本文是mybatis源码阅读计划的第二篇文章,本文简单介绍一下Mybatis的初始化过程,也就是解读一下Configuration和SqlSessionFactory的启动过程。
本文源码地址为:https://github.com/zouhuanli/MySpringBoot.git。
一、概述
Configuration类是是mybatis的核心配置类,保存了mybatis所有配置信息。既包括mybatis-config.xml和配置文件的配置如cacheEnabled,也包括解析之后生成的配置如mapperRegistry、interceptorChain。
“每个基于MyBatis的应用都是以一个SqlSessionFactory的实例为核心的。SqlSessionFactory的实例可以通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder获得。而SqlSessionFactoryBuilder则可以从XML配置文件或一个预先配置的Configuration实例来构建出SqlSessionFactory实例”。
SqlSessionFactory可以由SqlSessionFactoryBuilder或者SqlSessionFactoryBean创建。
SqlSessionFactoryBean#getObject方法如下。
@Override
public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception {
if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) {
afterPropertiesSet();
}
return this.sqlSessionFactory;
}
SqlSessionFactory顾名思义,就是用来创建SqlSession对象的。SqlSession提供CRUD、提交、回滚、获取Mapper等顶层API。
SqlSessionFactory一般是一个数据源创建一次,不需要多次创建。而SqlSession的实例不是线程安全的,因此是不能被共享的,所以它的最佳的作用域是请求或方法作用域。也就表明SqlSession应该随时创建后就销毁。
但SqlSessionTemplate实现了SqlSession,其被配置为了单例对象。SqlSessionTemplate并没有共用一个SqlSession,而是通过SqlSessionInterceptor创建代理对象每次执行Mapper的SQL方法时都创建一下新的SqlSession。
SqlSessionInterceptor如下:
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType, SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
try {
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
if (!isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
// force commit even on non-dirty sessions because some databases require
// a commit/rollback before calling close()
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
return result;
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
}
}
二、SqlSessionFactory创建过程
我们从MybatisAutoConfiguration#sqlSessionFactory方法作为入口,开始解读SqlSessionFactory创建过程。
sqlSessionFactory方法如下:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
if (properties.getConfiguration() == null || properties.getConfiguration().getVfsImpl() == null) {
factory.setVfs(SpringBootVFS.class);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation())) {
factory.setConfigLocation(this.resourceLoader.getResource(this.properties.getConfigLocation()));
}
applyConfiguration(factory);
if (this.properties.getConfigurationProperties() != null) {
factory.setConfigurationProperties(this.properties.getConfigurationProperties());
}
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.interceptors)) {
factory.setPlugins(this.interceptors);
}
if (this.databaseIdProvider != null) {
factory.setDatabaseIdProvider(this.databaseIdProvider);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeAliasesPackage())) {
factory.setTypeAliasesPackage(this.properties.getTypeAliasesPackage());
}
if (this.properties.getTypeAliasesSuperType() != null) {
factory.setTypeAliasesSuperType(this.properties.getTypeAliasesSuperType());
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeHandlersPackage())) {
factory.setTypeHandlersPackage(this.properties.getTypeHandlersPackage());
}
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.typeHandlers)) {
factory.setTypeHandlers(this.typeHandlers);
}
Resource[] mapperLocations = this.properties.resolveMapperLocations();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(mapperLocations)) {
factory.setMapperLocations(mapperLocations);
}
Set<String> factoryPropertyNames = Stream
