本文是mybatis源码阅读计划的第一篇文章,本文简单介绍一下Mybatis简单使用和整体架构。
这篇文章将介绍mybatis的分层架构,主要组件和相关关系,同时简单提及一些核心类核心处理流程。
主要参考资料为mybatis的官网和mybatis源码,示例过程将不是XML配置直接使用SpringBoot的示例项目。
本文源码地址为:https://github.com/zouhuanli/MySpringBoot.git。
一、基本介绍和简单使用
Mybatis是一款轻量级的ORM框架,支持高级映射、动态SQL,通过简单的注解或XML来使用简单的Java POJO来操作数据库。动态SQL是Mybatis最显著的优点,极大的提高了SQL操作的灵活性。
使用Mybatis是很简单的,首先mybatis本身可以作为一个独立的框架或者jar使用。只需要应用引入依赖即可。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
</dependency>
需要与Spring结合时只需加入mybatis-spring依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
</dependency>
在官网有一个简单的示例代码:
String resource = "org/mybatis/example/mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
try (SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
BlogMapper mapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
Blog blog = mapper.selectBlog(101);
}
别看示例很简陋,这已经包含了mybatis的全部流程:
通过配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory、Configuration,解析和注册全部的配置(静态配置、Sql、ResultMap等),注册Mapper接口和MapperProxy。通过MapperProxy执行SQL方法,得到执行结果和解析执行结果。
mybatis的源码远没有spring源码复杂,阅读mybatis源码会比spring源码简单。当然两者不能简单比较。
通过SpringBoot使用mybatis只需要引入mybatis-spring-boot-starter。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>${mybatis-spring-boot-starter.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<version>${mysql-connector.version}</version>
</dependency>
和Spring结合主要是创建创建SqlSessionFactory、SqlSessionTemplate,如下。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
if (properties.getConfiguration() == null || properties.getConfiguration().getVfsImpl() == null) {
factory.setVfs(SpringBootVFS.class);
//......
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
ExecutorType executorType = this.properties.getExecutorType();
if (executorType != null) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory, executorType);
} else {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
添加MapperScan自动扫描Mapper接口和注册MapperProxy。
@Configuration
//开启事务
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true, mode = AdviceMode.PROXY)
//使用MapperScan注册Mapper接口
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.homura.myspringboot.dao")
public class MyBatisConfig {
}
二、整体架构
mybatis的分层结构如下:
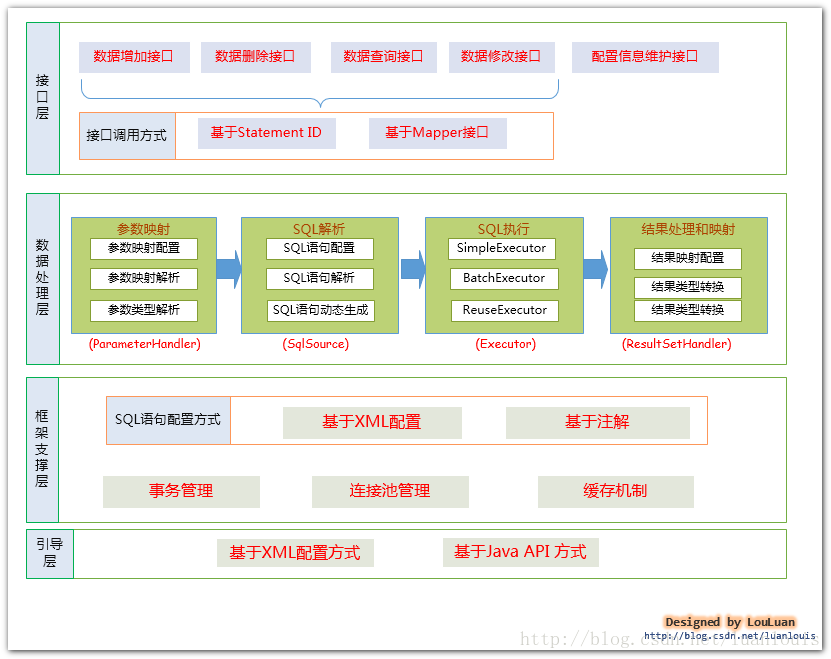
最顶层的主要是SqlSession、SqlSessionFactory等类,创建SqlSession来执行SQL方法。
数据处理层主要是XXXhandler,Sql,Executor等。
支持层主要是XML和注解配置,事务、连接池、缓存。
三、主要组件和关系
Mybatis主要的核心组件有(引用自https://louluan.blog.csdn.net/article/details/40422941):
- SqlSessionFactory:SqlSession的创建工厂,负责创建SqlSession
- SqlSession:作为MyBatis工作的主要顶层API,表示和数据库交互的会话,完成必要数据库增删改查功能
- Executor:MyBatis执行器,是MyBatis 调度的核心,负责SQL语句的生成和查询缓存的维护
- StatementHandler:封装了JDBC Statement操作,负责对JDBC statement 的操作,如设置参数、将Statement结果集转换成List集合。
- ParameterHandler:负责对用户传递的参数转换成JDBC Statement 所需要的参数,
