本文是Spring源码阅读计划的第十四篇文章,本文主要简单介绍一下Spring MVC的概念,重点介绍DispatcherServlet的初始化过程。
本文源码地址为:https://github.com/zouhuanli/SpringMvcDemo.git.
一、SpringMVC基础
1.什么是SpringMVC?
Spring MVC是Spring提供的轻量级的MVC框架,M-模型model,V-视图view,C-控制器controller。SpringMVC是基于servlet的轻量级的MVC框架,主要用于简化Java
Web应用的开发。
SpringMVC对应的组件分别是:Model主要指Service和DAO,主要功能是数据操作。
Controller主要指DispatcherServlet和controller,主要功能是流程控制。
View主要指JSP、FreeMaker等视图技术,主要功能是视图展示。
SpringMVC的源码模块主要是spring-webmvc,和spring-web。spring-web提供了处理web请求的更高层次的抽象,由Servlet栈的spring-webmvc和Reactive栈的spring-webflux引用。
spring-webmvc的一个核心类就是DispatcherServlet,通常翻译为前端控制器。DispatcherServlet实现了servlet接口,servlet接口的service接口最终在DispatcherServlet的doDispatch方法。
2.DispatcherServlet和ApplicationContext
DispatcherServlet是核心的前端控制器,主要用于Http请求分派。其类关系图如下:
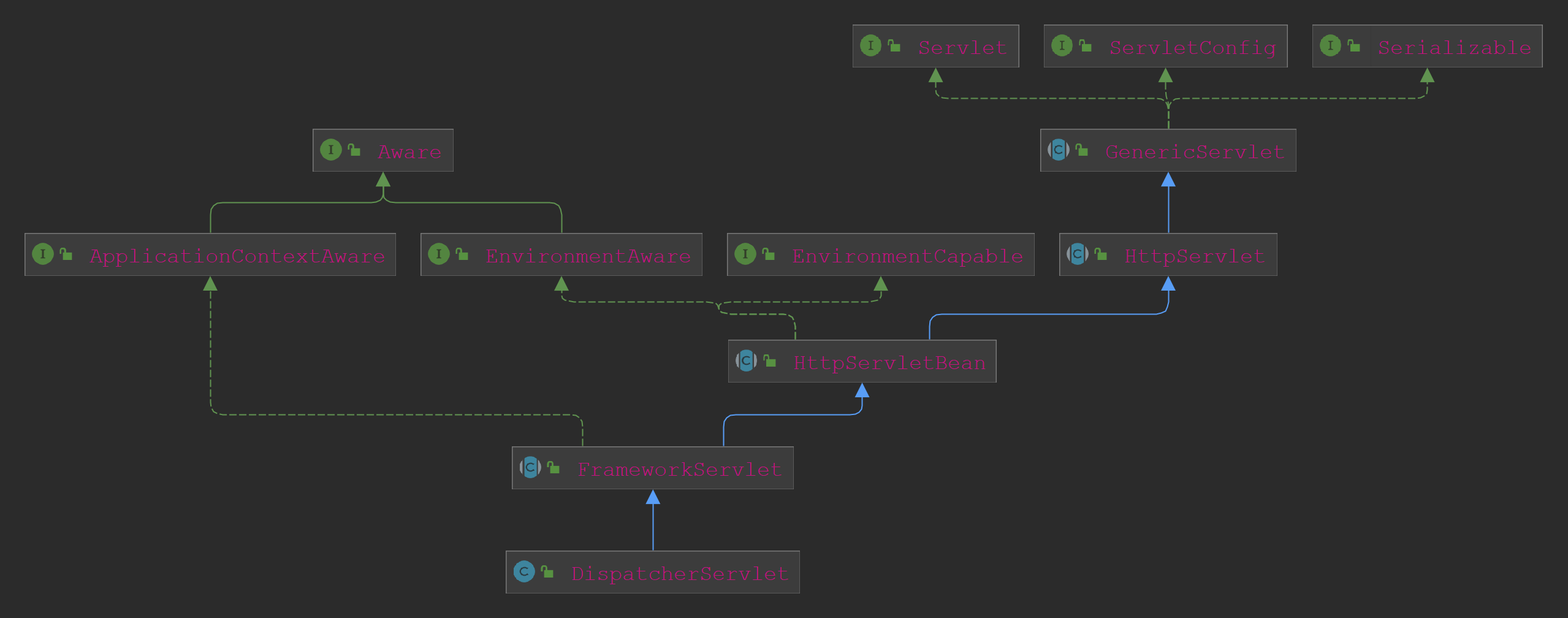
可以看到其顶层接口是Aware和Servlet。
DispatcherServlet和ApplicationContext我们可以看一下官网的这个图片。
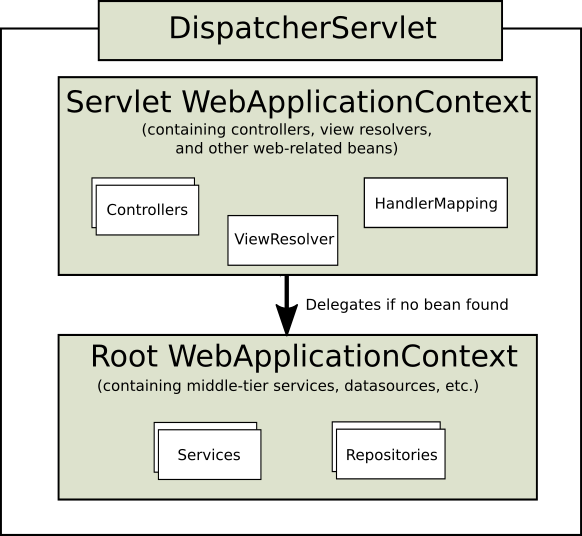
可以看到DispatcherServlet的Context主要是初始化web相关的bean,如Controller、Resolver、handleMapping等。
而RootWebApplicationContext主要是初始化基础Bean,如Service、DAO等,以及其他非web层的组件。
二、SpringMVC的简单示例
这里从一个简单的例子演示SpringMVC的使用。
实体类:
package com.homura.entity;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* entity
* @author zouhl
*/
@Data
public class User implements Serializable {
/**
* 用户ID
*/
private Integer uid;
/**
* 用户姓名
*/
private String uname;
/**
* 密码
*/
private String password;
/**
* 性别
*/
private String gender;
/**
* 手机号码
*/
private String phone;
/**
* 邮件
*/
private String email;
/**
* 地址
*/
private String address;
}
DAO接口:
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
/**
* 查找全部用户
*
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from user")
@ResultMap("BaseResultMap")
List<User> findUserList();
}
Service(接口或实现类):
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userDao;
/**
* 查找用户列表
*
* @return
*/
public List<User> findUserList() throws Exception {
return userDao.findUserList();
}
}
controller类:
@RequestMapping("/user")
@Controller
public class UserController {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserController.class);
@Autowired
private UserServiceImpl userService;
/**
* 查询所有的用户列表
*
* @param request
* @param response
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@RequestMapping("/userList")
public ModelAndView list(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("dateTime", LocalDateTime.now());
modelAndView.addObject("userList", userService.findUserList());