.of(new BeanWrapperImpl(SqlSessionFactoryBean.class).getPropertyDescriptors()).map(PropertyDescriptor::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
Class<? extends LanguageDriver> defaultLanguageDriver = this.properties.getDefaultScriptingLanguageDriver();
if (factoryPropertyNames.contains("scriptingLanguageDrivers") && !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.languageDrivers)) {
// Need to mybatis-spring 2.0.2+
factory.setScriptingLanguageDrivers(this.languageDrivers);
if (defaultLanguageDriver == null && this.languageDrivers.length == 1) {
defaultLanguageDriver = this.languageDrivers[0].getClass();
}
}
if (factoryPropertyNames.contains("defaultScriptingLanguageDriver")) {
// Need to mybatis-spring 2.0.2+
factory.setDefaultScriptingLanguageDriver(defaultLanguageDriver);
}
applySqlSessionFactoryBeanCustomizers(factory);
return factory.getObject();
}
这里基本就是读取MybatisProperties,设置SqlSessionFactoryBean对应的配置项。
再进入SqlSessionFactoryBean#getObject方法。
@Override
public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception {
if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) {
afterPropertiesSet();
}
return this.sqlSessionFactory;
}
此处使用afterPropertiesSet()创建sqlSessionFactory。
继续进入buildSqlSessionFactory方法,这里就是创建Configuration和sqlSessionFactory的方法了。
三、Configuration的创建过程
buildSqlSessionFactory方法如下。
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws Exception {
final Configuration targetConfiguration;
//创建xmlConfigBuilder,XML配置文件的解析器。解析mybatis-config.xml
XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null;
if (this.configuration != null) {
targetConfiguration = this.configuration;
if (targetConfiguration.getVariables() == null) {
targetConfiguration.setVariables(this.configurationProperties);
} else if (this.configurationProperties != null) {
targetConfiguration.getVariables().putAll(this.configurationProperties);
}
} else if (this.configLocation != null) {
xmlConfigBuilder = new XMLConfigBuilder(this.configLocation.getInputStream(), null, this.configurationProperties);
targetConfiguration = xmlConfigBuilder.getConfiguration();
} else {
LOGGER.debug(
() -> "Property 'configuration' or 'configLocation' not specified, using default MyBatis Configuration");
targetConfiguration = new Configuration();
Optional.ofNullable(this.configurationProperties).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setVariables);
}
//设置配置:objectFactory、objectWrapperFactory、vfs
Optional.ofNullable(this.objectFactory).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setObjectFactory);
Optional.ofNullable(this.objectWrapperFactory).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setObjectWrapperFactory);
Optional.ofNullable(this.vfs).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setVfsImpl);
//注册别名列表
if (hasLength(this.typeAliasesPackage)) {
scanClasses(this.typeAliasesPackage, this.typeAliasesSuperType).stream()
.filter(clazz -> !clazz.isAnonymousClass()).filter(clazz -> !clazz.isInterface())
.filter(clazz -> !clazz.isMemberClass()).forEach(targetConfiguration.getTypeAliasRegistry()::registerAlias);
}
if (!isEmpty(this.typeAliases)) {
Stream.of(this.typeAliases).forEach(typeAlias -> {
targetConfiguration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAlias(typeAlias);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered type alias: '" + typeAlias + "'");
});
}
//注册插件/拦截器,如PageHelper
if (!isEmpty(this.plugins)) {
