本文是Spring源码阅读计划的第十三篇文章,本文简单阅读一下tomcat的源码,认识一下tomcat的启动流程。
之前的文章对Spring的IoC和AOP的源码阅读已经告一段落,后面的文章开始阅读MVC的源码。
一、Tomcat基础
1.Servlet和Tomcat
tomcat是一个轻量级的Servlet容器。那么servlet是什么? servlet是javax/jakarta的一个顶层的接口,其描述如下:
/ **A servlet is a small Java program that runs within a Web server.Servlets receive and respond to requests from Web
*clients,usually across HTTP,the HyperText Transfer Protocol./
wiki的介绍是:
Servlet(Server Applet),全称Java Servlet。是用Java编写的服务器端程序。其主要功能在于交互式地浏览和修改数据,生成动态Web内容。
狭义的Servlet是指Java语言实现的一个接口,广义的Servlet是指任何实现了这个Servlet接口的类,一般情况下,人们将Servlet理解为后者。
Servlet运行于支持Java的应用服务器中。从实现上讲,Servlet可以响应任何类型的请求,但绝大多数情况下Servlet只用来扩展基于HTTP协议的Web服务器。
简而言之,Servlet是一个Java的处理Web网络请求的接口。 Servlet的接口定义非常简单,如下:
public interface Servlet {
/**
* Called by the servlet container to indicate to a servlet that the servlet is being placed into service.
*
* <p>
* The servlet container calls the <code>init</code> method exactly once after instantiating the servlet. The
* <code>init</code> method must complete successfully before the servlet can receive any requests. The container will
* ensure that actions performed in the <code>init</code> method will be visible to any threads that subsequently call
* the <code>service</code> method according to the rules in JSR-133 (i.e. there is a 'happens before' relationship
* between <code>init</code> and <code>service</code>).
*
* <p>
* The servlet container cannot place the servlet into service if the <code>init</code> method
* <ol>
* <li>Throws a <code>ServletException</code>
* <li>Does not return within a time period defined by the Web server
* </ol>
*
*
* @param config a <code>ServletConfig</code> object containing the servlet's configuration and initialization
* parameters
*
* @exception ServletException if an exception has occurred that interferes with the servlet's normal operation
*
* @see UnavailableException
* @see #getServletConfig
*
*/
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException;
/**
*
* Returns a {@link ServletConfig} object, which contains initialization and startup parameters for this servlet. The
* <code>ServletConfig</code> object returned is the one passed to the <code>init</code> method.
*
* <p>
* Implementations of this interface are responsible for storing the <code>ServletConfig</code> object so that this
* method can return it. The {@link GenericServlet} class, which implements this interface, already does this.
*
* @return the <code>ServletConfig</code> object that initializes this servlet
*
* @see #init
*
*/
public ServletConfig getServletConfig();
/**
* Called by the servlet container to allow the servlet to respond to a request.
*
* <p>
* This method is only called after the servlet's <code>init()</code> method has completed successfully.
*
* <p>
* The status code of the response always should be set for a servlet that throws or sends an error.
*
*
* <p>
* Servlets typically run inside multithreaded servlet containers that can handle multiple requests concurrently.
* Developers must be aware to synchronize access to any shared resources such as files, network connections, and as
* well as the servlet's class and instance variables.
*
* @param req the <code>ServletRequest</code> object that contains the client's request
*
* @param res the <code>ServletResponse</code> object that contains the servlet's response
*
* @exception ServletException if an exception occurs that interferes with the servlet's normal operation
*
* @exception IOException if an input or output exception occurs
*
*/
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException;
/**
* Returns information about the servlet, such as author, version, and copyright.
*
* <p>
* The string that this method returns should be plain text and not markup of any kind (such as HTML, XML, etc.).
*
* @return a <code>String</code> containing servlet information
*
*/
public String getServletInfo();
/**
*
* Called by the servlet container to indicate to a servlet that the servlet is being taken out of service. This method
* is only called once all threads within the servlet's <code>service</code> method have exited or after a timeout
* period has passed. After the servlet container calls this method, it will not call the <code>service</code> method
* again on this servlet.