modelAndView.setViewName("userList");
return modelAndView;
}
/**
* 返回Json数据示例
*
* @param requestBody
* @param request
* @param response
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello", method = RequestMethod.POST, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
@ResponseBody
public ResponseEntity<String> hello(@RequestBody String requestBody, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
LOGGER.info("receive requestBody:{} ", requestBody);
String responseJson = "{\"userName\":\"张三\",\"age\":18}";
return new ResponseEntity<>(responseJson, HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
db和mybatis配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${db.driver}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${db.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${db.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${db.password}"/>
<property name="connectionTestQuery" value="${db.connectionTestQuery}"/>
<!-- 生效超时 -->
<property name="validationTimeout" value="${db.validationTimeout}"/>
<!-- 连接只读数据库时配置为true, 保证安全 -->
<property name="readOnly" value="${db.readOnly}"/>
<!-- 等待连接池分配连接的最大时长(毫秒),超过这个时长还没可用的连接则发生SQLException, 缺省:30秒 -->
<property name="connectionTimeout" value="${db.connectionTimeout}"/>
<!-- 一个连接idle状态的最大时长(毫秒),超时则被释放(retired),缺省:10分钟 -->
<property name="idleTimeout" value="${db.idleTimeout}"/>
<!-- 一个连接的生命时长(毫秒),超时而且没被使用则被释放(retired),缺省:30分钟,建议设置比数据库超时时长少30秒,参考MySQL
wait_timeout参数(show variables like '%timeout%';) -->
<property name="maxLifetime" value="${db.maxLifetime}"/>
<!-- 连接池中允许的最大连接数。缺省值:10;推荐的公式:((core_count * 2) + effective_spindle_count) -->
<property name="maximumPoolSize" value="${db.maximumPoolSize}"/>
</bean>
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"/>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:mappers/*.xml"/>
</bean>
<bean id="mapperScanner" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<description>DAO接口所在包,自动扫描</description>
<property name="basePackage" value="com.homura.dao"/>
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
<bean id="sqlSession" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" proxy-target-class="true"/>
</beans>
数据库连接配置:
db.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
db.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sakila?useSSH=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
db.username=sakila
db.password=sakila
db.connectionTestQuery=SELECT 1
