = new ArrayList<>(mappingBeans.values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(mappings);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.unmodifiableList(mappings);
Map<String, HandlerAdapter> adapterBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(
context, HandlerAdapter.class, true, false);
this.handlerAdapters = new ArrayList<>(adapterBeans.values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerAdapters);
Map<String, HandlerResultHandler> beans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(
context, HandlerResultHandler.class, true, false);
this.resultHandlers = new ArrayList<>(beans.values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.resultHandlers);
}
里面创建的是按Type从BeanFactory获取或者创建对应的Bean。
这里的HandlerMapping就有我们非常熟悉的RequestMappingHandlerMapping:
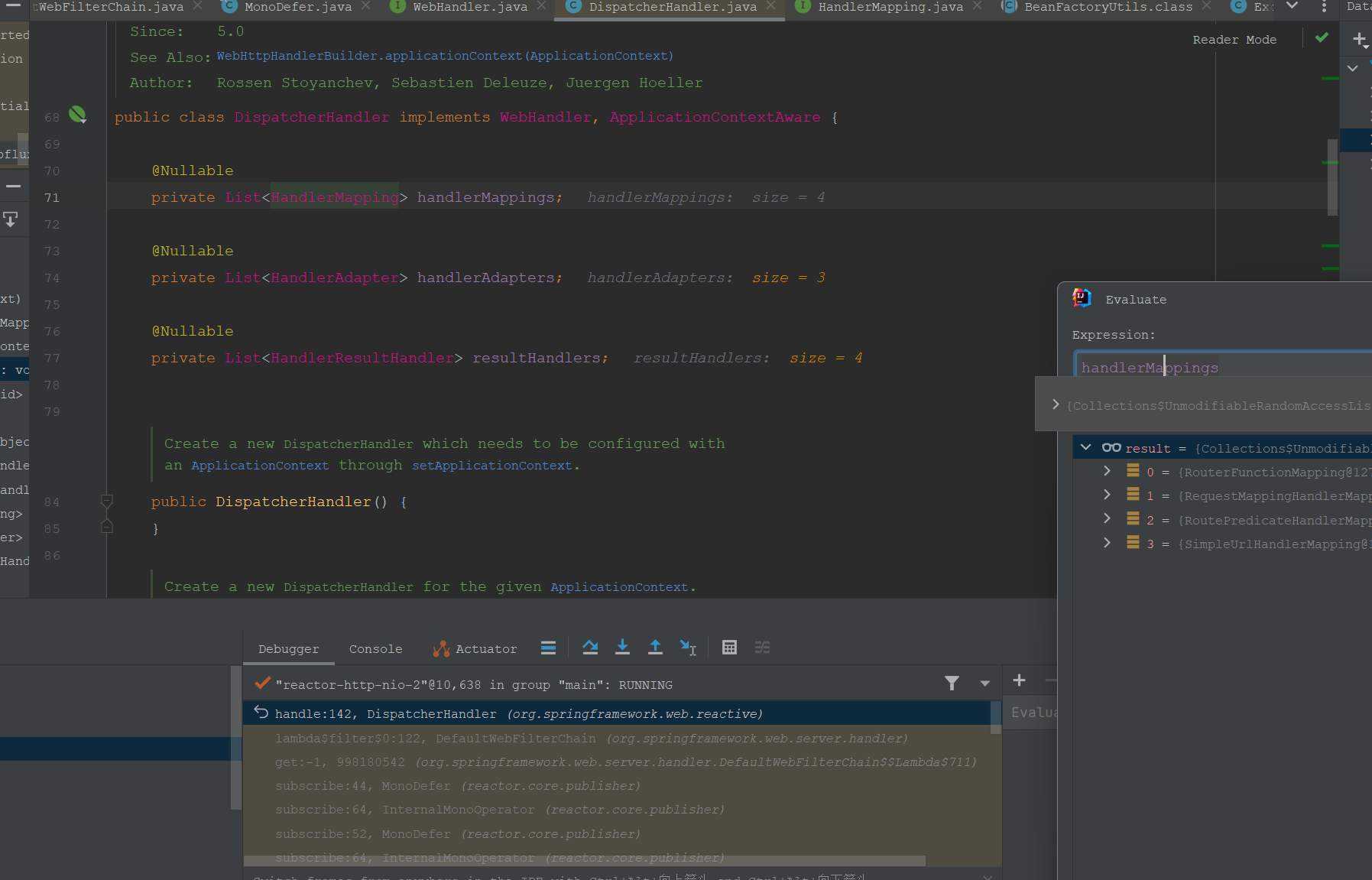
接着我们再进入handle方法:
@Override
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
return createNotFoundError();
}
return Flux.fromIterable(this.handlerMappings)
.concatMap(mapping -> mapping.getHandler(exchange))
.next()
.switchIfEmpty(createNotFoundError())
.flatMap(handler -> invokeHandler(exchange, handler))
.flatMap(result -> handleResult(exchange, result));
}
可以看到这里主要是三步:
-
通过handlerMapping获取Handler/Controller。
-
通过适配器实际调用Handler,获得调用结果。
-
结果交给结果处理器作处理。
3.1 HandlerMapping
我们继续阅读一下HandlerMapping如何获取Handler的源码:
@Override
public Mono<Object> getHandler(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
return getHandlerInternal(exchange).map(handler -> {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(exchange.getLogPrefix() + "Mapped to " + handler);
}
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration config = (this.corsConfigurationSource != null ? this.corsConfigurationSource.getCorsConfiguration(exchange) : null);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, exchange);
config = (config != null ? config.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
if (!this.corsProcessor.process(config, exchange) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return REQUEST_HANDLED_HANDLER;
}
}
return handler;
});
}
继续进入getHandlerInternal:
// Handler method lookup
/**
* Look up a handler method for the given request.
