本文是Spring源码阅读计划的第十五篇文章,本文着重介绍DispatcherServlet的请求处理流程,也就是DispatcherServlet.doDispatch()
方法。
上一篇文章已经介绍了SpringMVC的简单使用和DispatcherServlet的初始化流程,本文开始阅读doDispatch()方法的方法。
本文源码地址为:https://github.com/zouhuanli/SpringMvcDemo.git.
我们从Servlet的service方法开始阅读。
一、SpringMVC的请求流程
重新简单介绍一下SpringMVC的请求流程,也就是DispatcherServlet的doDispatch方法。
还是开涛老师的图,如下:
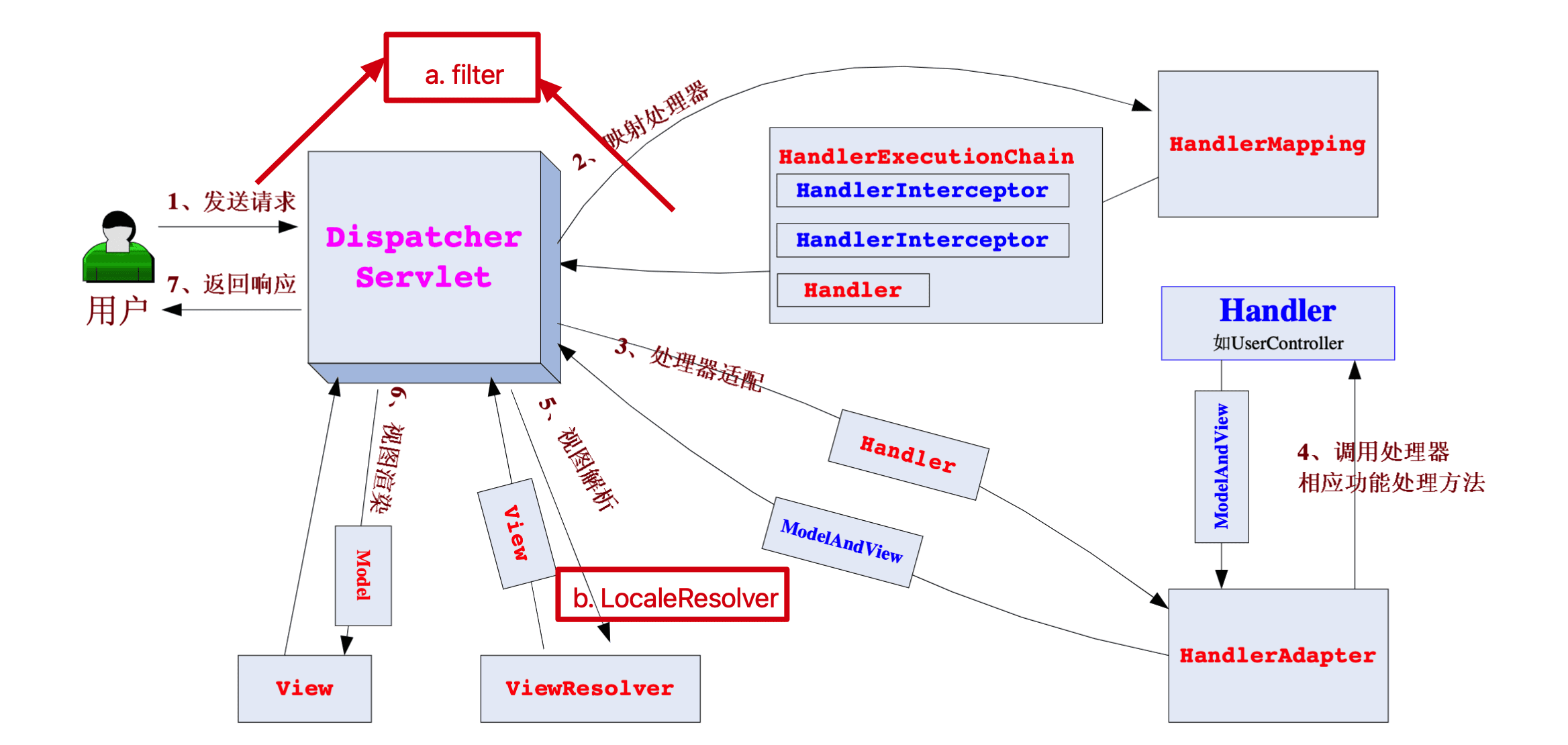
主要流程如下:
1.用户(前端)请求DispatcherServlet,DispatcherServlet作为核心的前端控制器,自己不处理请求,只做主流程串联,进行请求分派。
2.DispatcherServlet将请求转发给HandlerMapping,handlerMapping返回HandlerExecutionChain(包含Handler控制器和拦截器列表)。
3.DispatcherServlet再将Handler控制器转发给HandlerAdapter,获得Handler的适配器。
4.HandlerAdapter真正请求处理器的方法,返回ModelAndView对象。也能不返回ModelAndView对象,直接写回response数据,
如@ResponseBody,RequestMappingHandlerAdapter调用Handler的目标方法之后,直接返回null,后面的和View对象的流程就不用了。
5.ModelAndView再进行视图解析,解析为具体的视图View。
6.视图View执行render方法进行渲染,Model对象是一个Map结构。
7.DispatcherServlet将渲染后的数据返回给用户(前端)。
笔者现结合DispatcherServlet源码详细介绍请求流程。先从Servlet的service()方法作为入口开始阅读。
二、DispatcherServlet的请求处理流程
1.service()方法
service方法如下
/**
* Called by the servlet container to allow the servlet to respond to a request.
