本文是Spring源码阅读计划的第二十篇文章,本文简单解读一下BeanFactoryPostProcessor这个类,算是对Spring IoC容器(BeanFactory)初始流程的一个补充解读
BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在BeanFactory创建和初始化之后执行的容器级别后置处理器,之前解读IoC容器初始化流程(以及AnnotationConfigApplicationContext)中
有这个invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法,调用beanFactory的后置处理器:
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
在之前的这篇文AnnotationConfigApplicationContext初始化流程有提及到,
在invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors这个方法解析了注解注册的BeanDefinition等信息,本文重点介绍一下BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
本文源码地址为:https://github.com/zouhuanli/SpringMvcDemo.git.
一、概述
先看下顶层接口:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding
* properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
可以看到这个接口主要是在beanFactory已经创建好了,还未真正创建所有注册的Bean实例的时候定制修改beanFactory的逻辑。
我们看下官方有哪些实现类。
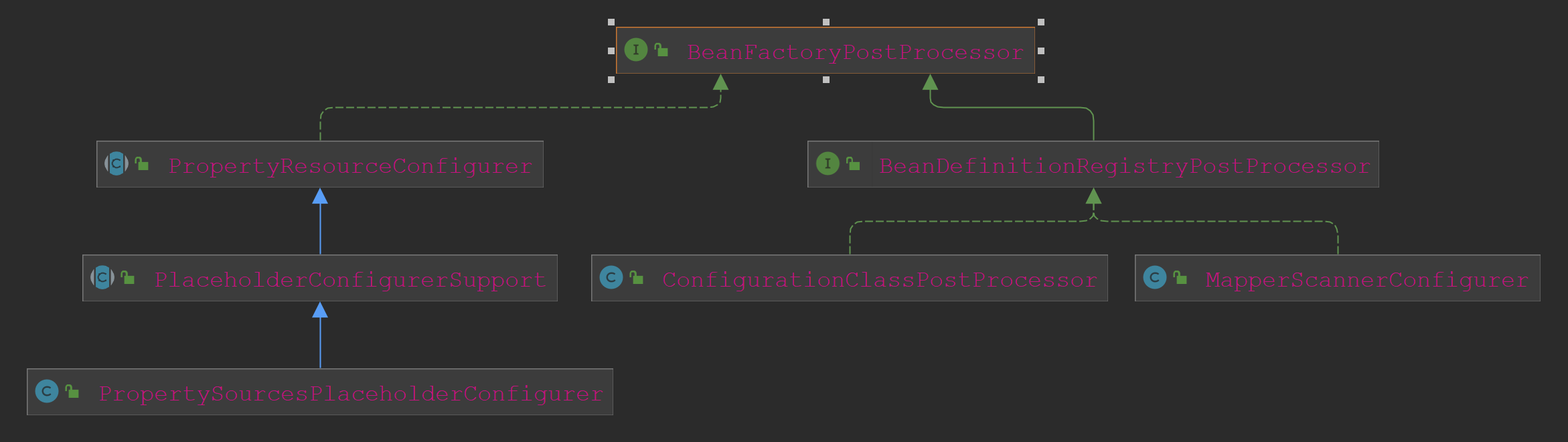
这里主要有两类:PropertyResourceConfigurer,获取配置资源的配置项的值。
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,如ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,注册Bean信息的后置处理器。
在解读AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的初始化流程那里,是通过BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor来解析和注册注解引入的bean信息的。
二、简单使用
自定义一个简单的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,如下:
@Component
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor.class);
/**
* 自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法
*
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
LOGGER.info("MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory");
}
}
注解上下文配置类:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.homura")
public class AnnotationContextConfig {
}
测试主类:
public class AnnotationContextTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AnnotationContextConfig.class);
System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("myFactoryBean"));
applicationContext.getBean(UserController.class).hello(null, null, null);
applicationContext.getBean(UserMapper.class).findUserList().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
执行纪录如下,具体代码参考GitHub项目的源码:
2023-10-26 21:42:19,799|TRACE|AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:522 |main|Finished creating instance of bean 'org.springframework.transaction.config.internalTransactionalEventListenerFactory'
2023-10-26 21:42:19,799|INFO |MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor.java:22 |main|MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory
2023-10-26 21:42:19,800|DEBUG|DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java:225 |main|Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor'
三、BeanFactoryPostProcessor作用位置
跟踪postProcessBeanFactory的调用关系,在自定义BeanFactoryPostProcessor的MapperScannerConfigurer有如下代码:
for (PropertyResourceConfigurer prc : prcs.values()) {
prc.postProcessBeanFactory(factory);
}
这里注入了配置项的配置值。
以及MapperScannerConfigurer#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry会在PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors内调用,
用以完成扫描mapper信息并注册mapper信息。
回到Spring Framework自身的源码,PropertyResourceConfigurer笔者这里不再解读,我们主要看下BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor。
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean definition registry after its
* standard initialization. All regular bean definitions will have been loaded,
* but no beans will have been instantiated yet. This allows for adding further
* bean definitions before the next post-processing phase kicks in.