* @param exchange the current exchange
*/
@Override
public Mono<HandlerMethod> getHandlerInternal(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod;
try {
handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(exchange);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
return Mono.error(ex);
}
if (handlerMethod != null) {
handlerMethod = handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean();
}
return Mono.justOrEmpty(handlerMethod);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
这里就是寻找和匹配具体的handlerMethod,比如我们使用@RequestMapping注解的方法。
/**
* Look up the best-matching handler method for the current request.
* If multiple matches are found, the best match is selected.
* @param exchange the current exchange
* @return the best-matching handler method, or {@code null} if no match
* @see #handleMatch
* @see #handleNoMatch
*/
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(ServerWebExchange exchange) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, exchange);
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(exchange));
matches.sort(comparator);
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(exchange.getLogPrefix() + matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(exchange.getRequest())) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
RequestPath path = exchange.getRequest().getPath();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + path + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, bestMatch.handlerMethod, exchange);
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), exchange);
}
}
可以看到,可能存在多个匹配的方法,这里会返回最合适的。
下面继续进入HandlerAdapter的流程。
3.2 HandlerAdapter
这里适配器调用Handler就是真正去调用Handler/Controller的方法。
@Override
public Mono<HandlerResult> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange, Object handler) {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler;
Assert.state(this.methodResolver != null && this.modelInitializer != null, "Not initialized");
InitBinderBindingContext bindingContext = new InitBinderBindingContext(
getWebBindingInitializer(), this.methodResolver.getInitBinderMethods(handlerMethod));
InvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = this.methodResolver.getRequestMappingMethod(handlerMethod);
Function<Throwable, Mono<HandlerResult>> exceptionHandler =
ex -> handleException(ex, handlerMethod, bindingContext, exchange);
return this.modelInitializer
.initModel(handlerMethod, bindingContext, exchange)
.then(Mono.defer(() -> invocableMethod.invoke(exchange, bindingContext)))
.doOnNext(result -> result.setExceptionHandler(exceptionHandler))
.doOnNext(result -> bindingContext.saveModel())
.onErrorResume(exceptionHandler);
}
InvocableHandlerMethod的handle方法基本和MVC的一致:
public Mono<HandlerResult> invoke(
ServerWebExchange exchange, BindingContext bindingContext, Object... providedArgs) {
return getMethodArgumentValues(exchange, bindingContext, providedArgs).flatMap(args -> {
Object value;
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(getBridgedMethod());
Method method = getBridgedMethod();
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinReflectPresent() &&
KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(method.getDeclaringClass()) &&
CoroutinesUtils.isSuspendingFunction(method)) {
value = CoroutinesUtils.invokeSuspendingFunction(method, getBean(), args);
}
else {
value = method.invoke(getBean(), args);
}
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
assertTargetBean(getBridgedMethod(), getBean(), args);
String text = (ex.getMessage() != null ? ex.getMessage() : "Illegal argument");
return Mono.error(new IllegalStateException(formatInvokeError(text, args), ex));
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
return Mono.error(ex.getTargetException());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Unlikely to ever get here, but it must be handled...