*
* <p>
* This method is only called after the servlet's <code>init()</code> method has completed successfully.
*
* <p>
* The status code of the response always should be set for a servlet that throws or sends an error.
*
*
* <p>
* Servlets typically run inside multithreaded servlet containers that can handle multiple requests concurrently.
* Developers must be aware to synchronize access to any shared resources such as files, network connections, and as
* well as the servlet's class and instance variables.
*
* @param req the <code>ServletRequest</code> object that contains the client's request
*
* @param res the <code>ServletResponse</code> object that contains the servlet's response
*
* @exception ServletException if an exception occurs that interferes with the servlet's normal operation
*
* @exception IOException if an input or output exception occurs
*
*/
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException;
这里的ServletRequest、ServletResponse不仅仅是http协议的请求,可以是任何的协议的Web请求。
GenericServlet的service()方法是空方法,继续阅读子类。
HttpServletRequest的service()方法如下,可以看到主要就是判断是否Http协议的请求。
/**
* Dispatches client requests to the protected <code>service</code> method. There's no need to override this method.
*
* @param req the {@link HttpServletRequest} object that contains the request the client made of the servlet
*
* @param res the {@link HttpServletResponse} object that contains the response the servlet returns to the client
*
* @throws IOException if an input or output error occurs while the servlet is handling the HTTP request
*
* @throws ServletException if the HTTP request cannot be handled or if either parameter is not an instance of its
* respective {@link HttpServletRequest} or {@link HttpServletResponse} counterparts.
*
* @see jakarta.servlet.Servlet#service
*/
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest request;
HttpServletResponse response;
if (!(req instanceof HttpServletRequest && res instanceof HttpServletResponse)) {
throw new ServletException("non-HTTP request or response");
}
request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
service(request, response);
}
}
继续阅读。
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason
// to go through further expensive logic
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified) {
// If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet()
// Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare
// A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req, resp);
} else {
//
// Note that this means NO servlet supports whatever
// method was requested, anywhere on this server.
//
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}
这里按Http Method分别请求对应的方法,我们选择doPost()方法进入FrameworkServlet的doPost()方法。
/**
* Delegate POST requests to {@link #processRequest}.
* @see #doService
*/
@Override
protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
这里是统一的处理HttpServletRequest的方法:
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
//获得之前请求的LocaleContext
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
//获得之前请求的参数
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
//初始化ContextHolders
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
//处理请求的方法
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new ServletException("Request processing failed: " + ex, ex);
}
finally {
//重置ContextHolders
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
//纪录日志和发布事件
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
继续深入,来到DispatcherServlet的doService方法。
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
//将WebApplicationContext、localeResolver、themeResolver等资源的引用存入reques的参数内
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
RequestPath previousRequestPath = null;
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
previousRequestPath = (RequestPath) request.getAttribute(ServletRequestPathUtils.PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
ServletRequestPathUtils.parseAndCache(request);
}
try {
//真正的处理请求方法
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
ServletRequestPathUtils.setParsedRequestPath(previousRequestPath, request);
}
}
}
通过层层转发,我们最终找到了真正的处理请求方法doDispatch()。
2.doDispatch()方法
这里就是DispatcherServlet处理Http请求的核心方法了。
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
//请求HandlerMapping获得HandlerExecutionChain(handler+interceptorList)
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
//获得handler的适配器HandlerAdapter
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = HttpMethod.GET.matches(method);
if (isGet || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
//拦截器前置处理
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
//调用handler(controller)的目标方法
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
//拦截器后置处理
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new ServletException("Handler dispatch failed: " + err, err);
}
//处理handler(controller)的目标方法的返回结果
//1.异常处理processHandlerException
//2.视图解析resolveViewName
//3.视图渲染view.render()
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
//拦截器最终处理
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new ServletException("Handler processing failed: " + err, err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
可以看到整个流程解读还是很简单,没有很高的复杂度,也没有非常多的分支。
下面简单阅读一下这些主要的处理方法。
2.1 getHandler()方法
getHandler()方法如下:
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
其从一个匹配的HandlerMapping获取处理请求的handler和拦截器列表。
@Override
@Nullable
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//获得handler
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String handlerName) {
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
//获得拦截器列表
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
return executionChain;
}
进入匹配HandlerMethod的方法:
// Handler method lookup
/**
* Look up a handler method for the given request.