Stream.of(this.plugins).forEach(plugin -> {
targetConfiguration.addInterceptor(plugin);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered plugin: '" + plugin + "'");
});
}
//注册类型处理器
if (hasLength(this.typeHandlersPackage)) {
scanClasses(this.typeHandlersPackage, TypeHandler.class).stream().filter(clazz -> !clazz.isAnonymousClass())
.filter(clazz -> !clazz.isInterface()).filter(clazz -> !Modifier.isAbstract(clazz.getModifiers()))
.forEach(targetConfiguration.getTypeHandlerRegistry()::register);
}
if (!isEmpty(this.typeHandlers)) {
Stream.of(this.typeHandlers).forEach(typeHandler -> {
targetConfiguration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(typeHandler);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered type handler: '" + typeHandler + "'");
});
}
targetConfiguration.setDefaultEnumTypeHandler(defaultEnumTypeHandler);
//注册脚本语言
if (!isEmpty(this.scriptingLanguageDrivers)) {
Stream.of(this.scriptingLanguageDrivers).forEach(languageDriver -> {
targetConfiguration.getLanguageRegistry().register(languageDriver);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered scripting language driver: '" + languageDriver + "'");
});
}
Optional.ofNullable(this.defaultScriptingLanguageDriver)
.ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setDefaultScriptingLanguage);
//数据库厂商标识
if (this.databaseIdProvider != null) {// fix #64 set databaseId before parse mapper xmls
try {
targetConfiguration.setDatabaseId(this.databaseIdProvider.getDatabaseId(this.dataSource));
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new IOException("Failed getting a databaseId", e);
}
}
Optional.ofNullable(this.cache).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::addCache);
if (xmlConfigBuilder != null) {
try {
//xml配置解析
xmlConfigBuilder.parse();
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Parsed configuration file: '" + this.configLocation + "'");
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IOException("Failed to parse config resource: " + this.configLocation, ex);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
targetConfiguration.setEnvironment(new Environment(this.environment,
this.transactionFactory == null ? new SpringManagedTransactionFactory() : this.transactionFactory,
this.dataSource));
//解析XMLMapper。如示例工程的UserMapper.xml
if (this.mapperLocations != null) {
if (this.mapperLocations.length == 0) {
LOGGER.warn(() -> "Property 'mapperLocations' was specified but matching resources are not found.");
} else {
for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) {
if (mapperLocation == null) {
continue;
}
try {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
targetConfiguration, mapperLocation.toString(), targetConfiguration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'");
}
}
} else {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified.");
}
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(targetConfiguration);
}
可以看到这个方法是解析了所有mybatis的配置,用以创建Configuration对象。
3.1 基本配置解析
mybatis的配置如下:
- properties(属性)
- settings(设置)
- typeAliases(类型别名)
- typeHandlers(类型处理器)
- objectFactory(对象工厂)
- plugins(插件)
- environments(环境配置)
- databaseIdProvider(数据库厂商标识)
- mappers(映射器)
和上面方法的顺序一样。
例如下面是解析objectFactory、typeAliases
Optional.ofNullable(this.objectFactory).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setObjectFactory);