- ResultSetHandler:负责将JDBC返回的ResultSet结果集对象转换成List类型的集合;
- TypeHandler:负责java数据类型和jdbc数据类型之间的映射和转换
-
MappedStatement:MappedStatement维护了一条<select update delete insert>节点的封装, - SqlSource:负责根据用户传递的parameterObject,动态地生成SQL语句,将信息封装到BoundSql对象中,并返回
- BoundSql:表示动态生成的SQL语句以及相应的参数信息
- Configuration:MyBatis所有的配置信息都维持在Configuration对象之中。
这些就是mybatis主要的核心类。
解读Mybatis的源码主要把握两个脉络:
- 1.SqlSessionFactory的构造过程,包括创建SqlSessionFactory、Configuration、Mapper接口注册、SQL解析和注册、MapperProxy的创建。这些主要是应用启动时候全部加载,解析,注册完成的。
- 2.SQL方法的执行过程,具体指的是MapperProxy的invoke方法开始涉及的SqlSession、SqlSessionTemplate、Executor、XXXHandler等对SQL方法的执行处理过程。这些是具体执行一个SQL方法的流程。
四、核心流程
4.1 初始化和SqlSessionFactory创建
SqlSessionFactory的创建的入口是MybatisAutoConfiguration#sqlSessionFactory方法。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
//通过MybatisProperties这个配置Bean设置SqlSessionFactoryBean的各项配置值
//......
// SqlSessionFactoryBean#getObject方法创建SqlSessionFactory
return factory.getObject();
}
在SqlSessionFactoryBean#buildSqlSessionFactory是创建SqlSessionFactory的真正的方法。单独使用mybatis通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder创建SqlSessionFactory。
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws Exception {
//创建Configuration
final Configuration targetConfiguration;
//加载、解析、注册各项配置,也会扫描Mapper
//创建SqlSessionFactory
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(targetConfiguration);
}
Configuration是一个非常大的配置类,注册了Mybatis的全部配置信息。
4.2 MapperProxy的创建过程
我们看下一个普通的Mapper接口。
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
/**
* 查找全部用户
* <p>
* 不要使用 select *
*
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from user")
@ResultMap("BaseResultMap")
List<User> findAll();
/**
* 添加用户
*
* @param user 用户
* @return
*/
@Insert(" insert into user (uid,uname,password,gender,phone,email,address) " +
" values " +
" (#{user.uid},#{user.uname},#{user.password},#{user.gender},#{user.phone},#{user.email},#{user.address})")
@ResultType(int.class)
int save(@Param("user") User user);
/**
* 根据id查询用户
* 不要使用 select *
*
* @param uid 用户id
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from user where uid = #{uid}")
@Results(id = "BaseResultMapByAnnotation", value =
{@Result(id = true, property = "uid", column = "uid", jdbcType = JdbcType.INTEGER)
, @Result(property = "uname", column = "uname", jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR)
, @Result(property = "password", column = "password", jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR)
, @Result(property = "gender", column = "gender", jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR)
, @Result(property = "phone", column = "phone", jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR)
, @Result(property = "email", column = "email", jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR)