*/
@Override
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = initLookupPath(request);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
for (Match match : matches) {
if (match.hasCorsConfig()) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
}
}
else {
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
}
//匹配到最合适的HandlerMethod
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.getHandlerMethod());
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.getHandlerMethod();
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
可以看到这里示例工程主要是按照RequestMapping的注册路径来匹配的。
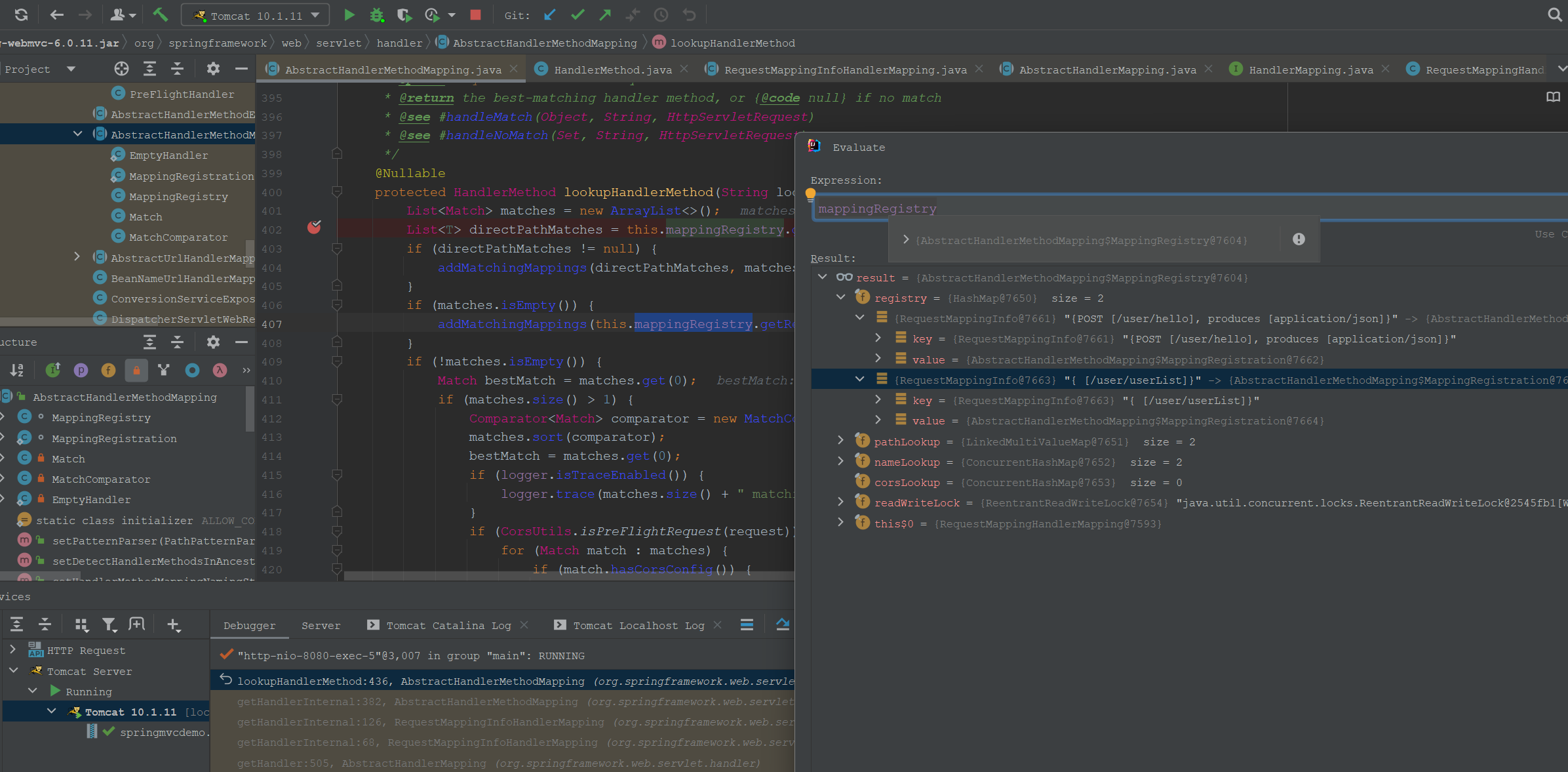
此外,这里示例工程这里Handler是一个Method,如”com.homura.controller.UserController#list(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse)”。

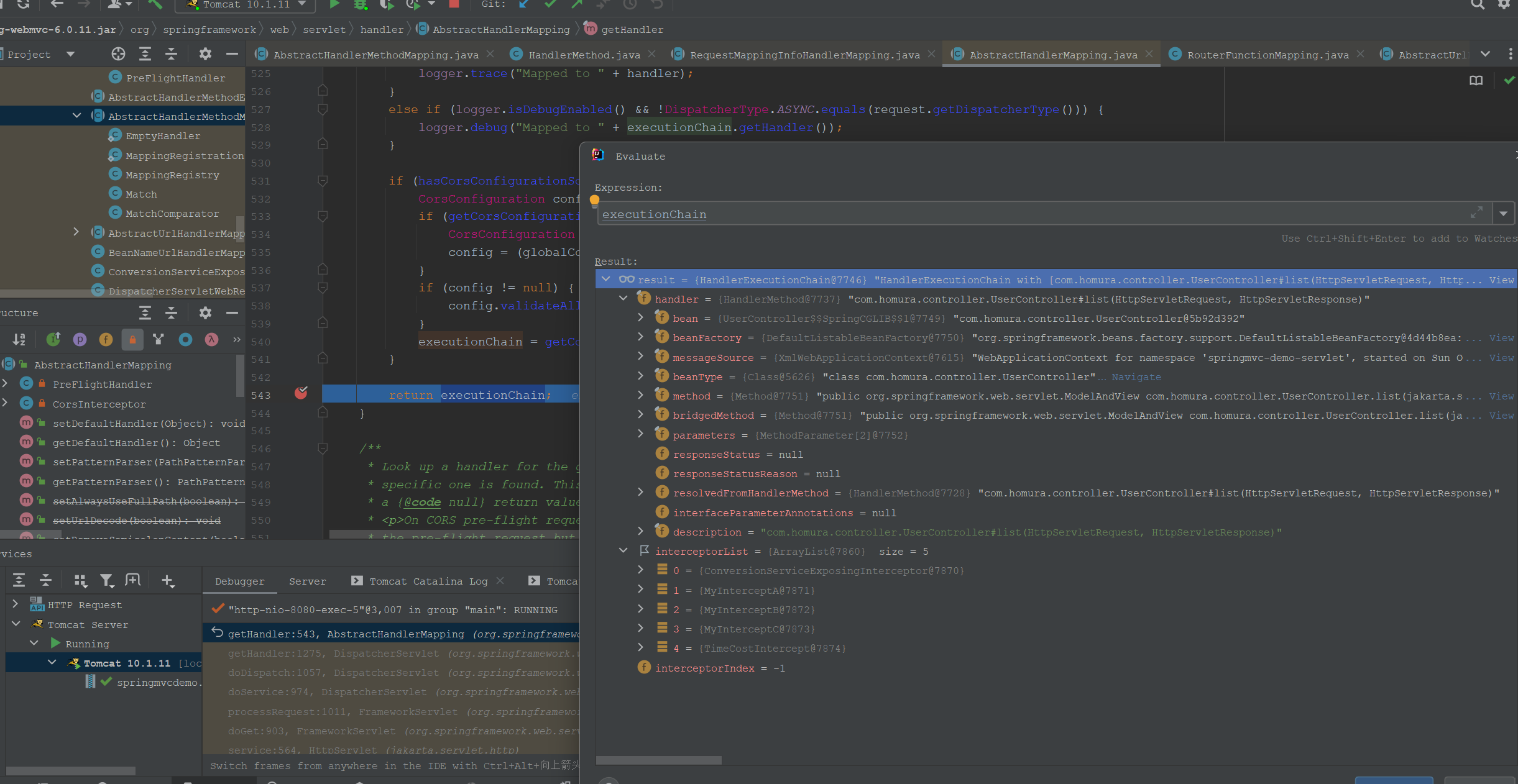
这里是匹配合适的拦截器列表。
完整的executionChain信息如下:
2.2 getHandlerAdapter()方法
这里依旧是从适配器列表匹配对应的适配器。
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
我们开始阅读supports()方法。 如AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter的supports()方法。
/**
* This implementation expects the handler to be an {@link HandlerMethod}.
* @param handler the handler instance to check
* @return whether this adapter can adapt the given handler
*/
@Override
public final boolean supports(Object handler) {
return (handler instanceof HandlerMethod handlerMethod && supportsInternal(handlerMethod));
}
而RequestMappingHandlerAdapter的supportsInternal()方法很简单的返回了true。
/**
* Always return {@code true} since any method argument and return value
* type will be processed in some way. A method argument not recognized
* by any HandlerMethodArgumentResolver is interpreted as a request parameter
* if it is a simple type, or as a model attribute otherwise. A return value
* not recognized by any HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler will be interpreted
* as a model attribute.