Optional.ofNullable(this.objectWrapperFactory).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setObjectWrapperFactory);
Optional.ofNullable(this.vfs).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setVfsImpl);
if (hasLength(this.typeAliasesPackage)) {
scanClasses(this.typeAliasesPackage, this.typeAliasesSuperType).stream()
.filter(clazz -> !clazz.isAnonymousClass()).filter(clazz -> !clazz.isInterface())
.filter(clazz -> !clazz.isMemberClass()).forEach(targetConfiguration.getTypeAliasRegistry()::registerAlias);
}
if (!isEmpty(this.typeAliases)) {
Stream.of(this.typeAliases).forEach(typeAlias -> {
targetConfiguration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAlias(typeAlias);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered type alias: '" + typeAlias + "'");
});
}
3.2 XML配置解析
来到这行代码:
xmlConfigBuilder.parse();
再来到parseConfiguration方法,如下:
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
// issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
这里是解析mybatis-config.xml里面的XML配置项,我们可以看到这个xml配置是在MybatisProperties之后的,所以这里xml配置会覆盖MybatisProperties设置的。
3.3 XMLMapper解析
我们继续进入这行代码:
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
targetConfiguration, mapperLocation.toString(), targetConfiguration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
这里解析了XMLMapper文件,如UserMapper.xml。
继续来到parse方法:
public void parse() {
//新的XMLMapper解析
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
继续来到configurationElement,这个解析XMLMapper的方法。
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
//命名空间
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.isEmpty()) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
//解析cache-ref、cache元素
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
//解析parameterMap元素,列表
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
//解析resultMap元素,列表
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
//解析Sql元素,列表。Sql是可以复用的SQL片段
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
//解析select|insert|update|delete元素,CRUD执行SQL的方法
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
我们再进入SQL方法的解析源码:
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list) {
if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {
buildStatementFromContext(list, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
buildStatementFromContext(list, null);
}
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context,
requiredDatabaseId);
try {
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}
最后来到了statementParser.parseStatementNode()这个方法,解析一个select|insert|update|delete元素。
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
StatementType statementType = StatementType
.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
if (resultTypeClass == null && resultMap == null) {
resultTypeClass = MapperAnnotationBuilder.getMethodReturnType(builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace(), id);
}
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
if (resultSetTypeEnum == null) {
resultSetTypeEnum = configuration.getDefaultResultSetType();
}
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
boolean dirtySelect = context.getBooleanAttribute("affectData", Boolean.FALSE);
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType, fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap,
parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass, resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets, dirtySelect);