*
* <p>
* This method gives the servlet an opportunity to clean up any resources that are being held (for example, memory, file
* handles, threads) and make sure that any persistent state is synchronized with the servlet's current state in memory.
*
*/
public void destroy();
}
init初始化方法由servlet container去初始化,service方法是核心方法,定义了如何处理Web请求,getServletConfig、getServletInfo是获取配置,destroy是销毁方法。 回到Tomcat,Tomcat是一个Servlet容器,支持Servlet和JSP,也可单独作为Web服务器。话说现在都是前后端分离的架构,JSP真的有必要用嘛?
2.tomcat的顶层架构设计
如图,这个图也是网络找到的,没找到原作者:
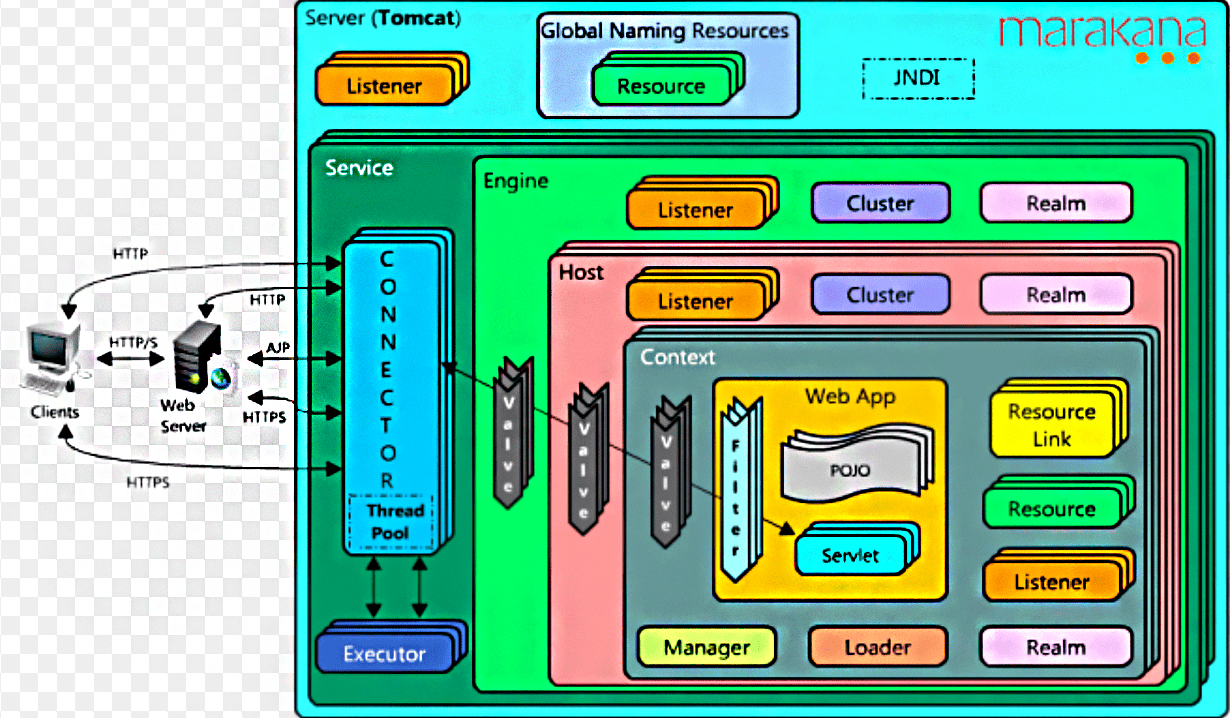
理解一下这些顶层的组件。
Server:服务器,表示整个tomcat服务器,顶层组件。StandardServer是默认实现类。
Service:服务,指的是具体的服务App。Service的默认实现类是StandardService。
Container:容器,看源码有Engine、Host、Context、Wrapper四类。
Connector:连接器,接受Web请求并封装之后转发给Container容器。
其他组件,主要是Tomcat管理和支持的组件:
Manager:管理器。
Logger:日志器。
Loader:加载器,类加载相关。
Pipeline:管道。
Valve:阀门。
Realm:认证和授权。
tomcat主要有这些组件组成,这里不做过多讨论。
二、start流程
Tomcat的启动是从Bootstrap开始。我们开始阅读一下这个类的源码。
/**
* Bootstrap loader for Catalina. This application constructs a class loader
* for use in loading the Catalina internal classes (by accumulating all of the
* JAR files found in the "server" directory under "catalina.home"), and
* starts the regular execution of the container. The purpose of this
* roundabout approach is to keep the Catalina internal classes (and any
* other classes they depend on, such as an XML parser) out of the system
* class path and therefore not visible to application level classes.