*/
@Override
protected boolean supportsInternal(HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
return true;
}
最后示例工程的适配器HandlerAdapter是RequestMappingHandlerAdapter。
2.2 applyPreHandle()方法
拦截器的三个方法非常简单,是开放给拓展者来自定义拦截器的,要注意执行顺序。
设n是拦截器的数量,执行顺序是前置处理顺序是拦截器列表索引0—>n-1,如果某一个拦截器的applyPreHandle返回false,则不会调用后面流程(handler的handle方法等)了。
若i=k返回false,则直接进入triggerAfterCompletion方法进行拦截器的最终处理,afterCompletion的执行顺序是k—>0。
而后置处理applyPostHandle的执行顺序是n-1—>0。
boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < this.interceptorList.size(); i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = this.interceptorList.get(i);
if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) {
triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
return false;
}
this.interceptorIndex = i;
}
return true;
}
这里的某个前置处理返回false,直接跳出了doDispatch()方法。
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
2.3 HandlerAdapter.handle()方法
这里是真正调用了Handler/Controller的处理方法。
这个方法是非常长的,不过我们可以把握一些基本流程:请求参数处理、调用目标方法、请求结果处理。
我们进入RequestMappingHandlerAdapter的handleInternal()方法。
@Override
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
checkRequest(request);
// Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required.
//在会话上同步处理请求
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No HttpSession available -> no mutex necessary
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No synchronization on session demanded at all...
//调用HandlerMethod的方法
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
}
else {
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
}
然后是invokeHandlerMethod方法。
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
//封装request
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
//创建ServletInvocableHandlerMethod
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
//创建ModeAndView
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);
asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor);
asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors);
asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors);
if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) {
Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult();
mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0];
asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult();
LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> {
String formatted = LogFormatUtils.formatValue(result, !traceOn);
return "Resume with async result [" + formatted + "]";
});
invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result);
}
//调用目标方法
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
//ModelAndView对象
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
继续阅读,来到invokeAndHandle()方法。
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
//调用目标方法
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
if (returnValue == null) {
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
disableContentCachingIfNecessary(webRequest);
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
}
else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers");
try {
//返回类型的处理器,如RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatErrorForReturnValue(returnValue), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
继续进入doInvoke()方法。
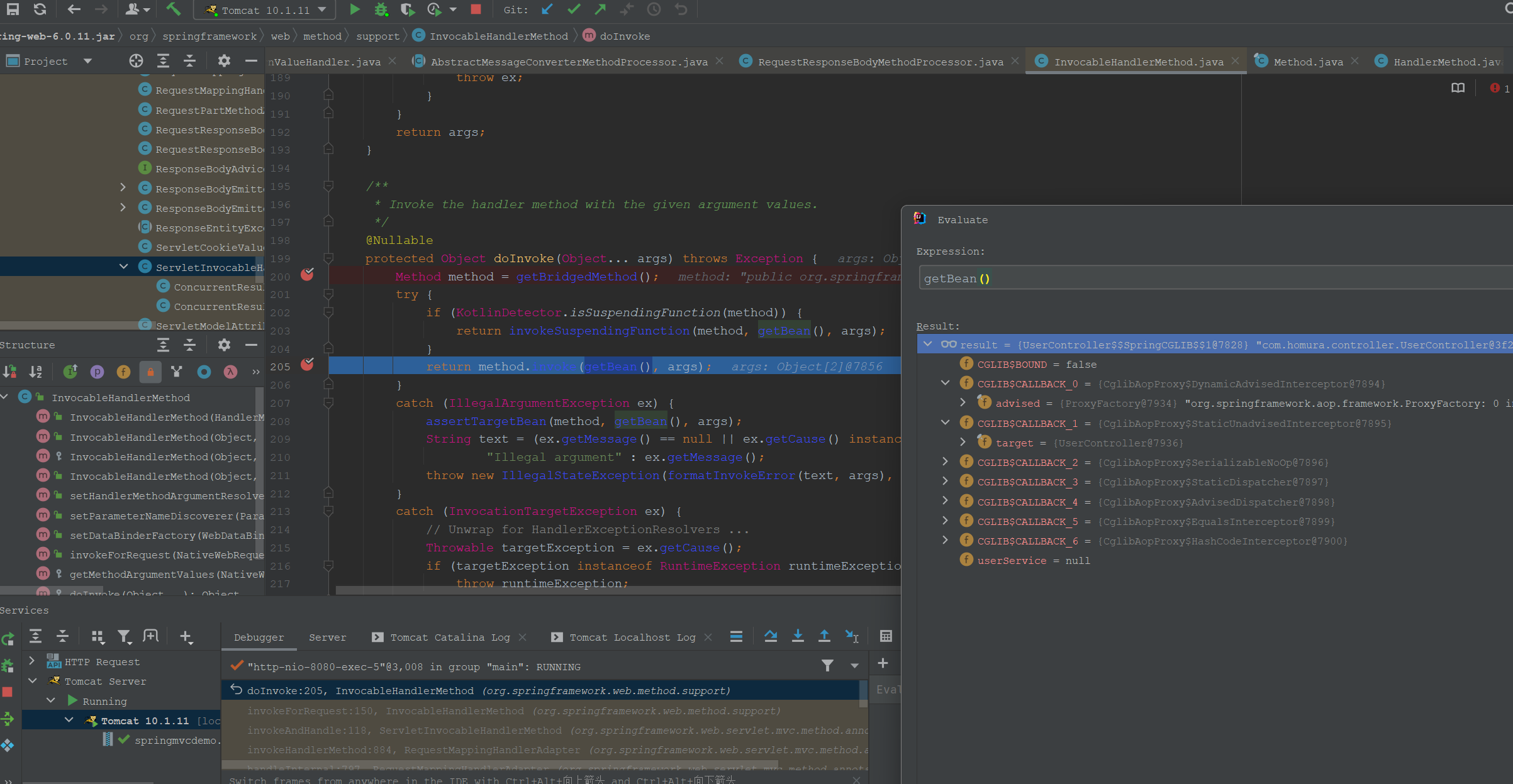
可以看到这里的controller是一个代理对象。
2.4 applyPostHandle()方法
如下。
/**
* Apply postHandle methods of registered interceptors.
*/
void applyPostHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable ModelAndView mv)
throws Exception {
for (int i = this.interceptorList.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = this.interceptorList.get(i);
interceptor.postHandle(request, response, this.handler, mv);
}
}
2.5 processDispatchResult()方法
这里主要就是对异常处理、进行视图解析、进行视图渲染。
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,
@Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException mavDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = mavDefiningException.getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned.");
}
}
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
}
if (mappedHandler != null) {
// Exception (if any) is already handled..