db.validationTimeout=3000
db.readOnly=false
db.connectionTimeout=60000
db.idleTimeout=60000
db.maxLifetime=60000
db.maximumPoolSize=10
使用maven编译打包,下载安装配置好tomcat。执行测试。 这里使用IDEA自带的HttpClient进行测试。 测试userList方法。如下。
GET http://localhost:8080/springmvcdemo_war/user/userList
HTTP/1.1 200
Set-Cookie: JSESSIONID=5FFE64E9A092CAACA2F90C74C2FD3A69; Path=/springmvcdemo_war; HttpOnly
Content-Type: text/html;charset=UTF-8
Content-Language: zh-CN
Content-Length: 2386
Date: Thu, 12 Oct 2023 15:31:23 GMT
Keep-Alive: timeout=20
Connection: keep-alive
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>User List</title>
<!-- Bootstrap -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="//cdn.bootcss.com/bootstrap/3.3.5/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<table class="table table-bordered table-striped">
<tr>
<th>id</th>
<th>name</th>
<th>phone</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>3</td>
<td>bb</td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>7</td>
<td>L</td>
<td>12345678900</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>8</td>
<td>123</td>
<td>321</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>11</td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>12</td>
<td>111</td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>13</td>
<td>333</td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>14</td>
<td>666</td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>15</td>
<td>777</td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>16</td>
<td>16</td>
<td>1340</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>17</td>
<td>17</td>
<td>111</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>18</td>
<td>19</td>
<td>222</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Response file saved.
> 2023-10-12T233123.200.html
Response code: 200; Time: 443ms (443 ms); Content length: 2386 bytes (2.39 kB)
再执行hello方法测试,如下。
POST http://localhost:8080/springmvcdemo_war/user/hello
content-type: application/json
charset: utf-8
Content-Length: 51
Connection: Keep-Alive
User-Agent: Apache-HttpClient/4.5.14 (Java/17.0.8)
Cookie: JSESSIONID=5FFE64E9A092CAACA2F90C74C2FD3A69
Accept-Encoding: br,deflate,gzip,x-gzip
{
"name": "李四",
"age": 19,
"id": "1111"
}
HTTP/1.1 200
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
Content-Length: 30
Date: Thu, 12 Oct 2023 15:36:18 GMT
Keep-Alive: timeout=20
Connection: keep-alive
{
"userName": "张三",
"age": 18
}
Response file saved.