*
* @author Craig R. McClanahan
* @author Remy Maucherat
*/
//启动引导类
public final class Bootstrap {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(Bootstrap.class);
/**
* Daemon object used by main.
*/
private static final Object daemonLock = new Object();
private static volatile Bootstrap daemon = null;
private static final File catalinaBaseFile;
private static final File catalinaHomeFile;
private static final Pattern PATH_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("(\"[^\"]*\")|(([^,])*)");
static {
//类初始化方法,这里先忽略
}
// -------------------------------------------------------------- Variables
/**
* Daemon reference.
*/
//真正的启动类的对象
private Object catalinaDaemon = null;
//三种类加载器
ClassLoader commonLoader = null;
ClassLoader catalinaLoader = null;
ClassLoader sharedLoader = null;
// -------------------------------------------------------- Private Methods
//初始化类加载器
private void initClassLoaders() {
try {
commonLoader = createClassLoader("common", null);
if (commonLoader == null) {
// no config file, default to this loader - we might be in a 'single' env.
commonLoader = this.getClass().getClassLoader();
}
catalinaLoader = createClassLoader("server", commonLoader);
sharedLoader = createClassLoader("shared", commonLoader);
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleThrowable(t);
log.error("Class loader creation threw exception", t);
System.exit(1);
}
}
private ClassLoader createClassLoader(String name, ClassLoader parent) throws Exception {
String value = CatalinaProperties.getProperty(name + ".loader");
if ((value == null) || (value.equals(""))) {
return parent;
}
value = replace(value);
List<Repository> repositories = new ArrayList<>();
String[] repositoryPaths = getPaths(value);
for (String repository : repositoryPaths) {
// Check for a JAR URL repository
try {
URI uri = new URI(repository);
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
URL url = uri.toURL();
repositories.add(new Repository(repository, RepositoryType.URL));
continue;
} catch (IllegalArgumentException | MalformedURLException | URISyntaxException e) {
// Ignore
}
// Local repository
if (repository.endsWith("*.jar")) {
repository = repository.substring
(0, repository.length() - "*.jar".length());
repositories.add(new Repository(repository, RepositoryType.GLOB));
} else if (repository.endsWith(".jar")) {
repositories.add(new Repository(repository, RepositoryType.JAR));
} else {
repositories.add(new Repository(repository, RepositoryType.DIR));
}
}
return ClassLoaderFactory.createClassLoader(repositories, parent);
}
/**
* Initialize daemon.
* @throws Exception Fatal initialization error
*/
//初始化Catalina类
public void init() throws Exception {
initClassLoaders();
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(catalinaLoader);
// Load our startup class and call its process() method
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Loading startup class");
}
//Catalina是真正的启动类
Class<?> startupClass = catalinaLoader.loadClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");
Object startupInstance = startupClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
// Set the shared extensions class loader
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Setting startup class properties");
}
String methodName = "setParentClassLoader";
Class<?> paramTypes[] = new Class[1];
paramTypes[0] = Class.forName("java.lang.ClassLoader");
Object paramValues[] = new Object[1];
paramValues[0] = sharedLoader;
Method method =
startupInstance.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);
method.invoke(startupInstance, paramValues);
catalinaDaemon = startupInstance;
}
/**
* Load daemon.