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}
2.6 resolveViewName()方法
解析视图主要是从视图名字解析出视图View对象。
@Nullable
protected View resolveViewName(String viewName, @Nullable Map<String, Object> model,
Locale locale, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.viewResolvers != null) {
for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) {
View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale);
if (view != null) {
return view;
}
}
}
return null;
}
2.7 View.render()方法
视图渲染方法,这里model是一个Map对象。
@Override
public void render(@Nullable Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("View " + formatViewName() +
", model " + (model != null ? model : Collections.emptyMap()) +
(this.staticAttributes.isEmpty() ? "" : ", static attributes " + this.staticAttributes));
}
Map<String, Object> mergedModel = createMergedOutputModel(model, request, response);
prepareResponse(request, response);
renderMergedOutputModel(mergedModel, getRequestToExpose(request), response);
}
这里是返回的完整页面数据。
2.8 triggerAfterCompletion()方法
如下。
void triggerAfterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Exception ex) {
for (int i = this.interceptorIndex; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = this.interceptorList.get(i);
try {
interceptor.afterCompletion(request, response, this.handler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
logger.error("HandlerInterceptor.afterCompletion threw exception", ex2);
}
}
}
三、拦截器
1.拦截器的简单测试
定义拦截器。
/**
* 拦截器1
*
* @author zouhl
*/
public class MyInterceptA implements HandlerInterceptor {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyInterceptA.class);
/**
* 前置处理
*
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @param handler chosen handler to execute, for type and/or instance evaluation
* @return 是否执行后续的拦截器和handle方法
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
LOGGER.info("MyInterceptA preHandle");
return true;
}
/**
* 后置处理
*
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @param handler the handler (or {@link HandlerMethod}) that started asynchronous
* execution, for type and/or instance examination
* @param modelAndView the {@code ModelAndView} that the handler returned
* (can also be {@code null})
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler,
@Nullable ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
LOGGER.info("MyInterceptA postHandle");
}
/**
* 最终处理,我自己翻译的
*
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @param handler the handler (or {@link HandlerMethod}) that started asynchronous
* execution, for type and/or instance examination
* @param ex any exception thrown on handler execution, if any; this does not
* include exceptions that have been handled through an exception resolver
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler,
@Nullable Exception ex) throws Exception {
LOGGER.info("MyInterceptA afterCompletion");
}
}
配置拦截器。
<!--拦截器-->
<mvc:interceptors>
<bean class="com.homura.intercept.MyInterceptA"/>
<bean class="com.homura.intercept.MyInterceptB"/>
<bean class="com.homura.intercept.MyInterceptC"/>
<bean class="com.homura.intercept.TimeCostIntercept"/>
</mvc:interceptors>
执行测试结果,结果如下。
2023-10-15 21:15:55,340|INFO | MyFilter.java:57 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|MyFilter.beforeDo()
2023-10-15 21:15:55,362|DEBUG| LogFormatUtils.java:120 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|GET "/springmvcdemo_war/user/userList", parameters={}
2023-10-15 21:15:55,377|DEBUG|AbstractHandlerMapping.java:528 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|Mapped to com.homura.controller.UserController#list(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse)
2023-10-15 21:15:55,380|INFO | MyInterceptA.java:32 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|MyInterceptA preHandle
2023-10-15 21:15:55,381|INFO | MyInterceptB.java:32 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|MyInterceptB preHandle
2023-10-15 21:15:55,381|INFO | MyInterceptC.java:31 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|MyInterceptC preHandle
2023-10-15 21:15:55,381|INFO | TimeCostIntercept.java:34 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|TimeCostIntercept preHandle