}
这里具体解析一个select|insert|update|delete方法,解析其内部的各种属性。里面的SQL语句解析为sqlSource对象。
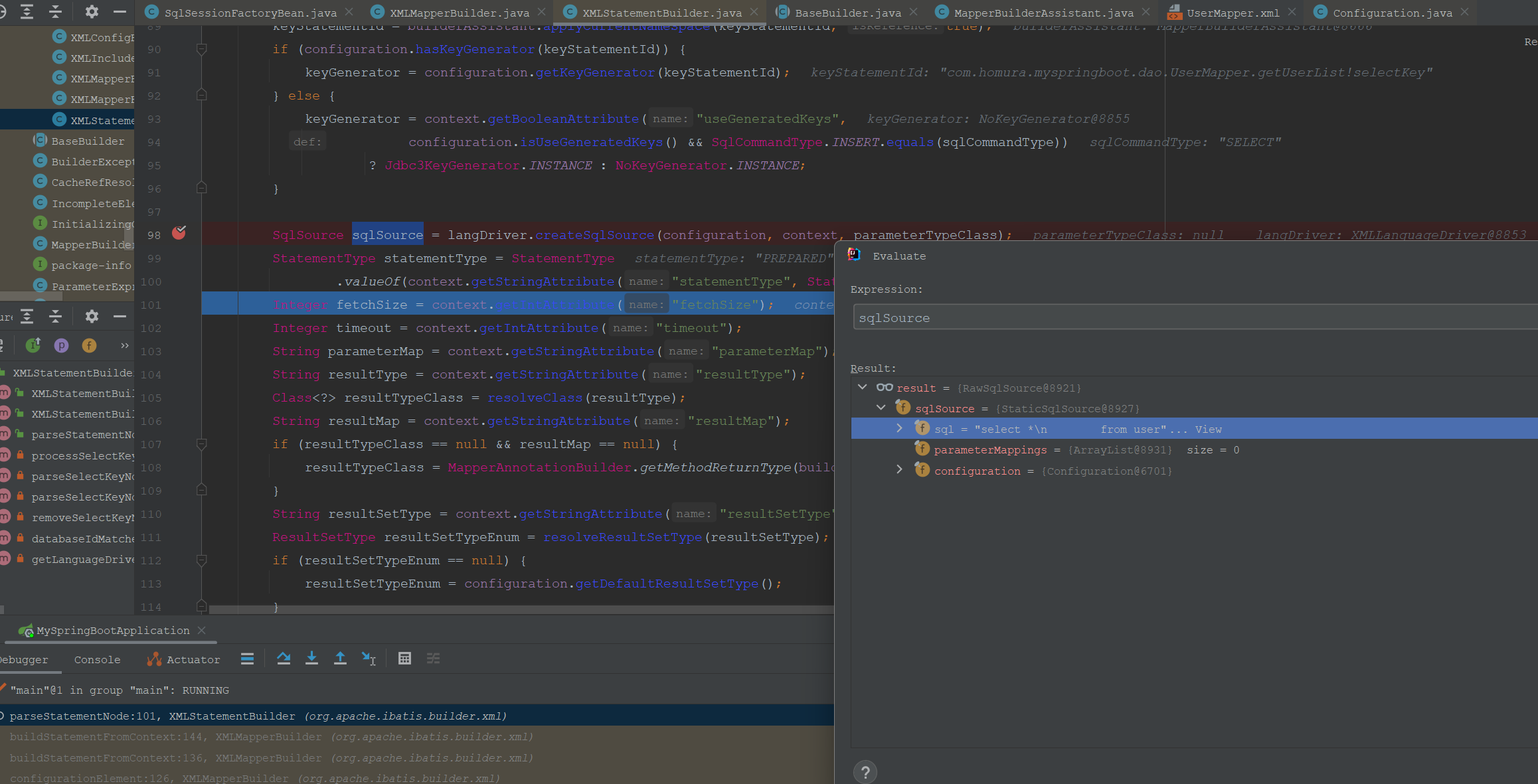
然后将SQL方法的元素解析为MappedStatement,存入mappedStatements集合。
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(String id, SqlSource sqlSource, StatementType statementType,
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType, Integer fetchSize, Integer timeout, String parameterMap, Class<?> parameterType,
String resultMap, Class<?> resultType, ResultSetType resultSetType, boolean flushCache, boolean useCache,
boolean resultOrdered, KeyGenerator keyGenerator, String keyProperty, String keyColumn, String databaseId,
LanguageDriver lang, String resultSets, boolean dirtySelect) {
if (unresolvedCacheRef) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Cache-ref not yet resolved");
}
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType)
.resource(resource).fetchSize(fetchSize).timeout(timeout).statementType(statementType)
.keyGenerator(keyGenerator).keyProperty(keyProperty).keyColumn(keyColumn).databaseId(databaseId).lang(lang)
.resultOrdered(resultOrdered).resultSets(resultSets)
.resultMaps(getStatementResultMaps(resultMap, resultType, id)).resultSetType(resultSetType)
.flushCacheRequired(flushCache).useCache(useCache).cache(currentCache).dirtySelect(dirtySelect);
ParameterMap statementParameterMap = getStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, id);
if (statementParameterMap != null) {
statementBuilder.parameterMap(statementParameterMap);
}
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}
public void addMappedStatement(MappedStatement ms) {
mappedStatements.put(ms.getId(), ms);
}
MappedStatement对象如下:
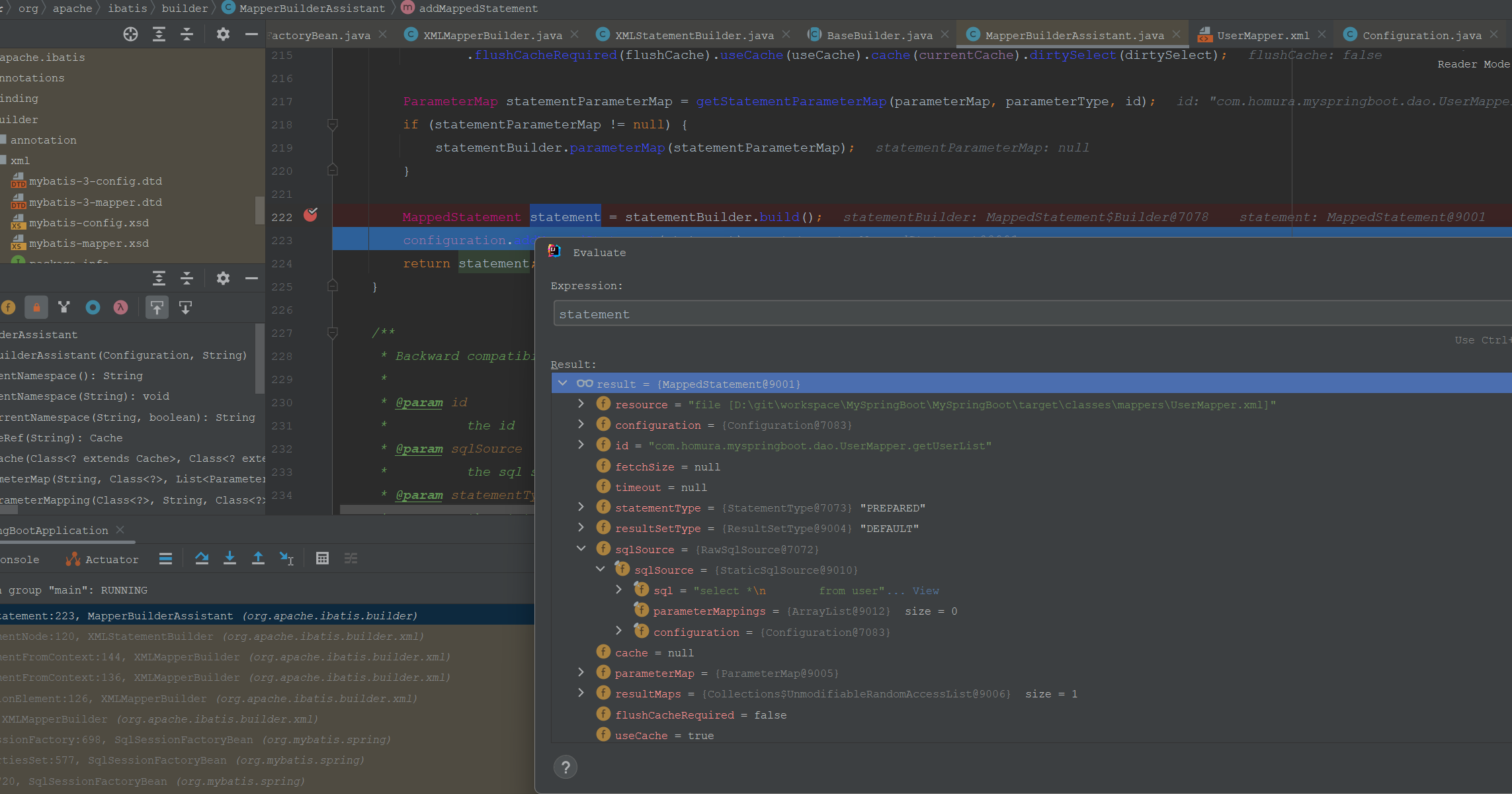
这里一个SQL方法就解析为了一个MappedStatement对象。注意MappedStatement是namespace+ID唯一的,MapperInterface的方法名字不能重复的。
再回到XMLMapperBuilder#parse()方法,进入bindMapperForNamespace()方法。
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
if (namespace != null) {
Class<?> boundType = null;
try {
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ignore, bound type is not required
}
if (boundType != null && !configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we set a flag
// to prevent loading again this resource from the mapper interface
// look at MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResource
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
这里注册了Mapper接口到mapperRegistry。
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
最后是存入knownMappers这个集合。
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
这里knownMappers存入的对象是MapperProxyFactory,用以创建MapperProxy对象的工厂。
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
阅读newInstance方法,这里创建了mapperInterface的代理对象。
继续来到这行代码:
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
这里解析了MapperInterface接口的方法。
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
//解析每个方法
for (Method method : type.getMethods()) {
if (!canHaveStatement(method)) {
continue;
}
if (getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, Select.class, SelectProvider.class).isPresent()
&& method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class) == null) {
//解析ResultMap,解析完成后存入resultMaps集合
parseResultMap(method);
}
try {
//解析SQL方法
parseStatement(method);
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}
这里parseStatement解析SQL方法,如:
@Select("select * from user")
@ResultMap("BaseResultMap")
List<User> findAll();
这里依旧是从接口方法+注解解析成MappedStatement:
void parseStatement(Method method) {
final Class<?> parameterTypeClass = getParameterType(method);
final LanguageDriver languageDriver = getLanguageDriver(method);
getAnnotationWrapper(method, true, statementAnnotationTypes).ifPresent(statementAnnotation -> {
//解析SQL语句,解析的参数会替换为?,参数化时候设置实参
final SqlSource sqlSource = buildSqlSource(statementAnnotation.getAnnotation(), parameterTypeClass,
languageDriver, method);
final SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = statementAnnotation.getSqlCommandType();
final Options options = getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, Options.class).map(x -> (Options) x.getAnnotation())
.orElse(null);
final String mappedStatementId = type.getName() + "." + method.getName();
final KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyProperty = null;
String keyColumn = null;
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType) || SqlCommandType.UPDATE.equals(sqlCommandType)) {
// first check for SelectKey annotation - that overrides everything else
SelectKey selectKey = getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, SelectKey.class)
.map(x -> (SelectKey) x.getAnnotation()).orElse(null);
if (selectKey != null) {
keyGenerator = handleSelectKeyAnnotation(selectKey, mappedStatementId, getParameterType(method),
languageDriver);
keyProperty = selectKey.keyProperty();
} else if (options == null) {
keyGenerator = configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
} else {
keyGenerator = options.useGeneratedKeys() ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
keyProperty = options.keyProperty();
keyColumn = options.keyColumn();
}
} else {
keyGenerator = NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
Integer fetchSize = null;
Integer timeout = null;
StatementType statementType = StatementType.PREPARED;
ResultSetType resultSetType = configuration.getDefaultResultSetType();
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = !isSelect;
boolean useCache = isSelect;
if (options != null) {
if (FlushCachePolicy.TRUE.equals(options.flushCache())) {
flushCache = true;
} else if (FlushCachePolicy.FALSE.equals(options.flushCache())) {
flushCache = false;
}
useCache = options.useCache();
// issue #348
fetchSize = options.fetchSize() > -1 || options.fetchSize() == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? options.fetchSize() : null;
timeout = options.timeout() > -1 ? options.timeout() : null;
statementType = options.statementType();
if (options.resultSetType() != ResultSetType.DEFAULT) {
resultSetType = options.resultSetType();
}
}
String resultMapId = null;
if (isSelect) {
ResultMap resultMapAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class);
if (resultMapAnnotation != null) {
resultMapId = String.join(",", resultMapAnnotation.value());
} else {
resultMapId = generateResultMapName(method);
}
}
//注册MappedStatement(
assistant.addMappedStatement(mappedStatementId, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType, fetchSize, timeout,
// ParameterMapID
null, parameterTypeClass, resultMapId, getReturnType(method, type), resultSetType, flushCache, useCache,
// TODO gcode issue #577
false, keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, statementAnnotation.getDatabaseId(), languageDriver,