*/
//调用Catalina的load方法
private void load(String[] arguments) throws Exception {
// Call the load() method
String methodName = "load";
Object param[];
Class<?> paramTypes[];
if (arguments==null || arguments.length==0) {
paramTypes = null;
param = null;
} else {
paramTypes = new Class[1];
paramTypes[0] = arguments.getClass();
param = new Object[1];
param[0] = arguments;
}
Method method =
catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Calling startup class " + method);
}
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, param);
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------- Main Program
/**
* Load the Catalina daemon.
* @param arguments Initialization arguments
* @throws Exception Fatal initialization error
*/
public void init(String[] arguments) throws Exception {
init();
load(arguments);
}
/**
* Start the Catalina daemon.
* @throws Exception Fatal start error
*/
//调用Catalina的start方法
public void start() throws Exception {
if (catalinaDaemon == null) {
init();
}
Method method = catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("start", (Class [])null);
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, (Object [])null);
}
/**
* Stop the Catalina Daemon.
* @throws Exception Fatal stop error
*/
//调用Catalina的stop方法
public void stop() throws Exception {
Method method = catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("stop", (Class []) null);
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, (Object []) null);
}
/**
* Stop the standalone server.
* @throws Exception Fatal stop error
*/
//调用Catalina的stopServer方法
public void stopServer() throws Exception {
Method method =
catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("stopServer", (Class []) null);
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, (Object []) null);
}
/**
* Stop the standalone server.
* @param arguments Command line arguments
* @throws Exception Fatal stop error
*/
//调用Catalina的stopServer方法
public void stopServer(String[] arguments) throws Exception {
Object param[];
Class<?> paramTypes[];
if (arguments == null || arguments.length == 0) {
paramTypes = null;
param = null;
} else {
paramTypes = new Class[1];
paramTypes[0] = arguments.getClass();
param = new Object[1];
param[0] = arguments;
}
Method method =
catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("stopServer", paramTypes);
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, param);
}
/**
* Main method and entry point when starting Tomcat via the provided
* scripts.
*
* @param args Command line arguments to be processed
*/
//我们在ps或者启动脚本看到的执行主类
public static void main(String args[]) {
//初始化Catalina对象
synchronized (daemonLock) {
if (daemon == null) {
// Don't set daemon until init() has completed
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
try {
bootstrap.init();
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleThrowable(t);
t.printStackTrace();
return;
}
daemon = bootstrap;
} else {
// When running as a service the call to stop will be on a new
// thread so make sure the correct class loader is used to
// prevent a range of class not found exceptions.
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(daemon.catalinaLoader);
}
}
//这几个都是调用Catalina的方法
try {
String command = "start";
if (args.length > 0) {
command = args[args.length - 1];
}
if (command.equals("startd")) {
args[args.length - 1] = "start";
daemon.load(args);
daemon.start();
} else if (command.equals("stopd")) {
args[args.length - 1] = "stop";
daemon.stop();
} else if (command.equals("start")) {
daemon.setAwait(true);
daemon.load(args);
daemon.start();
if (null == daemon.getServer()) {
System.exit(1);
}
} else if (command.equals("stop")) {
daemon.stopServer(args);
} else if (command.equals("configtest")) {
daemon.load(args);
if (null == daemon.getServer()) {
System.exit(1);
}
System.exit(0);
} else {
log.warn("Bootstrap: command \"" + command + "\" does not exist.");
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Unwrap the Exception for clearer error reporting
if (t instanceof InvocationTargetException &&
t.getCause() != null) {
t = t.getCause();
}
handleThrowable(t);
t.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
我们阅读源码发现bootstrap的启动,关闭方法都是通过catalinaDaemon这个Catalina对象实现。我们继续阅读Catalina类源码。如下,笔者有删减:
/**
* Startup/Shutdown shell program for Catalina. The following command line
* options are recognized:
* <ul>
* <li><b>-config {pathname}</b> - Set the pathname of the configuration file
* to be processed. If a relative path is specified, it will be
* interpreted as relative to the directory pathname specified by the
* "catalina.base" system property. [conf/server.xml]</li>
* <li><b>-help</b> - Display usage information.</li>
* <li><b>-nonaming</b> - Disable naming support.</li>
* <li><b>configtest</b> - Try to test the config</li>
* <li><b>start</b> - Start an instance of Catalina.</li>
* <li><b>stop</b> - Stop the currently running instance of Catalina.</li>
* </ul>
*
* @author Craig R. McClanahan
* @author Remy Maucherat
*/
public class Catalina {
/**
* The string manager for this package.