2023-10-15 21:15:55,399|INFO | LogAspect.java:38 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|环绕通知:进入方法
2023-10-15 21:15:55,399|INFO | LogAspect.java:49 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|前置通知
2023-10-15 21:15:55,406|DEBUG| Logger.java:49 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|Creating a new SqlSession
2023-10-15 21:15:55,411|DEBUG| Logger.java:49 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|SqlSession [org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession@46a83c03] was not registered for synchronization because synchronization is not active
2023-10-15 21:15:55,420|DEBUG| DataSourceUtils.java:117 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|Fetching JDBC Connection from DataSource
2023-10-15 21:15:55,421|WARN | HikariConfig.java:1089|http-nio-8080-exec-4|HikariPool-1 - idleTimeout has been set but has no effect because the pool is operating as a fixed size pool.
2023-10-15 21:15:55,887|DEBUG| Logger.java:49 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|JDBC Connection [HikariProxyConnection@1551966288 wrapping com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@55a762d7] will not be managed by Spring
2023-10-15 21:15:55,893|DEBUG| BaseJdbcLogger.java:135 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|==> Preparing: select * from user
2023-10-15 21:15:55,918|DEBUG| BaseJdbcLogger.java:135 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|==> Parameters:
2023-10-15 21:15:55,942|DEBUG| BaseJdbcLogger.java:135 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|<== Total: 11
2023-10-15 21:15:55,950|DEBUG| Logger.java:49 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|Closing non transactional SqlSession [org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession@46a83c03]
2023-10-15 21:15:55,957|INFO | LogAspect.java:67 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|后置通知,返回值:ModelAndView [view="userList"; model={dateTime=2023-10-15T21:15:55.399821800, userList=[User(uid=3, uname=bb, password=123, gender=null, phone=null, email=null, address=null), User(uid=7, uname=L, password=123, gender=男, phone=12345678900, email=123@qq.com, address=我家), User(uid=8, uname=123, password=213, gender=男, phone=321, email=213, address=3), User(uid=11, uname=, password=, gender=null, phone=null, email=null, address=null), User(uid=12, uname=111, password=222, gender=null, phone=null, email=null, address=null), User(uid=13, uname=333, password=333, gender=null, phone=null, email=null, address=null), User(uid=14, uname=666, password=666, gender=null, phone=null, email=null, address=null), User(uid=15, uname=777, password=777, gender=null, phone=null, email=null, address=null), User(uid=16, uname=16, password=16, gender=女, phone=1340, email=11, address=16道路), User(uid=17, uname=17, password=17, gender=男, phone=111, email=11, address=111), User(uid=18, uname=19, password=20, gender=222, phone=222, email=222, address=222)]}]
2023-10-15 21:15:55,957|INFO | LogAspect.java:57 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|最终通知
2023-10-15 21:15:55,957|INFO | LogAspect.java:40 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|环绕通知:退出方法
2023-10-15 21:15:55,967|INFO | TimeCostIntercept.java:52 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|TimeCostIntercept postHandle
2023-10-15 21:15:55,967|INFO | MyInterceptC.java:55 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|MyInterceptC postHandle
2023-10-15 21:15:55,967|INFO | MyInterceptB.java:50 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|MyInterceptB postHandle
2023-10-15 21:15:55,967|INFO | MyInterceptA.java:49 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|MyInterceptA postHandle
2023-10-15 21:15:55,981|DEBUG| HikariPool.java:414 |HikariPool-1 housekeeper|HikariPool-1 - Pool stats (total=1, active=0, idle=1, waiting=0)