// ResultSets
options != null ? nullOrEmpty(options.resultSets()) : null, statementAnnotation.isDirtySelect());
});
}
最后融合XML的SQL方法和MapperInterface的SQL方法的mappedStatements集合如下。
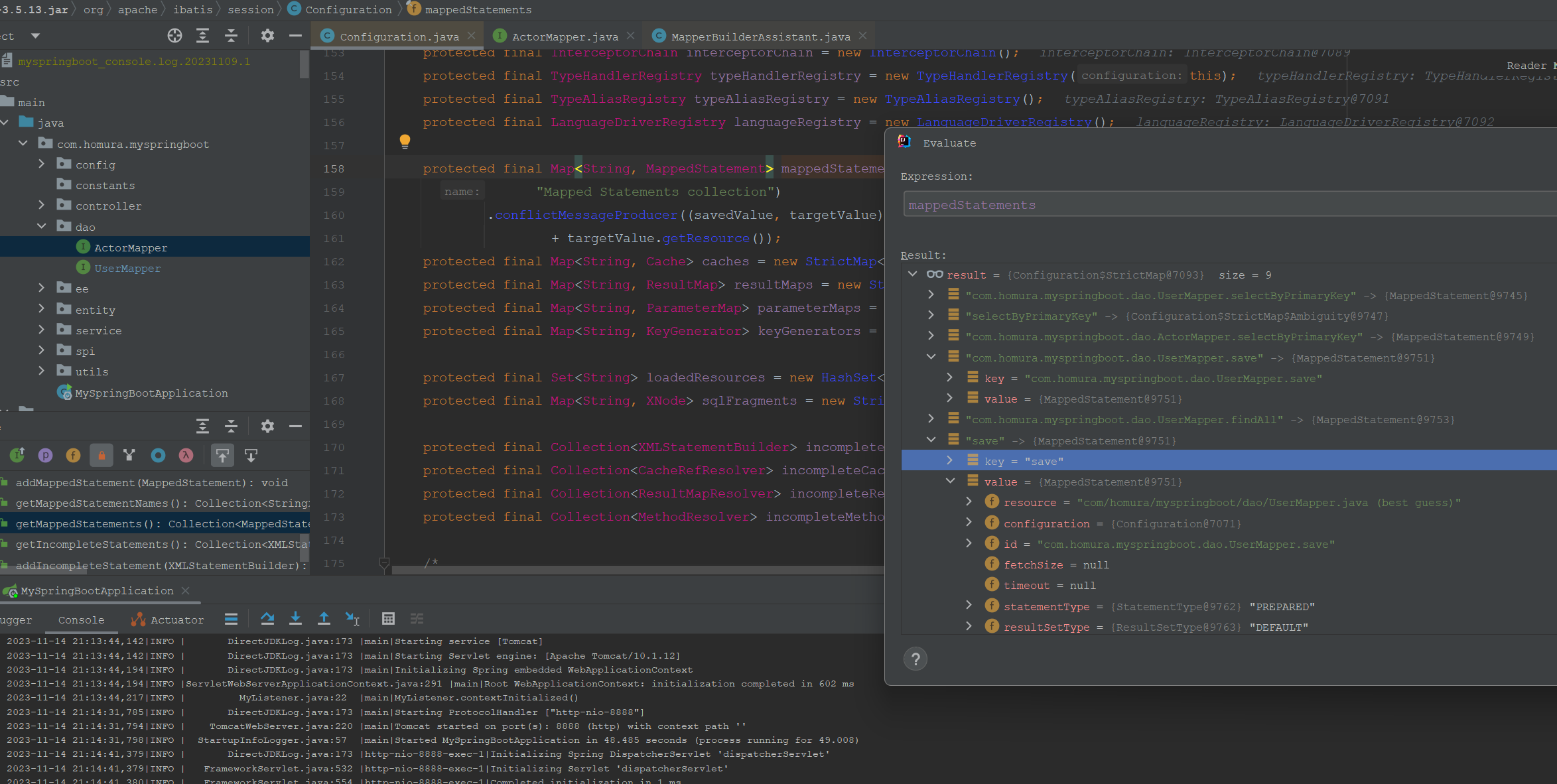
XMLMapper不是必须的,不过一些复杂的动态SQL使用XML会比较简单。官方的解释是:
映射器类是 Java 类,它们包含 SQL 映射注解从而避免依赖 XML 映射文件。不过,由于 Java 注解的一些限制以及某些 MyBatis 映射的复杂性,要使用大多数高级映射(比如:嵌套联合映射),仍然需要使用 XML 映射文件进行映射。
这里要注意的一点是看上面的图,mapperStatements里面是有短方法作为key的。如果有两个短方法相同,而获取MapperStatement使用短方法会报错。因此使获取MapperStatement要使用namespace+ID获取。
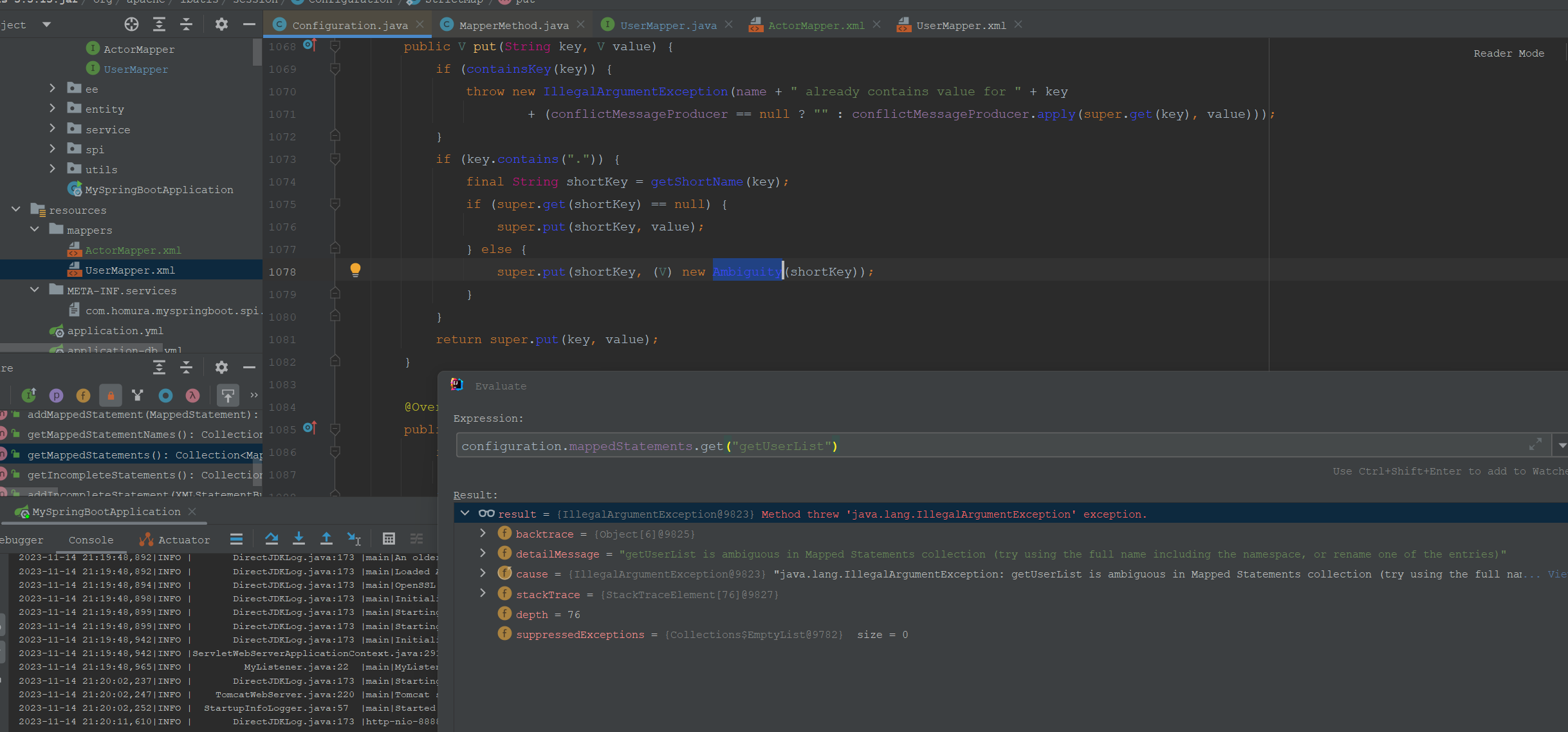
其原因是这里存入了Ambiguity对象。
public V put(String key, V value) {
if (containsKey(key)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(name + " already contains value for " + key
+ (conflictMessageProducer == null ? "" : conflictMessageProducer.apply(super.get(key), value)));
}
if (key.contains(".")) {
final String shortKey = getShortName(key);
if (super.get(shortKey) == null) {
super.put(shortKey, value);
} else {
super.put(shortKey, (V) new Ambiguity(shortKey));
}
}
return super.put(key, value);
}
这里还判断了mapperStatement的ID必须唯一,mapperStatement的ID为Namespace+SQL的ID(MapperInterface的接口名称)。
四、SqlSessionTemplate解读
SqlSessionTemplate实现了SqlSession接口,是一个特殊的SqlSession对象。
在官网的这个示例中,提到”SqlSession 的实例不是线程安全的,因此是不能被共享的,所以它的最佳的作用域是请求或方法作用域”,也就是SqlSession是请求/方法内创建使用完成然后销毁的。
try (SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
BlogMapper mapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
// 你的应用逻辑代码
}
而MybatisAutoConfiguration创建的SqlSessionTemplate是一个单例。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
ExecutorType executorType = this.properties.getExecutorType();
if (executorType != null) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory, executorType);
} else {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
其原因就在于SqlSessionTemplate内部创建了sqlSessionProxy这样一个代理对象,每次通过SqlSessionTemplate执行SQL方法都由sqlSessionProxy去执行。
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) newProxyInstance(SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { SqlSession.class }, new SqlSessionInterceptor());
我们进入SqlSessionInterceptor这个拦截器。
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//创建或获取SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType, SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
try {
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
if (!isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
// force commit even on non-dirty sessions because some databases require
// a commit/rollback before calling close()
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
Throwable unwrapped = unwrapThrowable(t);
if (SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator != null && unwrapped instanceof PersistenceException) {
// release the connection to avoid a deadlock if the translator is no loaded. See issue #22
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
sqlSession = null;
Throwable translated = SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator
.translateExceptionIfPossible((PersistenceException) unwrapped);
if (translated != null) {
unwrapped = translated;
}
}
throw unwrapped;
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
}
}
这里可以看到每次执行SQL方法,都创建一个新的SqlSession对象,这样和官网描述相符合的。
但是SqlSession也不是总会新建一个的。
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
notNull(executorType, NO_EXECUTOR_TYPE_SPECIFIED);