> 2023-10-12T233618.200.json
Response code: 200; Time: 3ms (3 ms); Content length: 26 bytes (26 B)
三、DispatcherServlet的初始化流程
DispatcherServlet的初始化流程是此篇文章的主要内容。
在tomcat的StandardWrapper的loadServlet()方法中,有如下代码:
/**
* Load and initialize an instance of this servlet, if there is not already an initialized instance. This can be
* used, for example, to load servlets that are marked in the deployment descriptor to be loaded at server startup
* time.
*
* @return the loaded Servlet instance
*
* @throws ServletException for a Servlet load error
*/
public synchronized Servlet loadServlet() throws ServletException {
Servlet servlet;
try {
InstanceManager instanceManager = ((StandardContext) getParent()).getInstanceManager();
try {
//实例化Servlet
servlet = (Servlet) instanceManager.newInstance(servletClass);
}
// Special handling for ContainerServlet instances
// Note: The InstanceManager checks if the application is permitted
// to load ContainerServlets
if (servlet instanceof ContainerServlet) {
((ContainerServlet) servlet).setWrapper(this);
}
//初始化Servlet
initServlet(servlet);
fireContainerEvent("load", this);
}
return servlet;
}
initServlet(servlet)这行代码开始初始化Servlet,我们从Servlet的init方法作为入口开始研读源码。我们从Servlet—>GenericServlet—>HttpServlet —->HttpServletBean—>FrameworkServlet—>DispatcherServlet这样的顺序阅读init方法的源码。
HttpServletBean的init方法如下。
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
}
这里解析了web.xml的配置信息。
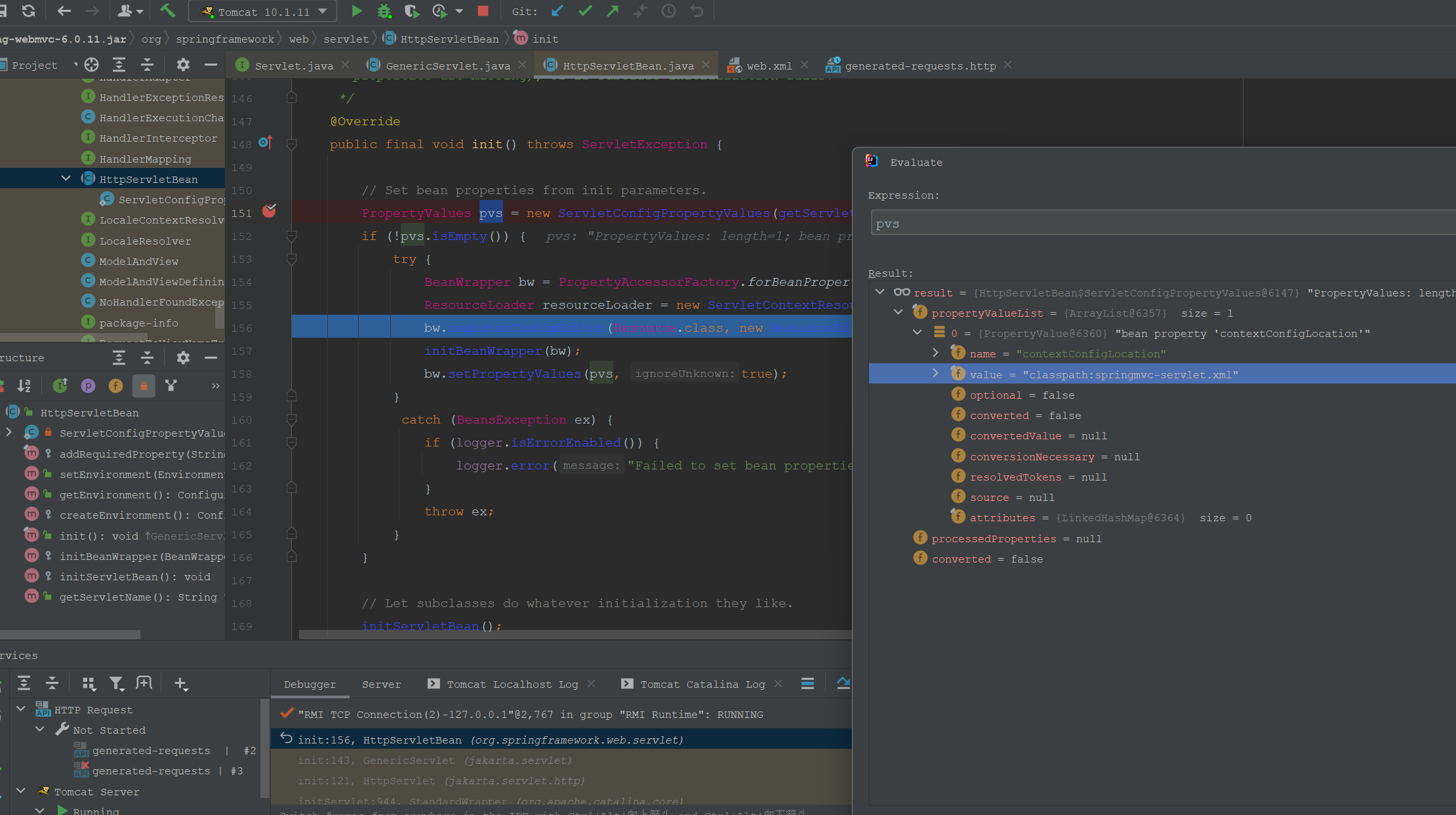
继续跟踪源码,进入FrameworkServlet.initServletBean()方法:
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
}
然后是initWebApplicationContext()方法。
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac && !cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
//刷新方法
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
//ServletContext中设置ApplicationContex引用
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
继续阅读createWebApplicationContext():
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
//创建ApplicationContext
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
wac.setParent(parent);
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