*/
protected static final StringManager sm =
StringManager.getManager(Constants.Package);
public static final String SERVER_XML = "conf/server.xml";
// ----------------------------------------------------- Instance Variables
/**
* Use await.
*/
protected boolean await = false;
/**
* Pathname to the server configuration file.
*/
protected String configFile = SERVER_XML;
// XXX Should be moved to embedded
/**
* The shared extensions class loader for this server.
*/
protected ClassLoader parentClassLoader =
Catalina.class.getClassLoader();
/**
* The server component we are starting or stopping.
*/
protected Server server = null;
/**
* Use shutdown hook flag.
*/
protected boolean useShutdownHook = true;
/**
* Shutdown hook.
*/
protected Thread shutdownHook = null;
/**
* Is naming enabled ?
*/
protected boolean useNaming = true;
/**
* Prevent duplicate loads.
*/
protected boolean loaded = false;
/**
* Rethrow exceptions on init failure.
*/
protected boolean throwOnInitFailure =
Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE");
/**
* Generate Tomcat embedded code from configuration files.
*/
protected boolean generateCode = false;
/**
* Location of generated sources.
*/
protected File generatedCodeLocation = null;
/**
* Value of the argument.
*/
protected String generatedCodeLocationParameter = null;
/**
* Top package name for generated source.
*/
protected String generatedCodePackage = "catalinaembedded";
/**
* Use generated code as a replacement for configuration files.
*/
protected boolean useGeneratedCode = false;
// ----------------------------------------------------------- Constructors
// ------------------------------------------------------ Protected Methods
/**
* Return a File object representing our configuration file.
* @return the main configuration file
*/
protected File configFile() {
File file = new File(configFile);
if (!file.isAbsolute()) {
file = new File(Bootstrap.getCatalinaBase(), configFile);
}
return file;
}
protected void parseServerXml(boolean start) {
// Set configuration source
ConfigFileLoader.setSource(new CatalinaBaseConfigurationSource(Bootstrap.getCatalinaBaseFile(), getConfigFile()));
File file = configFile();
// Init source location
File serverXmlLocation = null;
String xmlClassName = null;
if (generateCode || useGeneratedCode) {
xmlClassName = start ? generatedCodePackage + ".ServerXml" : generatedCodePackage + ".ServerXmlStop";
}
ServerXml serverXml = null;
if (useGeneratedCode) {
serverXml = (ServerXml) Digester.loadGeneratedClass(xmlClassName);
}
if (serverXml != null) {
serverXml.load(this);
}
}
public void stopServer() {
stopServer(null);
}
public void stopServer(String[] arguments) {
Server s = getServer();
s.stop();
s.destroy();
}
/**
* Start a new server instance.
*/
public void load() {
if (loaded) {
return;
}
loaded = true;
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
// Before digester - it may be needed
initNaming();
// Parse main server.xml
parseServerXml(true);
Server s = getServer();
if (s == null) {
return;
}
getServer().setCatalina(this);
getServer().setCatalinaHome(Bootstrap.getCatalinaHomeFile());
getServer().setCatalinaBase(Bootstrap.getCatalinaBaseFile());
// Stream redirection
initStreams();
// Start the new server
getServer().init();
}
/*
* Load using arguments
*/
public void load(String args[]) {
load();
}
/**
* Start a new server instance.
*/
public void start() {
if (getServer() == null) {
load();
}
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
// Start the new server
try {
getServer().start();
}
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(shutdownHook);
if (await) {
await();
stop();
}
}
/**
* Stop an existing server instance.