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
//若已有SqlSession,直接返回
SqlSession session = sessionHolder(executorType, holder);
if (session != null) {
return session;
}
//创建新的SqlSession
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Creating a new SqlSession");
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);
return session;
}
TransactionSynchronizationManager这个类,笔者有在«TransactionManager事务管理器»这篇文章有做简单解读。
TransactionSynchronization:事务同步信息,允许自定义资源托管到TransactionSynchronizationManager。如Mybatis的SqlSessionSynchronization。
这里主要的作用是将事务相关信息绑定到resources这个线程本地变量中,和注册TransactionSynchronization到synchronizations。
因此在Spring事务启动后,注册同步资源信息(SqlSession)到TransactionSynchronizationManager,其源码如下:
/**
* Register session holder if synchronization is active (i.e. a Spring TX is active).
* <p>
* Note: The DataSource used by the Environment should be synchronized with the transaction either through
* DataSourceTxMgr or another tx synchronization. Further assume that if an exception is thrown, whatever started the
* transaction will handle closing / rolling back the Connection associated with the SqlSession.
*
* @param sessionFactory
* sqlSessionFactory used for registration.
* @param executorType
* executorType used for registration.
* @param exceptionTranslator
* persistenceExceptionTranslator used for registration.
* @param session
* sqlSession used for registration.
*/
private static void registerSessionHolder(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator, SqlSession session) {
SqlSessionHolder holder;
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
Environment environment = sessionFactory.getConfiguration().getEnvironment();
if (environment.getTransactionFactory() instanceof SpringManagedTransactionFactory) {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registering transaction synchronization for SqlSession [" + session + "]");
holder = new SqlSessionHolder(session, executorType, exceptionTranslator);
//绑定session到TransactionSynchronizationManager内的resources,绑定key为sessionFactory对象。
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(sessionFactory, holder);
//SqlSessionSynchronization,SqlSessionSynchronization实现了TransactionSynchronization,允许拓展类对象在Spring事务处理阶段注册回调方法
//回调方法有suspend()、resume()、flush()、beforeCommit()、beforeCompletion()、afterCommit()、afterCompletion()
TransactionSynchronizationManager
.registerSynchronization(new SqlSessionSynchronization(holder, sessionFactory));
holder.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
holder.requested();
} else {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(environment.getDataSource()) == null) {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "SqlSession [" + session
+ "] was not registered for synchronization because DataSource is not transactional");
} else {
throw new TransientDataAccessResourceException(
"SqlSessionFactory must be using a SpringManagedTransactionFactory in order to use Spring transaction synchronization");
}
}
} else {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "SqlSession [" + session
+ "] was not registered for synchronization because synchronization is not active");
}
}
可以看到,这里使用TransactionSynchronizationManager主要的作用就是mybatis为了支持Spring事务功能,开始事务后支持多个SQL执行方法可以共享一个SqlSession对象。
五、参考材料
1.https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/
2.Mybatis源码(版本3.5.13)