2023-10-15 21:15:55,992|DEBUG| AbstractView.java:307 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|View name 'userList', model {dateTime=2023-10-15T21:15:55.399821800, userList=[User(uid=3, uname=bb, password=123, gender=null, phone=null, email=null, address=null), User(uid=7, uname=L, password=123, gender=男, phone=12345678900, email=123@qq.com, address=我家), User(uid=8, uname=123, password=213, gender=男, phone=321, email=213, address=3), User(uid=11, uname=, password=, gender=null, phone=null, email=null, address=null), User(uid=12, uname=111, password=222, gender=null, phone=null, email=null, address=null), User(uid=13, uname=333, password=333, gender=null, phone=null, email=null, address=null), User(uid=14, uname=666, password=666, gender=null, phone=null, email=null, address=null), User(uid=15, uname=777, password=777, gender=null, phone=null, email=null, address=null), User(uid=16, uname=16, password=16, gender=女, phone=1340, email=11, address=16道路), User(uid=17, uname=17, password=17, gender=男, phone=111, email=11, address=111), User(uid=18, uname=19, password=20, gender=222, phone=222, email=222, address=222)]}
2023-10-15 21:15:56,004|DEBUG| HikariPool.java:738 |HikariPool-1 connection adder|HikariPool-1 - Added connection com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@10656430
2023-10-15 21:15:56,019|DEBUG|InternalResourceView.java:169 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|Forwarding to [/WEB-INF/views/userList.jsp]
2023-10-15 21:15:56,277|DEBUG| HikariPool.java:414 |HikariPool-1 connection adder|HikariPool-1 - After adding stats (total=10, active=0, idle=10, waiting=0)
2023-10-15 21:15:56,739|INFO | TimeCostIntercept.java:71 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|TimeCostIntercept afterCompletion,time cost:1358
2023-10-15 21:15:56,739|INFO | MyInterceptC.java:71 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|MyInterceptC afterCompletion
2023-10-15 21:15:56,739|INFO | MyInterceptB.java:67 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|MyInterceptB afterCompletion
2023-10-15 21:15:56,739|INFO | MyInterceptA.java:66 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|MyInterceptA afterCompletion
2023-10-15 21:15:56,742|DEBUG| FrameworkServlet.java:1135|http-nio-8080-exec-4|Completed 200 OK
2023-10-15 21:15:56,744|INFO | MyFilter.java:49 |http-nio-8080-exec-4|MyFilter.afterDo()
2023-10-15 21:16:25,986|DEBUG| HikariPool.java:414 |HikariPool-1 housekeeper|HikariPool-1 - Pool stats (total=10, active=0, idle=10, waiting=0)
2023-10-15 21:16:25,986|DEBUG| HikariPool.java:521 |HikariPool-1 housekeeper|HikariPool-1 - Fill pool skipped, pool has sufficient level or currently being filled (queueDepth=0).
主要是注意拦截器的三个方法的执行顺序:MyInterceptA preHandle、MyInterceptB preHandle、MyInterceptC preHandle、TimeCostIntercept preHandle,
TimeCostIntercept postHandle、MyInterceptC postHandle、MyInterceptB postHandle、MyInterceptA postHandle,
TimeCostIntercept afterCompletion、MyInterceptC afterCompletion、MyInterceptB afterCompletion、MyInterceptA afterCompletion。
前置处理方法是正序的,后置处理和最终处理是倒序的。
2.过滤器、拦截器、自定义AOP切面三者的执行顺序
定义拦截器。
/**
* 一个简单的过滤器
*
* @author zouhl
*/
@WebFilter("/*")
public class MyFilter extends HttpFilter {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyFilter.class);
/**
* @param req a {@link ServletRequest} object that contains the request the client has made of the filter
* @param res a {@link ServletResponse} object that contains the response the filter sends to the client
* @param chain the <code>FilterChain</code> for invoking the next filter or the resource
* @throws IOException
* @throws ServletException
*/
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (!(req instanceof HttpServletRequest && res instanceof HttpServletResponse)) {
throw new ServletException("non-HTTP request or response");
}
beforeDo(req);
chain.doFilter(req, res);
afterDo(req, res);
}
/**
* 前置处理
* @param req
* @param res
*/
private void afterDo(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) {
LOGGER.info("MyFilter.afterDo()");
}
/**
* 后置处理
* @param req
*/
private void beforeDo(ServletRequest req) {
LOGGER.info("MyFilter.beforeDo()");
}
}
配置拦截器:@WebFilter(“/*”),或者配置在Xml。
进行测试,测试结果如上面。可以看到执行顺序是:拦截器–>过滤器–>AOP切面–>目标方法–>AOP切面–>过滤器–>拦截器。
到这里,doDispatch()方法解读完毕。下一篇文章笔者将解读一下@ResponseBody的处理流程。这@ResponseBody,@RequestBody两个注解是直接返回数据到response中, 不返回View,不进行View对象的相关流程。
四、参考材料
1.Spring源码(版本6.0.11)
2.《spring源码深度解析》(郝佳)
3.《Spring Framework Documentation》(Version 6.0.8)