//classpath:springmvc-servlet.xml
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
//配置ApplicationContext
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
再阅读配置ApplicationContext方法,如下。
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
//在ApplicationContext设置ServletContext和ServletConfig
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment cwe) {
cwe.initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
//后置处理,目前是空方法,预留的拓展点
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
//执行初始化器
applyInitializers(wac);
//刷新方法,就是IoC容器那些文章讲到的AbstractApplicationContext的刷新方法
wac.refresh();
}
回到FrameworkServlet,其方法initFrameworkServlet()是一个空方法作为预留的拓展点。
再看onRefresh方法,监听刷新事件的钩子方法。如下:
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
刷新策略组,看名字应该使用了策略模式。
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
这里初始化了所谓的九大组件:MultipartResolver、LocaleResolver、ThemeResolver、HandlerMapping、HandlerAdapter、HandlerExceptionResolver、RequestToViewNameTranslator、ViewResolver、FlashMapManager。 这里debug一下,看下组件的具体Type。
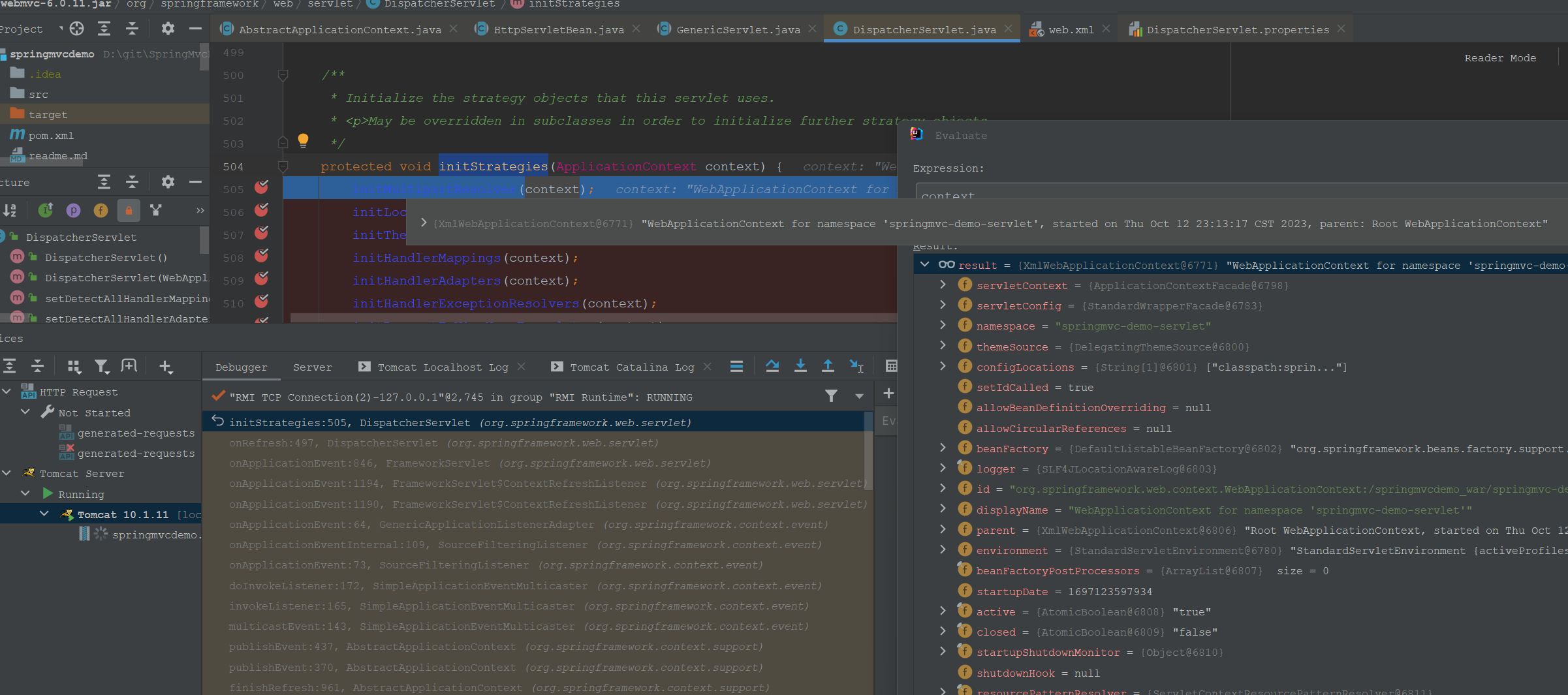
初始化后的实例:
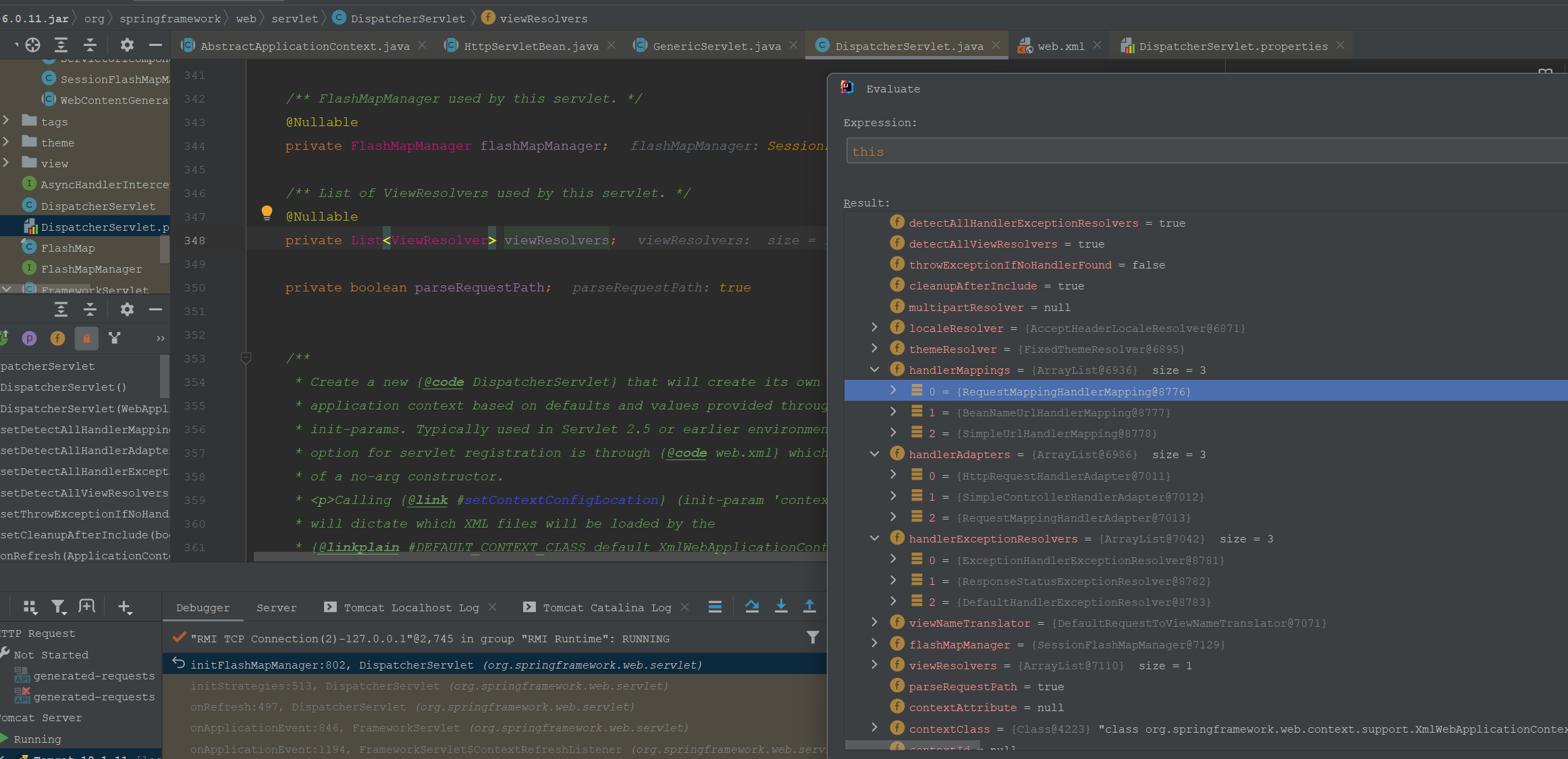
初始化这些组件的默认类型在DispatcherServlet.properties文件里面。
# Default implementation classes for DispatcherServlet's strategy interfaces.
# Used as fallback when no matching beans are found in the DispatcherServlet context.
# Not meant to be customized by application developers.
org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.RouterFunctionMapping
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.HandlerFunctionAdapter
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator
org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager
到此,DispatcherServlet的初始化流程已完成。
四、SpringMVC的请求流程