, @Result(property = "address", column = "address", jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR)})
User selectByPrimaryKey(@Param("uid") Integer uid);
}
要使用该Mapper接口,可以直接使用Spring自动注入依赖接口,其原理是启动时自动创建MapperProxy注册到Spring容器。首先接口方法肯定没法直接执行的,mybatis是对每一个接口创建一个MapperProxy这样的代理对象来代理所有的接口方法。
session.getMapper方法最终会来到下面代码,来创建MapperProxy代理对象。
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
而knownMappers是应用启动时候创建SqlSessionFactory时候注册所有的Mapper接口到这个集合。
和Spring结合使用会自动扫描Mapper路径和注册MapperProxy,启动时通过ClassPathMapperScanner#processBeanDefinitions方法的注册MapperProxyFactoryBean,MapperProxyFactoryBean是一类factoryBean,
MapperProxyFactoryBean最终在Spring容器注册的是MapperProxy对象,其源码如下。
//注意看这个注释
// the mapper interface is the original class of the bean
// but, the actual class of the bean is MapperFactoryBean
definition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(beanClassName); // issue #59
try {
// for spring-native,设置mapper的接口类型
definition.getPropertyValues().add("mapperInterface", Resources.classForName(beanClassName));
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ignore) {
// ignore
}
//bean的类型是MapperProxyFactoryBean
definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass);
definition.getPropertyValues().add("addToConfig", this.addToConfig);
// Attribute for MockitoPostProcessor
// https://github.com/mybatis/spring-boot-starter/issues/475
definition.setAttribute(FACTORY_BEAN_OBJECT_TYPE, beanClassName);
boolean explicitFactoryUsed = false;
//注入sqlSessionFactory
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName)) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory",
new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionFactory != null) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", this.sqlSessionFactory);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
//注入sqlSessionTemplate
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
LOGGER.warn(
() -> "Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate",
new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionTemplate != null) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
LOGGER.warn(
() -> "Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", this.sqlSessionTemplate);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
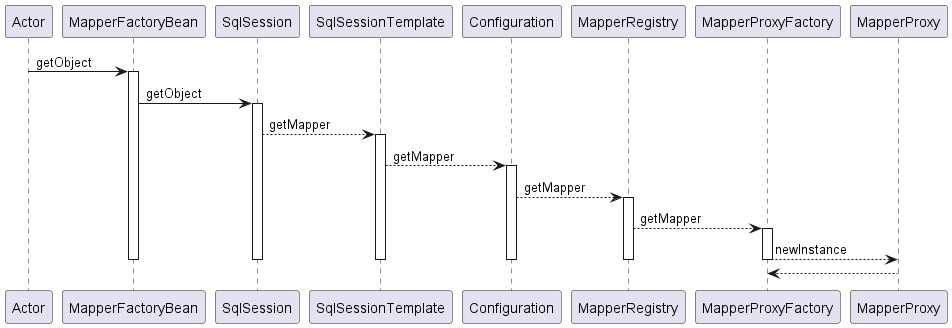
MapperProxy的创建流程如下:
4.3 SQL的执行流程
上面已经创建好了MapperProxy,执行Mapper接口的方法自然就进入了MapperProxy的方法。如下。
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
}
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
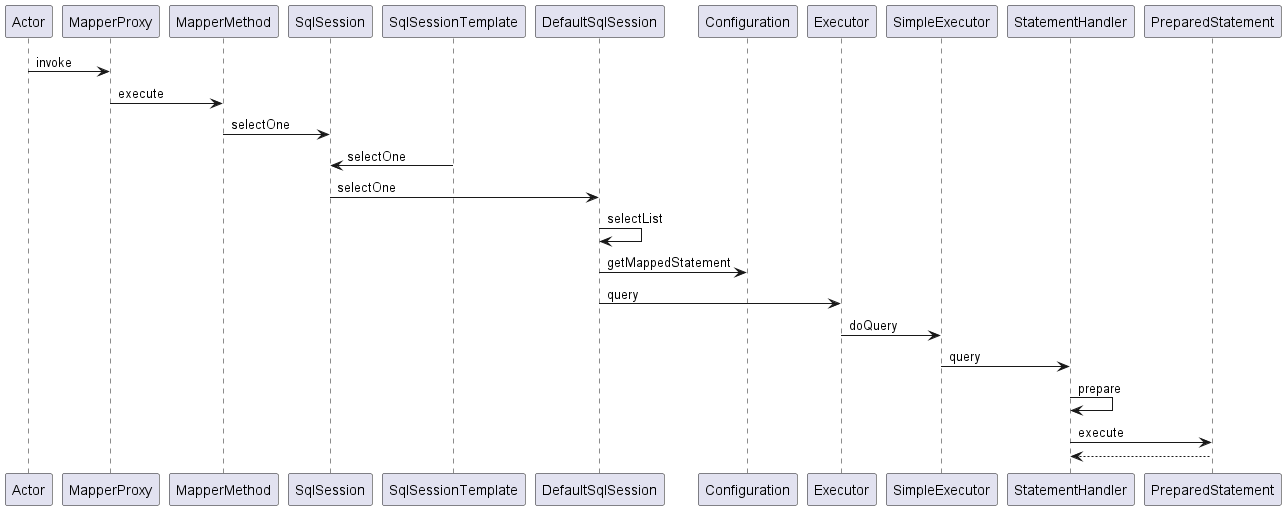
SQL方法的执行流程如下:
五、参考材料
1.https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/
2.Mybatis源码(版本3.5.13)
3.https://louluan.blog.csdn.net/article/details/40422941