*/
public void stop() {
s.stop();
s.destroy();
}
/**
* Await and shutdown.
*/
public void await() {
getServer().await();
}
public interface ServerXml {
void load(Catalina catalina);
}
// --------------------------------------- CatalinaShutdownHook Inner Class
// XXX Should be moved to embedded !
/**
* Shutdown hook which will perform a clean shutdown of Catalina if needed.
*/
protected class CatalinaShutdownHook extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
if (getServer() != null) {
Catalina.this.stop();
}
} catch (Throwable ex) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(ex);
log.error(sm.getString("catalina.shutdownHookFail"), ex);
} finally {
// If JULI is used, shut JULI down *after* the server shuts down
// so log messages aren't lost
LogManager logManager = LogManager.getLogManager();
if (logManager instanceof ClassLoaderLogManager) {
((ClassLoaderLogManager) logManager).shutdown();
}
}
}
}
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(Catalina.class);
}
我们看到先load加载和初始化Server,再调用Server的start启动方法。我们继续阅读StandardServer的start方法。
@Override
public final synchronized void start() throws LifecycleException {
//检查状态,初始化或者停止
if (state.equals(LifecycleState.NEW)) {
init();
} else if (state.equals(LifecycleState.FAILED)) {
stop();
} else if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.INITIALIZED) &&
!state.equals(LifecycleState.STOPPED)) {
invalidTransition(BEFORE_START_EVENT);
}
try {
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP, null, false);
//真正的启动方法
startInternal();
}
}
看来我们要继续阅读startInternal方法,如下。
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
fireLifecycleEvent(CONFIGURE_START_EVENT, null);
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Initialize utility executor
synchronized (utilityExecutorLock) {
reconfigureUtilityExecutor(getUtilityThreadsInternal(utilityThreads));
register(utilityExecutor, "type=UtilityExecutor");
}
globalNamingResources.start();
// Start our defined Services
//启动service列表
synchronized (servicesLock) {
for (Service service : services) {
service.start();
}
}
if (periodicEventDelay > 0) {
monitorFuture = getUtilityExecutor().scheduleWithFixedDelay(this::startPeriodicLifecycleEvent, 0, 60,
TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
接下来我们继续阅读Service的start流程。我们继续阅读StandardService的startInternal方法。
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(sm.getString("standardService.start.name", this.name));
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Start our defined Container first
if (engine != null) {
synchronized (engine) {
engine.start();
}
}
synchronized (executors) {
for (Executor executor : executors) {
executor.start();
}
}
mapperListener.start();
// Start our defined Connectors second
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
for (Connector connector : connectors) {
// If it has already failed, don't try and start it
if (connector.getState() != LifecycleState.FAILED) {
connector.start();
}
}
}
}
接下来阅读这里启动了三个组件Engine-引擎,Executor-线程池,Connector-连接器。 我们继续阅读Connector的启动方法。
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Validate settings before starting
String id = (protocolHandler != null) ? protocolHandler.getId() : null;
if (id == null && getPortWithOffset() < 0) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("coyoteConnector.invalidPort", Integer.valueOf(getPortWithOffset())));
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Configure the utility executor before starting the protocol handler
if (protocolHandler != null && service != null) {
protocolHandler.setUtilityExecutor(service.getServer().getUtilityExecutor());
}
try {
//启动协议处理ProtocolHandler
protocolHandler.start();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Includes NPE - protocolHandler will be null for invalid protocol if throwOnFailure is false
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerStartFailed"), e);
}
}
我们继续跟踪。进入ProtocolHandler类。
@Override
public void start() throws Exception {
if (getLog().isInfoEnabled()) {
getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.start", getName()));
logPortOffset();
}
endpoint.start();
monitorFuture = getUtilityExecutor().scheduleWithFixedDelay(() -> {
startAsyncTimeout();
}, 0, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
这里主要是Endpoint的启动方法。
StandardEngine添加Host到children这个map中,然后依次启动Host、Context。
三、参考材料
1.Tomcat源码(apache-tomcat-11.0.0-M9)