SpringMVC的请求流程主要就是DispatcherServlet的doDispatch方法。
这里引用开涛老师的一张图,如下:
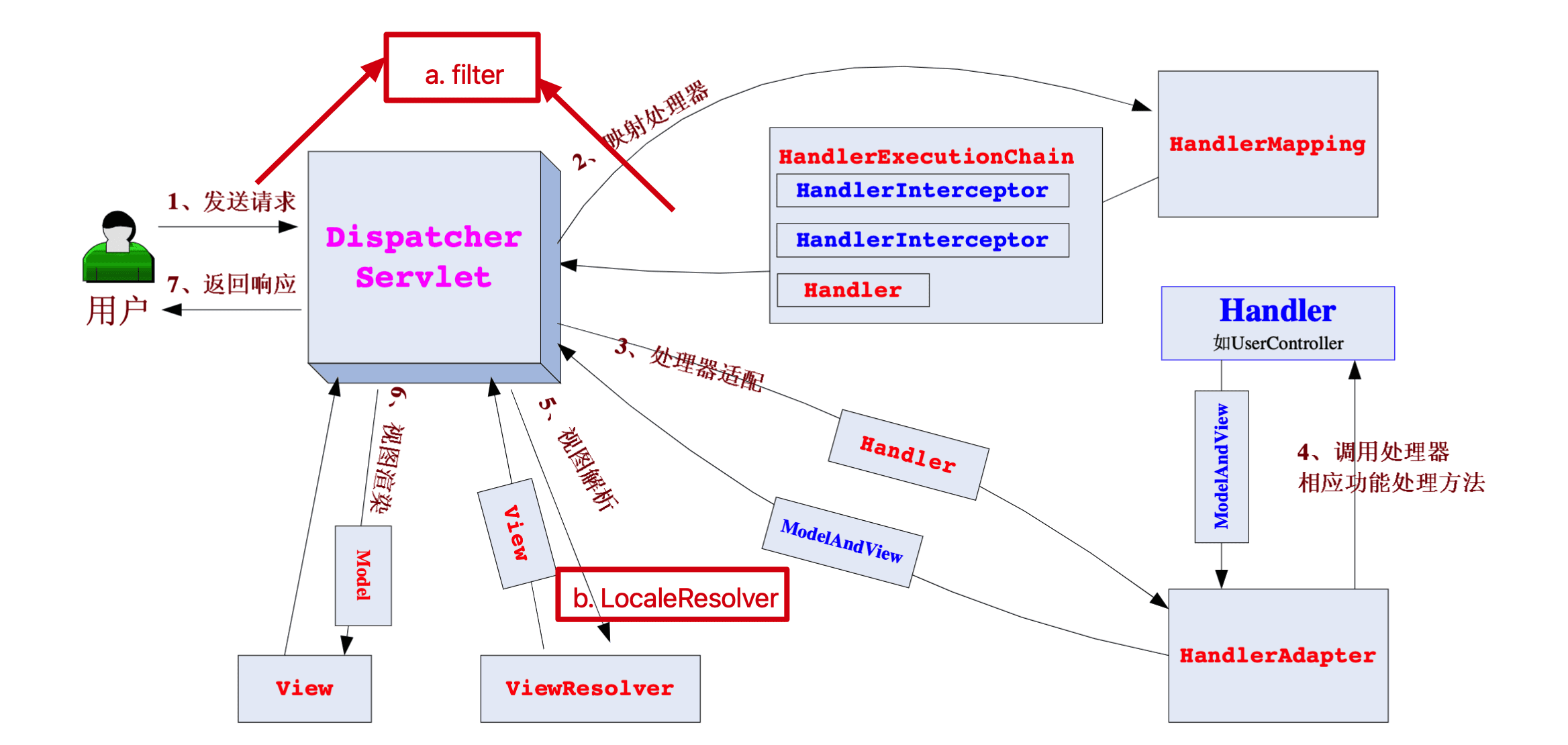
主要流程如下:
- 客户端(前端)发送请求到DispatcherServlet,DispatcherServlet请求handlerMapping,handlerMapping返回HandlerExecutionChain(包含handler/controller,和拦截器列表)。
- DispatcherServlet请求HandlerAdapter,HandlerAdapter请求handler/Controller。handler/Controller执行请求的方法,返回ModelAndView,或者不返回View只返回数据给response。
- DispatcherServlet请求ViewResolver,进行视图解析,得到View对象。
- DispatcherServlet将Model数据应用于View对象,进行视图渲染,返回前端数据。
笔者将在下一篇文章结合DispatcherServlet源码详细介绍请求流程。
五、参考材料
1.Spring源码(版本6.0.11)
2.《spring源码深度解析》(郝佳)
3.《Spring Framework Documentation》(Version 6.0.8)
4.http://jinnianshilongnian.iteye.com/