* @param registry the bean definition registry used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
}
这里可以修改或者增加beanFactory的BeanDefinition信息,可以注册注解定义的Bean信息。
我们继续阅读ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,我们看下这两个方法:
/**
* Derive further bean definitions from the configuration classes in the registry.
*/
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
int registryId = System.identityHashCode(registry);
if (this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
this.registriesPostProcessed.add(registryId);
processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry);
}
从@Configuration类加载更多的bean配置信息BeanDefinitions。
/**
* Build and validate a configuration model based on the registry of
* {@link Configuration} classes.
*/
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (beanDef.getAttribute(ConfigurationClassUtils.CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);
}
}
else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));
}
}
// Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found
if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// Sort by previously determined @Order value, if applicable
configCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> {
int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition());
int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition());
return Integer.compare(i1, i2);
});
// Detect any custom bean name generation strategy supplied through the enclosing application context
SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null;
if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry _sbr) {
sbr = _sbr;
if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) {
BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(
AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR);
if (generator != null) {
this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator;
this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator;
}
}
}
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
}
// Parse each @Configuration class
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);
Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());
do {
StartupStep processConfig = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.config-classes.parse");
//解析 @Configuration类以及其引入的@Bean, @Import,@ComponentScan等引入的Bean信息
parser.parse(candidates);
parser.validate();
Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);
// Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content
if (this.reader == null) {
this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
processConfig.tag("classCount", () -> String.valueOf(configClasses.size())).end();
candidates.clear();
if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {
String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Set<String> oldCandidateNames = Set.of(candidateNames);
Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();
for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {
BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
!alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {
candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));
}
}
}
candidateNames = newCandidateNames;
}
}
while (!candidates.isEmpty());
// Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classes
if (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) {
sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
// Store the PropertySourceDescriptors to contribute them Ahead-of-time if necessary
this.propertySourceDescriptors = parser.getPropertySourceDescriptors();
if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory cachingMetadataReaderFactory) {
// Clear cache in externally provided MetadataReaderFactory; this is a no-op
// for a shared cache since it'll be cleared by the ApplicationContext.
cachingMetadataReaderFactory.clearCache();
}
}
这里注册和解析了注册配置的Bean。继续进入,来到:
/**
* Apply processing and build a complete {@link ConfigurationClass} by reading the
* annotations, members and methods from the source class. This method can be called
* multiple times as relevant sources are discovered.
* @param configClass the configuration class being build
* @param sourceClass a source class
* @return the superclass, or {@code null} if none found or previously processed
*/
@Nullable
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass, Predicate<String> filter)
throws IOException {
if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) {
// Recursively process any member (nested) classes first
processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
}
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {
if (this.propertySourceRegistry != null) {
this.propertySourceRegistry.processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
else {
logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() +
"]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");
}
}
// Process any @ComponentScan annotations
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
}
// Process any @Import annotations
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), filter, true);
// Process any @ImportResource annotations
AnnotationAttributes importResource =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class);
if (importResource != null) {
String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations");
Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader> readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader");
for (String resource : resources) {
String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource);
configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass);
}
}
// Process individual @Bean methods
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
// Process default methods on interfaces
processInterfaces(configClass, sourceClass);
// Process superclass, if any
if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) {
String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName();
if (superclass != null && !superclass.startsWith("java") &&
!this.knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) {
this.knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass);
// Superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recurse
return sourceClass.getSuperClass();
}
}
// No superclass -> processing is complete
return null;
}
很明显,这里注册了@ComponentScan、@ImportResource、@Bean 等注解注册的Bean信息。 而最外层的执行入口是refresh方法内的这行代码:
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
其执行的方法是PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors,如下:
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// WARNING: Although it may appear that the body of this method can be easily
// refactored to avoid the use of multiple loops and multiple lists, the use
// of multiple lists and multiple passes over the names of processors is
// intentional. We must ensure that we honor the contracts for PriorityOrdered
// and Ordered processors. Specifically, we must NOT cause processors to be
// instantiated (via getBean() invocations) or registered in the ApplicationContext
// in the wrong order.
//
// Before submitting a pull request (PR) to change this method, please review the
// list of all declined PRs involving changes to PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate
// to ensure that your proposal does not result in a breaking change:
// https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/issues?q=PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate+is%3Aclosed+label%3A%22status%3A+declined%22
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor) {
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
可以看到这里invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors解析Bean注册信息之前还对BeanFactotyPostProcessors做了排序处理。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor的简单解读就先到这里,可以简单总结一下就是BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在BeanFactory创建和初始化之后执行的容器级别后置处理器,允许客户端定制化一些BeanFactory初始化之后的行为,如增加注册注解引入的Bean配置等。
四、参考材料
1.Spring源码(版本6.0.11)
2.《spring源码深度解析》(郝佳)
3.《Spring Framework Documentation》(Version 6.0.8)