return Mono.error(new IllegalStateException(formatInvokeError("Invocation failure", args), ex));
}
HttpStatus status = getResponseStatus();
if (status != null) {
exchange.getResponse().setStatusCode(status);
}
MethodParameter returnType = getReturnType();
ReactiveAdapter adapter = this.reactiveAdapterRegistry.getAdapter(returnType.getParameterType());
boolean asyncVoid = isAsyncVoidReturnType(returnType, adapter);
if ((value == null || asyncVoid) && isResponseHandled(args, exchange)) {
return (asyncVoid ? Mono.from(adapter.toPublisher(value)) : Mono.empty());
}
HandlerResult result = new HandlerResult(this, value, returnType, bindingContext);
return Mono.just(result);
});
}
通过具体Handler的调用,我们得到调用结果result。下面来到结果处理器。
3.3 HandlerResultHandler
结果处理器也是匹配具体的结果处理器去处理result:
private Mono<Void> handleResult(ServerWebExchange exchange, HandlerResult result) {
return getResultHandler(result).handleResult(exchange, result)
.checkpoint("Handler " + result.getHandler() + " [DispatcherHandler]")
.onErrorResume(ex ->
result.applyExceptionHandler(ex).flatMap(exResult -> {
String text = "Exception handler " + exResult.getHandler() +
", error=\"" + ex.getMessage() + "\" [DispatcherHandler]";
return getResultHandler(exResult).handleResult(exchange, exResult).checkpoint(text);
}));
}
如ResponseBodyResultHandler的处理:
@Override
public Mono<Void> handleResult(ServerWebExchange exchange, HandlerResult result) {
Object body = result.getReturnValue();
MethodParameter bodyTypeParameter = result.getReturnTypeSource();
return writeBody(body, bodyTypeParameter, exchange);
}
到这里,handler处理完成请求的结果就写回response,整个请求流程就处理完成了。
四、总结
这里简单总结一下本文的内容。
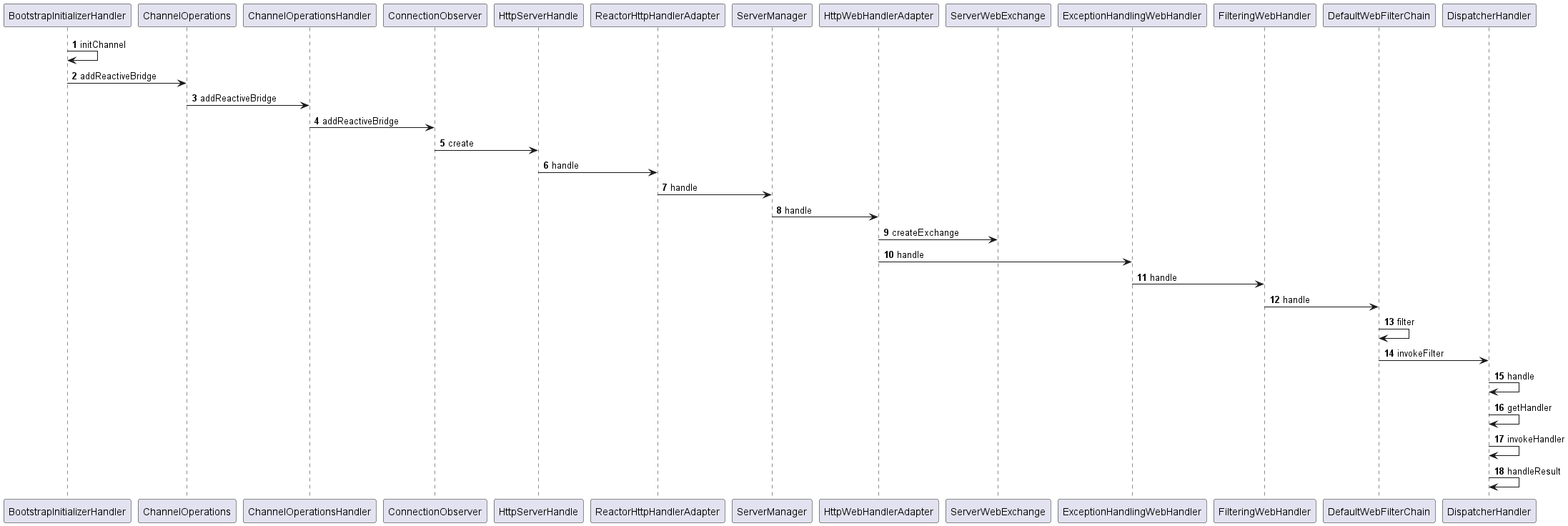
-
首先NettyWebServer创建ChannelHandler时候,会加入BootstrapInitializerHandler在pipeline的尾部,并添加请求监听器ConnectionObserver。
-
ConnectionObserver收到请求时会首先交给HttpHandler处理,按照ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter,ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext$ServerManager,HttpWebHandlerAdapter顺序转派请求。
-
请求转派到WebHandler,分别经过ExceptionHandlingWebHandler,FilteringWebHandler,DefaultWebFilterChain,DispatcherHandler等处理,经过过滤器链调用最终请求DispatcherHandler。
-
DispatcherHandler是实际调用具体的handler/controller的核心分派类,内部先由handlerMapping获得具体的handler/controller,再由HandlerAdapter实际调用目标类型和目标方法得到结果,最后交由HandlerResultHandler处理调用结果。
整体流程如下图:
五、参考材料
- spring-cloud-gateway源码(版本2.2.9)
